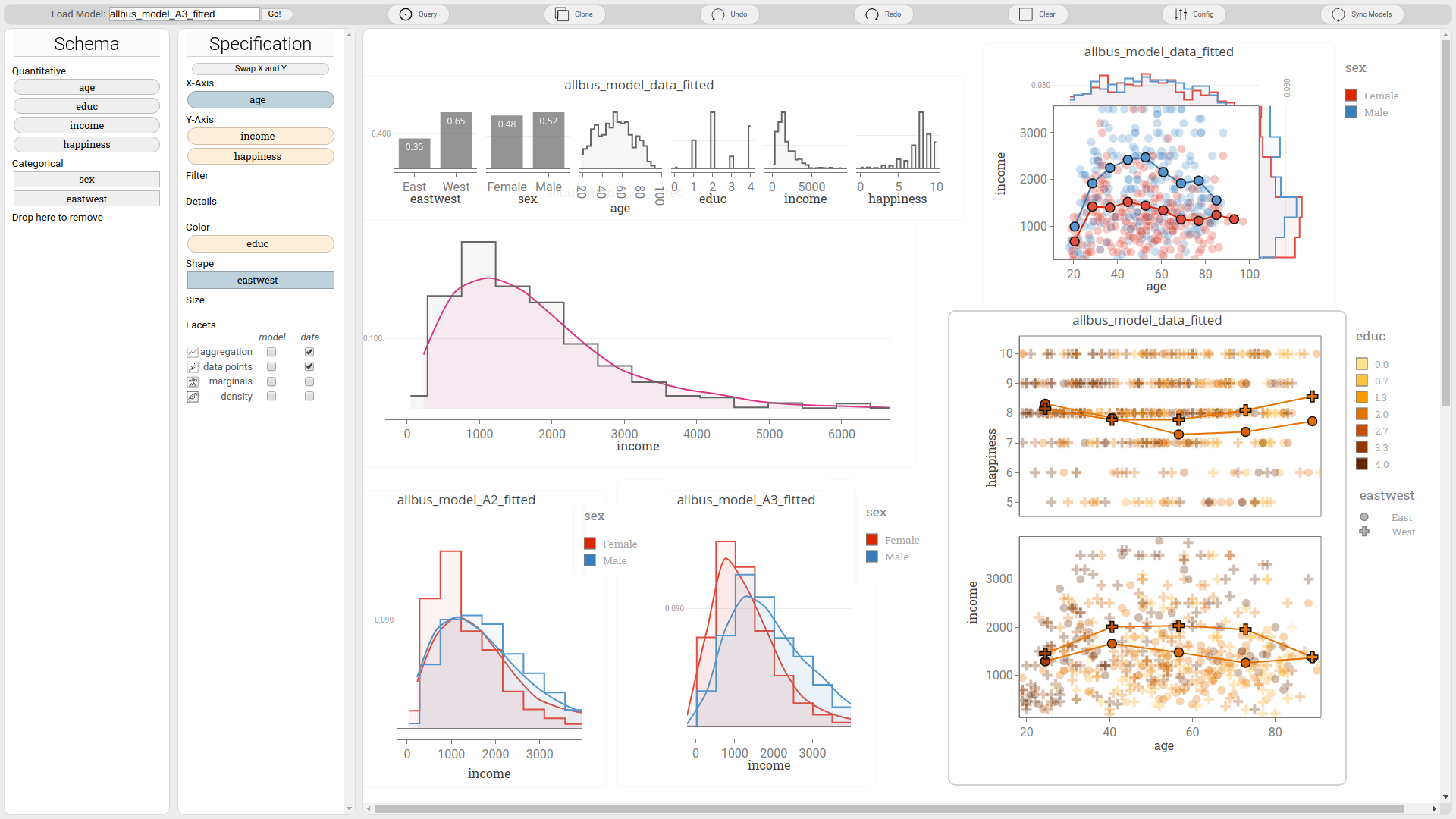
lumen is an interactive web-application for the visualization and exploration of probabilistic machine learning models.
Its main feature is the ability to rapidly and incrementally build flexible and potentially complex visualizations of both probabilistic machine learning models and the data these models were trained on.
lumen aims to make a particular class of machine learning/statistical models, namely probabilistic models, more easily accessible to humans.
A probabilistic model models a set of target variables by means of a probability distribution.
That is, different to many classic ML methods which predict a particular value of the target variable(s), probabilistic models instead capture the distribution of the target variables.
lumen lets you 'see' your model, understand how it performs, where it 'fails', and compare this to previous versions of the model or alternative models.
A manual-style description of the UI, the visual encodings, lumens usage, its features, and available interactions is available here.
A walk-through-style introduction to lumen is available here. It demonstrates some of the feature for exploration of probabilistic models in lumen.
In particular lumen lets you:
- plot any marginals of your models. Here, marginal means not just 1d but also higher dimensional marginals. Studying multiple multi-variate 'slices' of a model may help to understand the interactions between the variables. We believe this also helps you to fix model degrading artifacts. Such artifacts may indicate a problem in your model specification, model parameterization or possibly a bug in the machine learning algorithm of your model.
- plot the model marginals together with data marginals. This lets you directly check the models fit to data.
- plot predictions of your model along side corresponding data aggregations. This lets you understand its predictive behaviour, and also compare it observed quantities.
- combine any of the above 'layers' into a single visualization.
- change visualizations by flexibly assigning variables/data attributes to visual channels.
- create as many of these visualizations side by side on an virtually infinite canvas. This lets you compare various stages of a model, compare different modelling approaches, and get a better overall understanding by combining many different visualizations of the same model.
Probabilistic programming language (PPLs), such as PyMC3, BLOG, or Stan, provide a framework to define probabilistic models by explicitly declaring the likelihood of the observed data as a probability density function.
The analyst typically starts with an exploration of the data.
Based on insights gained from data exploration and on the analyst's domain knowledge, the analyst creates an initial simple model involving only some data.
Subsequently, this model is iteratively made more complex until it meets the expert's goals.
In particular, the model must be validated after each iteration.
lumen supports this model building process by
(i) enabling visual-interactive data exploration,
(ii) supporting model validation by means of a visual comparison of data queries to semantically equivalent model queries, and
(iii) enabling a direct comparison of model iterates.
Even for a machine learning expert it may be hard to know whether a model has been trained on the data as expected. Possible reasons for artifacts in a model include an inappropriate application of the machine learning method, implementation bugs in the machine learning method, and issues in the training data. Direct visual inspection of the probabilistic model provides an approach to model debugging that enables the analyst to literally spot model artifacts that may cause degrading performance. Classical approaches to validation would rely on aggregating measures like information criterions or predictive accuracy scores.
By its intuitive visual representations of models, Lumen aims to promote understanding of the underlying modelling techniques. For instance, the effect of varying a parameter value for a modelling method on the probabilistic model can be observed visually rather than remaining an abstract description in a textbook. Similarly, the differences between models/model types can be visually illustrated by plotting them side by side. Also, probabilistic concepts such as conditioning or marginalization, which are often difficult to grasp, can be tried out interactively, providing immediate feedback.
You don't do any Machine Learning but simply would like to conveniently browse, explore, and compare tabular data?
lumen is the right place for you too!
This is not what lumen was built for originally, but regard it as your 'free lunch'.
This explains how to install and configure lumen and its dependencies.
Note that lumen is build on top of the modelbase back-end, which provides a SQL-like interface for querying models and its data.
-
lumenis a web application that requires access to a web-service instance of the Python3-basedmodelbasebackend.lumenallows a user to interactively compile data/model queries and visualize the queries results.modelbasedoes the computation and actually answers the queries. You can getmodelbasehere where you also find information on how to set it up and run it as a web-service. -
lumenandmodelbaseneed to be configured correctly with 'matching' settings. By default (both run locally on the same physical machine) this is the case and you do not need to change these settings:- hostname set in the configuration of
lumenmust match the actual hostname ofmodelbase. - port must match
- protocol must match (http or https)
- hostname set in the configuration of
-
lumenallows you to explore the models and data that are hosted by themodelbasebackend. You can use themodelbasePython package to (1) train/create models from data, and then (2) host them by an instance of themodelbaseweb-service. See the documentation and introductory jupyter notebooks in thedocfolder for more information. Also, a number of example models are created during the setup process ofmodelbasefor your convenience.
Clone/download this repository into a folder <path> of your choice.
Just pull/download the lasted branch/version you'd like.
- make sure the
modelbasebackend is running and hosting the models that you'd like to explore. - it's dead simple: Open
<path>/index.htmlin your browser. If everything is fine you should now see a model dialog that lists the available models. Select one and start exploring it!
Notes:
- Using chrome/chromium as a browser is recommended, since it provides the best performance from our experience.
If you have any trouble using lumen, need some additional explanation, or even just want to provide some feedback, please don't hesitate to contact us at philipp.lucas@dlr.de.
If you encounter any bugs you can also submit an issue.
-
Confirm that the backend server actually running
-
Check the developer console log of the browser where you are loading the front-end. If it shows something like:
Failed to load http://127.0.0.1:5000/web-service: Response to preflight request doesn't pass access control check: The 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header has a value 'null' that is not equal to the supplied origin. Origin 'null' is therefore not allowed access.
Then your probably run into some CORS issue because you serve the file directly from the file system, instead from a webserver running locally. See here for the issues:
Solutions:
- serve it from a local web-service (preferred)
- disable CORS control in chrome (kind of hacky)
- Confirm that the backend server is actually running
- Did the backend server load the particular model that you are trying to retrieve? Loaded models are listed in the terminal output of the backend server on its start up.
You wanna contribute? Awesome! Let's get in touch: philipp.lucas@dlr.de !
This is only for you, if you want to contribute to the project.
- Do the steps as described in the Setup section above.
- Install node-js. For questions refer to the getting started guide.
- Update npm (part of node-js):
sudo npm install -g npm - Install all npm-dependencies as provided by the projects
package.json:- run from
<path>:npm install
- run from
For any questions, feedback, bug reports, feature requests, spam, rants, etc please contact: philipp.lucas@dlr.de
© 2016-2021 Philipp Lucas (philipp.lucas@dlr.de)
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License along with this program. If not, see https://www.gnu.org/licenses/.