Documentation for Rancher Token Management Service
Overview
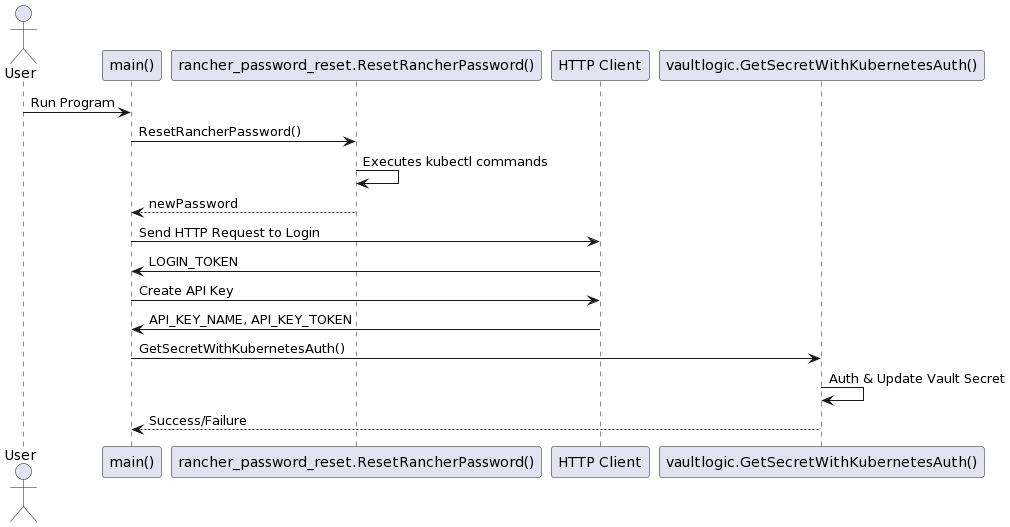
This service is designed to automate the management of Rancher API tokens by interacting with the Rancher Server. It resets the Rancher password, logs in to the Rancher Server, creates a new API key, and finally stores the API key details in a Vault.
Dependencies
Rancher API
Hashicorp Vault API
Kubernetes API
Standard Go Libraries
Environment Variables
RANCHER_SERVER: The URL of the Rancher Server.
USERNAME: The username used for logging in to Rancher.
SKIP_TLS_VERIFY: If set to "true", the client will skip TLS verification (not recommended for production).
VAULT_ADDR: Vault address
VAULT_SECRET_ENGINE: Vault engine e.g. kv-v2
VAULT_SECRET_PATH: Vault secret path e.g. credentials
TOKEN_TTL: TTL of the token in Rancher
Packages
Main Package
Functions
main(): The main function to kick off the token management flow.
Methods
logJSON(message string): Logs messages in JSON format.
Rancher Password Reset Package (rancher_password_reset)
Functions
ResetRancherPassword() -> (string, error): Resets the Rancher password and returns the new password.
Vault Logic Package (vaultlogic)
Functions
GetSecretWithKubernetesAuth(dataToStore map[string]interface{}) -> (string, error): Retrieves or updates a secret in Vault using Kubernetes authentication.
Methods
logJSON(message string): Logs messages in JSON format.
logAndReturnError(errMessage string, originalErr error) -> error: Logs an error message and returns the error.
Flow of Control
main() initializes environment variables and triggers ResetRancherPassword().
ResetRancherPassword() uses kubectl commands to reset the Rancher password and returns the new password.
main() proceeds to make an HTTP POST request to log in to the Rancher server using the new password.
Once logged in, an API key is generated.
The API key details (API_KEY_NAME and API_KEY_TOKEN) are stored in Vault via GetSecretWithKubernetesAuth().
Error Handling
The application logs errors in JSON format and returns from the function in which the error occurred.
How to Run
Ensure that all environment variables are set.
Build the project: make build-push
Install on Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl apply -f -R deploy/
Note
If you're running this in a production environment, it is highly recommended to not use the "SKIP_TLS_VERIFY" feature for security reasons.