A python package of Zeroth-Order Optimization (ZOOpt).
Zeroth-order optimization (a.k.a. derivative-free optimization/black-box optimization) does not rely on the gradient of the objective function, but instead, learns from samples of the search space. It is suitable for optimizing functions that are nondifferentiable, with many local minima, or even unknown but only testable.
Install: pip install zoopt
We define the Ackley function for minimization using Theano
import math, theano, theano.tensor as T
x = T.dvector('x')
f = theano.function([x], -20 * T.exp(-0.2 * T.sqrt((T.dot(x - 0.2, x - 0.2))/T.shape(x))) - T.exp(
(T.cos(2 * math.pi * (x - 0.2))).mean()) + math.e + 20)Ackley function is a classical function with many local minima. In 2-dimension, it looks like (from wikipedia)
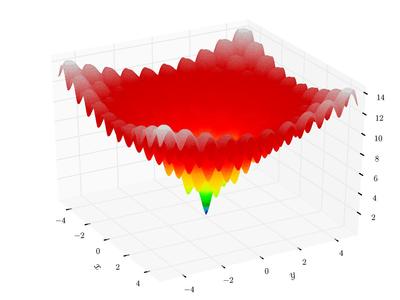 |
Then, use ZOOpt to optimize a 100-dimension Ackley function
from zoopt import Dimension, Objective, Parameter, Opt, Solution
dim = 100 # dimension
obj = Objective(lambda s: f(s.get_x()), Dimension(dim, [[-1, 1]] * dim, [True] * dim)) # setup objective
# perform optimization
solution = Opt.min(obj, Parameter(budget=100 * dim))
# print result
solution.print_solution()For a few seconds, the optimization is done. Then, we can visualize the optimization progress
from matplotlib import pyplot
pyplot.plot(obj.get_history_bestsofar())
pyplot.savefig('figure.png')which looks like
 |
More examples are available in the example fold.
- Include the general optimization method RACOS (AAAI'16) and Sequential RACOS (AAAI'17), and the subset selection method POSS (NIPS'15).
- The algorithm selection is automatic. See examples in the
examplefold. - Default parameters work well on many problems, while parameters are fully controllable
- Running speed optmized for Python
