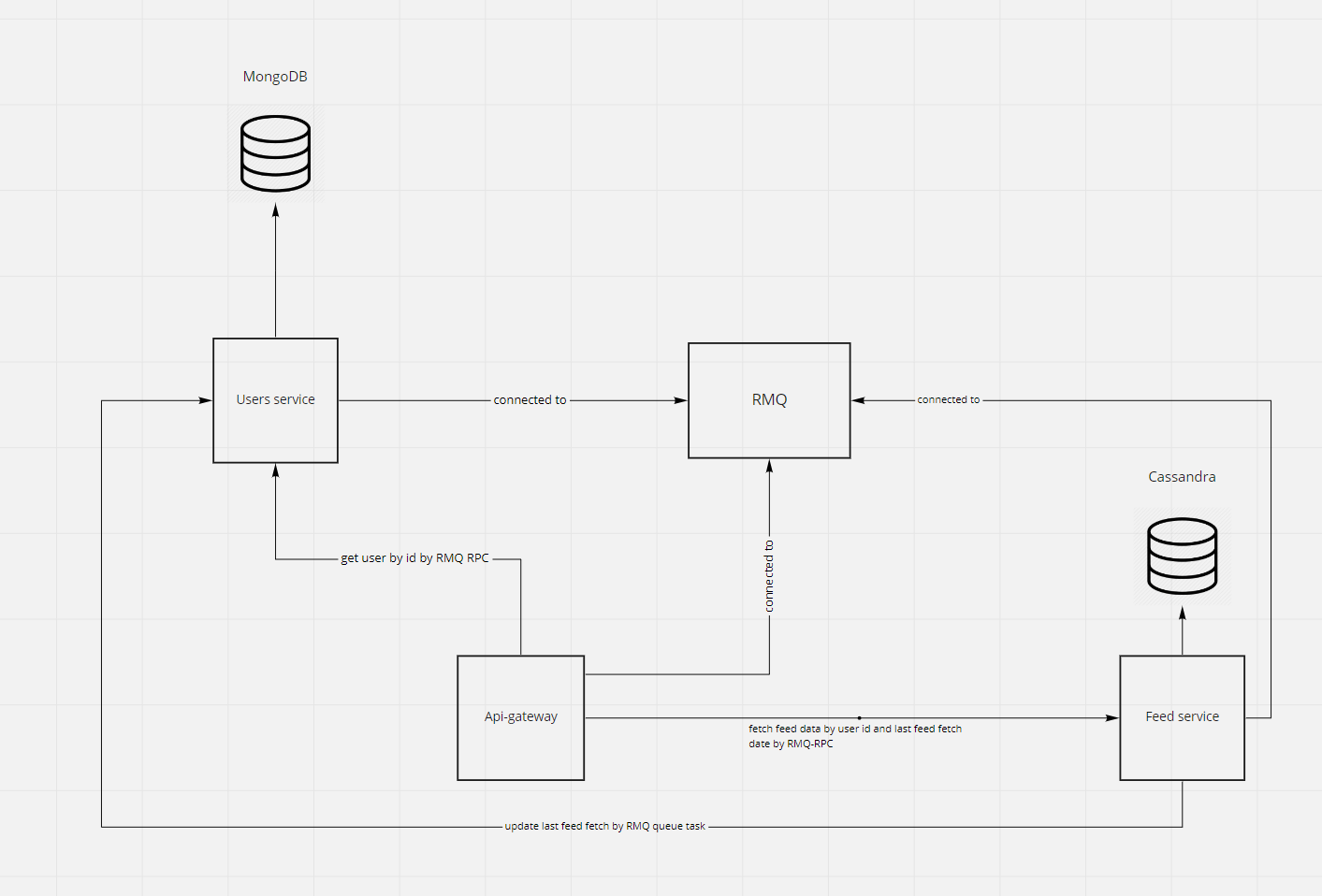
- api-gateway - gateway for request from outside world, handles request auth and communication between microservices
- expose 80 port with
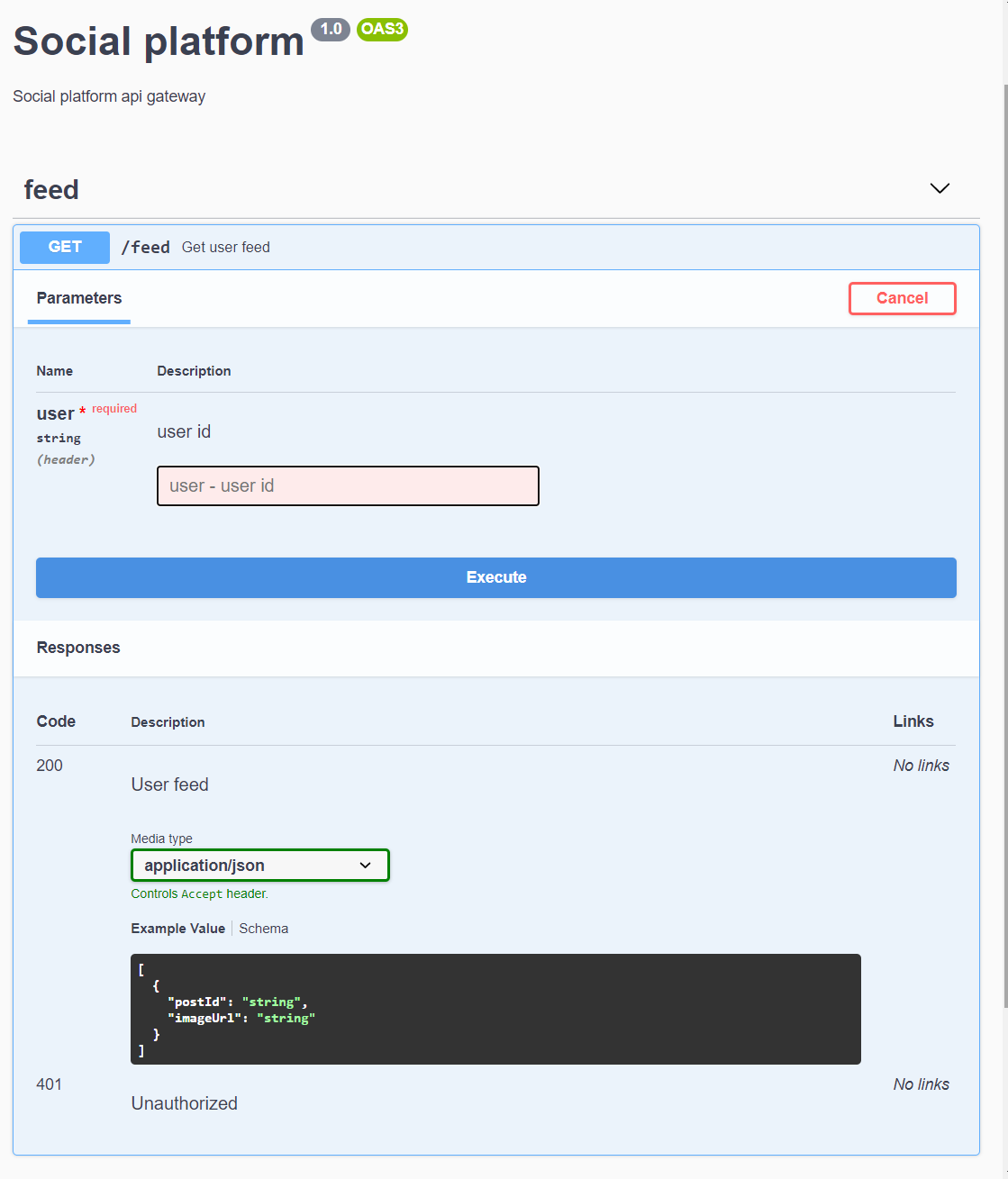
GET /feed - communication with
usersandfeedvia RMQ-RPC
- expose 80 port with
- users - should handle users related actions, in scope of this task the only action exposed by this service is fetching user by id for api-gateway authorization purposes
- database mongo chosen due to ease of scaling and non-relation data, port is exposed to host due to development purposes (connecting with external database tools)
- feed - should handle fetching user feed (in scope of a task), in a current version it's also storing information about when user fetched the feed last time.
- casandra is chosen because feed will be spammed with inserts and reads, it scales well and is prepared for heavy writes scenarios
- casandra database with exposed port for development purposes, in real env should be only internal
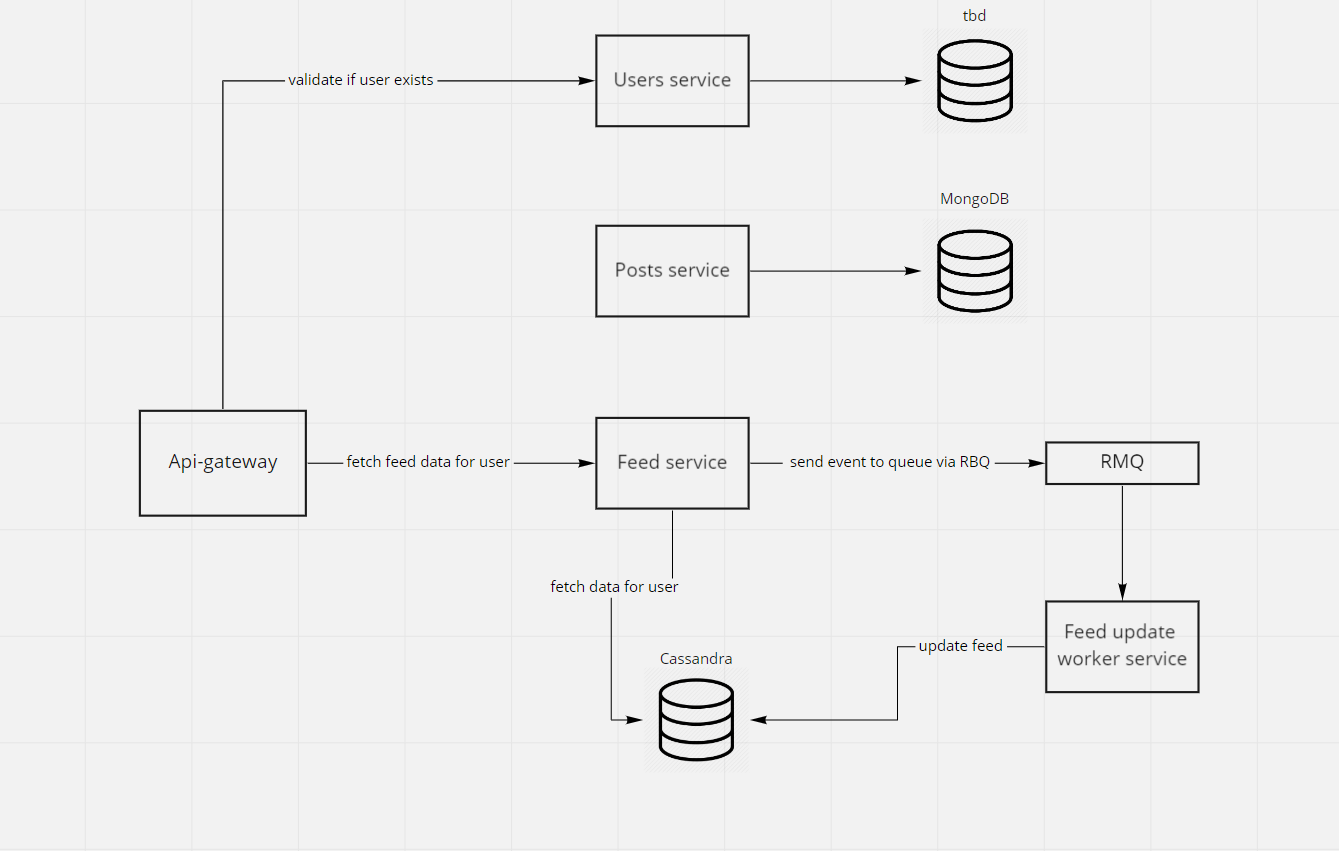
- posts - should handle all posts related logic but in scope of node task it was not necessary to implement at all, because all posts data are pre-loaded inside
feedservice database asfeed entries - feed-worker - not implement due to nature of task, it was not necessary to insert/update/delete posts (thus to create feed entries). If posts crud was required, then feed-worker must be implemented to handle communication and expensive upserts in cassandra.
Then it can be implemented like this:
- User add post via ->
POST /postsin api gateway - Gateway sends RMQ task to
postsservice - Post service consumes event and fetch related users to the post (from post service by RMQ-RPC) and sends RMQ task to
feed - Feed service consumes event and create tasks for feed workers
- Feed worker upserts data into feed
- User add post via ->
- app-network - all services are inside external
app-networkprovided by main docker-compose file (with RabbitMQ container), this allows communication with external docker-compose projects/services
- project is a monorepo solution, but does not use solution like lerna. In this simple case it was not necessary to use it, but in a large project I would like to have that, or git-submodule option.
- there are minor code duplications, like
RabbitMQModule. In bigger project there should be something like@sharedpackage or common repository with all common modules, interfaces, responses etc there are minor code quality inconsistencies issues regarding a configuration of queuese2e testing is lacking of test for creating new feed entry (command for that is already prepared, but is not connected)- databases and rabbit are exposed for host for development purposes
use of generated mongo ids style, should be uuid4- validation of data transfered between services is not done, it can be done by class-validator
I do not like the current implementation ofuser-latest-feed-fetchplaced infeedservice, it is a bottleneck, but I struggled to find a better place where it should be implemented. Now after implementation of this version, I think the correct way will be to store lastFetchAt datetime in User entity, and later on pass date to feed service (user data in already in api-gateway due to auth), and feed service after sending fetching feed entries should create async task for user service to update lastFetchAt
chmod -R +x scripts && ./scripts/down.sh && ./scripts/up.sh && ./scripts/seed.sh && ./scripts/e2e.sh
expected output
PASS test/app.e2e-spec.ts (5.047 s)
FeedController (e2e)
✓ /feed (GET) and should fail on auth (281 ms)
✓ /feed (GET) and get two feed entries (92 ms)
✓ /feed (GET) and get zero feed entries (1085 ms)
✓ as user with empty feed /feed (GET) and get zero feed entries (77 ms)
...
PASS test/after-feed-upsert.e2e-spec.ts
FeedController (e2e)
✓ after seeding /feed (GET) and get one feed entry (287 ms)
✓ after seeding /feed (GET) and zero feed entries (79 ms)
GET /api/