put to rest verb: to finish dealing with something and forget about it
Put it to REST! is a library that seamlessly integrates various REST- and HTTP-related client-side tools in the easiest and convenient way possible. It solves a recurring problem of bootstrapping and wiring different libraries together whenever interaction with a remote service is required. Spinning up new clients couldn't get any easier!
- Technology stack: Spring Boot
- Status: Beta
rest.clients:
example:
base-url: http://example.com
oauth.scopes:
- example.read@RestClient("example")
private Rest example;- Seamless integration of:
- Spring Boot Auto Configuration
- Sensible defaults
- Java 8
- Any build tool using Maven Central, or direct download
- Spring Boot
- Apache HTTP Async Client
Add the following dependency to your project:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.zalando</groupId>
<artifactId>put-it-to-rest</artifactId>
<version>${put-it-to-rest.version}</version>
</dependency>If you want OAuth support you need to additionally add stups-spring-oauth2-support to your project. It comes with Tokens equipped.
<!-- if you need OAuth support additionally add: -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.zalando.stups</groupId>
<artifactId>stups-http-components-oauth2</artifactId>
<version>$stups-http-components-oauth2.version}{</version>
</dependency>You can now define new REST clients and override default configuration in your application.yml:
rest:
oauth:
access-token-url: https://auth.example.com
scheduling-period: 10
timeouts:
connect: 1000
connect-unit: milliseconds
read: 1500
read-unit: milliseconds
clients:
example:
base-url: https://example.com
timeouts:
connect: 2
connect-unit: seconds
read: 3
read-unit: seconds
oauth:
scopes:
- uid
- example.readClients are identified by a Client ID, for instance example in the sample above. You can have as many clients as you want.
For a complete overview of available properties, they type and default value please refer to the following table:
| Configuration | Type | Required | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
rest.oauth.access-token-url |
URI |
no | env var ACCESS_TOKEN_URL |
rest.oauth.scheduling-period |
int |
no | 5 |
rest.oauth.timeouts.connect |
int |
no | 1 |
rest.oauth.timeouts.connect-unit |
TimeUnit |
no | seconds |
rest.oauth.timeouts.read |
int |
no | 2 |
rest.oauth.timeouts.read-unit |
TimeUnit |
no | seconds |
rest.clients.<id>.base-url |
URI |
no | none |
rest.clients.<id>.timeouts.connect |
int |
no | 5 |
rest.clients.<id>.timeouts.connect-unit |
TimeUnit |
no | seconds |
rest.clients.<id>.timeouts.read |
int |
no | 5 |
rest.clients.<id>.timeouts.read-unit |
TimeUnit |
no | seconds |
rest.clients.<id>.oauth |
no | none, disables OAuth2 if omitted | |
rest.clients.<id>.oauth.scopes |
List<String> |
no | none |
After configuring your clients, as shown in the last section, you can now easily inject them:
@RestClient("example")
private Rest example;All beans that are created for each client use the Client ID, in this case example, as their qualifier.
Besides Rest, you can also alternatively inject any of the following types per client directly:
RestTemplateAsyncRestTemplateClientHttpRequestFactoryAsyncClientHttpRequestFactoryHttpClientClientHttpMessageConverters
A global AccessTokens bean is also provided.
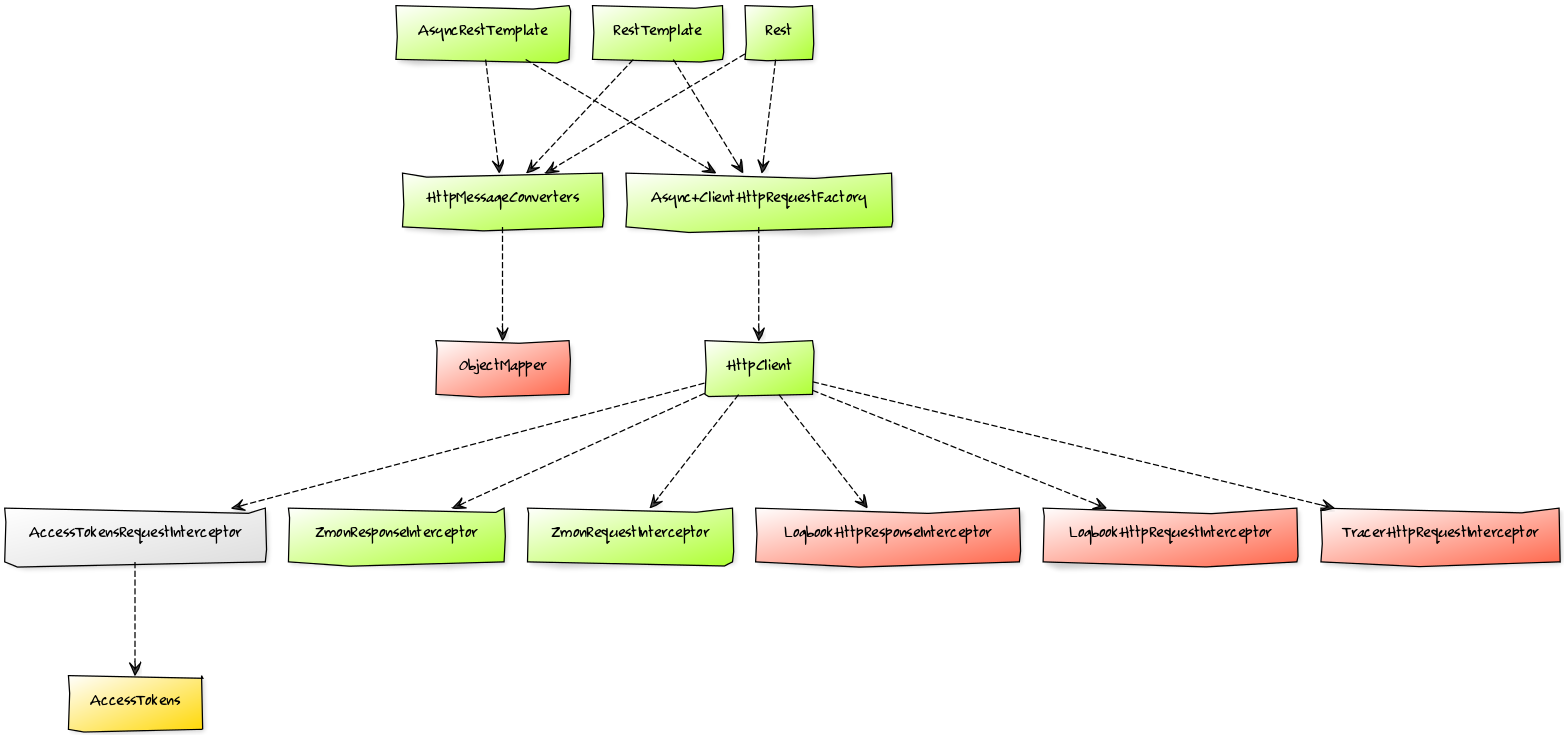
For every client that is defined in your configuration the following graph of beans, indicated by the green color, will be created:
Regarding the other colors:
- yellow: will be created once and then shared across different clients (if needed)
- red: mandatory dependency
- grey: optional dependency
Every single bean in the graph can optionally be replaced by your own, custom version of it. Beans can only be
overridden by name, not by type. As an example, the following code would add XML support to the example client:
@Bean
@Qualifier("example")
public HttpMessageConverters exampleHttpMessageConverters() {
return new HttpMessageConverters(new Jaxb2RootElementHttpMessageConverter());
}The following table shows all beans with their respective name (for the example client) and type:
| Bean Name | Bean Type | Configures by default |
|---|---|---|
accessToken (no client prefix!) |
AccessTokens |
OAuth settings |
exampleClientHttpMessageConverters |
ClientHttpMessageConverters |
Text, JSON and JSON Stream |
exampleHttpClient |
HttpClient |
Interceptors |
exampleAsyncClientHttpRequestFactory |
AsyncClientHttpRequestFactory |
Timeouts |
exampleRest |
Rest |
Base URL |
exampleRestTemplate |
RestTemplate |
Base URL |
exampleAsyncRestTemplate |
AsyncRestTemplate |
Base URL |
If you override a bean then all of its dependencies (see the graph), will not be registered, unless required by some other bean.
If you have questions, concerns, bug reports, etc., please file an issue in this repository's Issue Tracker.
To contribute, simply make a pull request and add a brief description (1-2 sentences) of your addition or change. For more details, check the contribution guidelines.