A LVGL porting for Cortex-M55 running on an Arm official FPGA prototyping development board called MPS3 (AN547), see Figure 1. It is also possible to run the project template on an emulator called Corstone-300-FVP, which is free.
Figure 1 Arm MPS3 FPGA prototyping board
-
LVGL 9.0.0-dev (CMSIS-Pack)
-
[New] Arm-2D (Helium) acceleration is added !!!
- see
lv_gpu_arm2d.candlv_gpu_arm2d.h - Attach acceleration in
lv_port_disp_template.c - Arm-2D CMSIS-Pack
- see
-
320 * 240 RGB565 LCD Display connected with an Integrated Color LCD parallel interface.
-
Default System Clock: 32MHz (50MHz Max)
-
CPU: Cortex-M55 with Helium
- DCache
- ICache
- ITCM: 512KB
- DTCM: 512KB
-
NPU: Ethos-U55
-
PRAM (Used for Code and RO-Data): 2MByte
-
SRAM: 4MByte
-
DDR4: 1GByte
-
MDK Project with Arm Compiler 6
A benchmark report shows the advantage of using arm-2d to accelerate LVGL when Helium technology is available.
- Download the Corstone-300-FVP and install it.
- Open the project in MDK
- Select the 'Cortex-M55_FVP' configuration.
- Open the 'Options for Target' window and select the 'Debug' panel
- Press the 'Settings' button on the right corner
- Click the '...' button on the top-right corner, browse to the folder where Corstone-300-FVP is installed and select the executable file, i.e. FVP_Corstone_SSE-300_EThos-U55.exe.
Usually the Corstone-300-FVP is located in the following path:
C:\Program Files\ARM\FVP_Corstone_SSE-300\models\Win64_VC2017\FVP_Corstone_SSE-300_Ethos-U55.exe
- Click the '...' button next to the 'Target' textbox and select the cpu0 in the popup dialog. Click OK to confirm.
- Click the OK button to close the 'Models Armv8-M Target Driver Setup' window.
- Compile and Debug. You should be able to see the LVGL benchmark running on a FVP window as shown below:
-
FVP can ONLY be used to verify the correctness of firmware functionality
-
NO performance data generated from FVP is trustworthy. FVP is simply NOT designed for performance evaluation.
For example, the '-O0' optimization might run as fast as -Ofast, in contrast, the '-Ofast+LTO (Link-Time-Optimization)' runs very slow. In fact, in the real hardware, -Ofast+LTO > -Ofast >> -O0.
- Open the project in MDK
- Select the 'Cortex-M55_MPS3' configuration
- Compile and Debug
For people who want to learn and practice porting LVGL to a LCD-Ready MDK project using the LVGL cmsis-pack, a dedicated branch called "lvgl_porting_exercise" is introduced, which contains a clean project and provides:
- Low-level LCD APIs
extern int32_t GLCD_Initialize (void);
extern int32_t GLCD_Uninitialize (void);
extern int32_t GLCD_SetForegroundColor (uint32_t color);
extern int32_t GLCD_SetBackgroundColor (uint32_t color);
extern int32_t GLCD_ClearScreen (void);
extern int32_t GLCD_SetFont (GLCD_FONT *font);
extern int32_t GLCD_DrawPixel (uint32_t x, uint32_t y);
extern int32_t GLCD_DrawHLine (uint32_t x, uint32_t y, uint32_t length);
extern int32_t GLCD_DrawVLine (uint32_t x, uint32_t y, uint32_t length);
extern int32_t GLCD_DrawRectangle (uint32_t x, uint32_t y, uint32_t width, uint32_t height);
extern int32_t GLCD_DrawChar (uint32_t x, uint32_t y, int32_t ch);
extern int32_t GLCD_DrawString (uint32_t x, uint32_t y, const char *str);
extern int32_t GLCD_DrawBitmap (uint32_t x, uint32_t y,
uint32_t width, uint32_t height, const uint8_t *bitmap);-
A simple main() function
-
A simple way to display string on LCD
extern
int32_t GLCD_DrawString(uint32_t x, uint32_t y, const char *str);
#define __LL_LCD_PRINT_BANNER(__STR) \
do { \
GLCD_DrawString( (GLCD_HEIGHT) / 2 - 8, \
(GLCD_WIDTH - sizeof(__STR) * 6) / 2, \
__STR); \
} while(0)- printf() is retargeted to USART0 (telnet in FVP emulation).
- A function, GLCD_DrawBitmap(), for flushing display buffer to LCD, which supports window-mode (partial flush).
extern
int32_t GLCD_DrawBitmap (uint32_t x, uint32_t y,
uint32_t width, uint32_t height,
const uint8_t *bitmap);- Ready to Compile and Debug in FVP (Emulation) as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 A Clean Project Template for practicing LVGL Porting using LVGL CMSIS-Pack
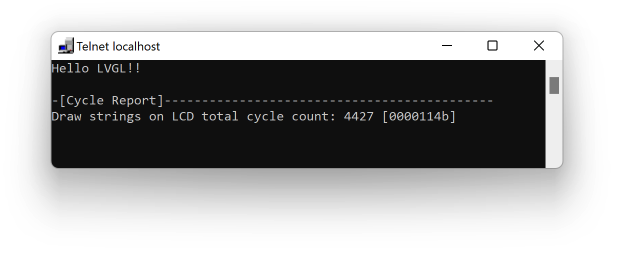
- A new method, __cycleof__(), for measuring cpu cycles consumed by specified code segment.
__cycleof__("Draw strings on LCD") {
__LL_LCD_PRINT_BANNER("Hello LVGL!!");
}Figure 3 printf() and __cycleof__
- LVGL used in this project is under MIT license.
- This project template is under Apache 2.0 license.
- Arm-2D used in this project is under Apache 2.0 license.