A swift package that adds validation to views.
Add to your project using swift package manager.
There are 3 main things this package exposes. Validator, ValidatingTextField, and an errorModifier view modifiier.
The validatable text field is similar to a normal text field however it adds the abilitiy to validate the text value, and display an error message(s) if invalid. There are two ways to create a validatable text field.
You can use a single validator, or combine validators with &&, ||, and ! operators.
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var nameText: String
@State private var emailText: String
var body: some View {
Form {
Section(header: Text("Name")) {
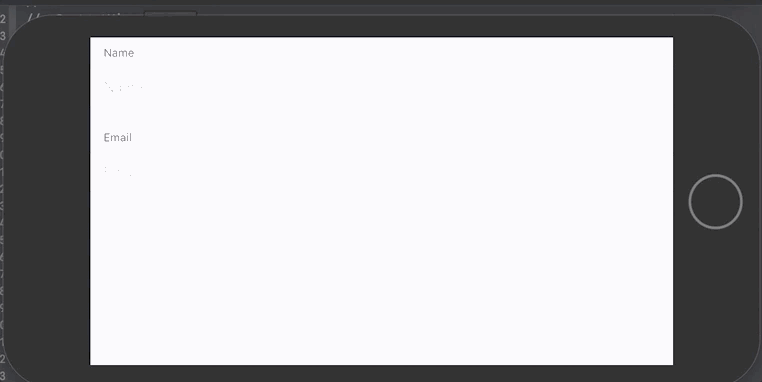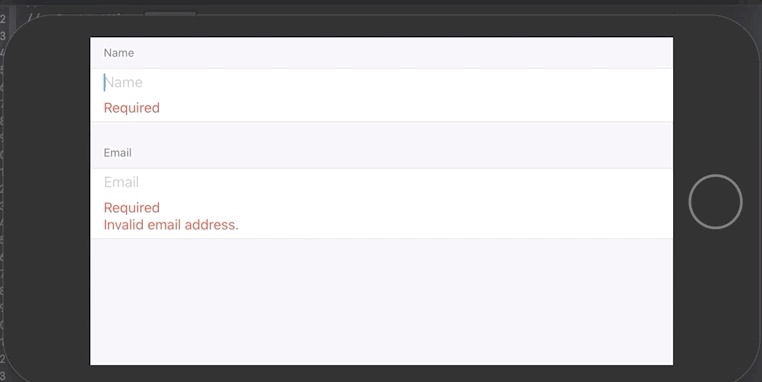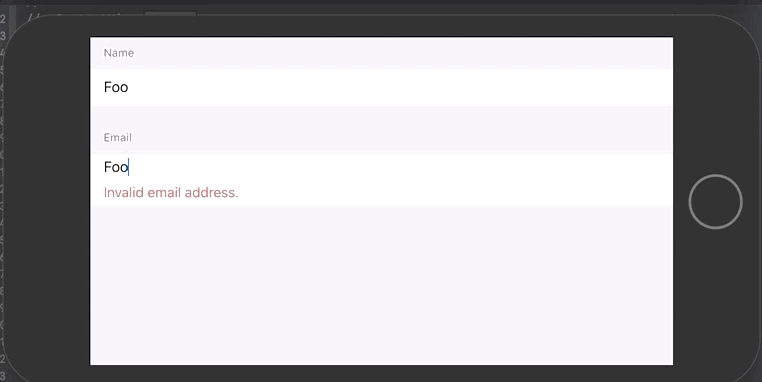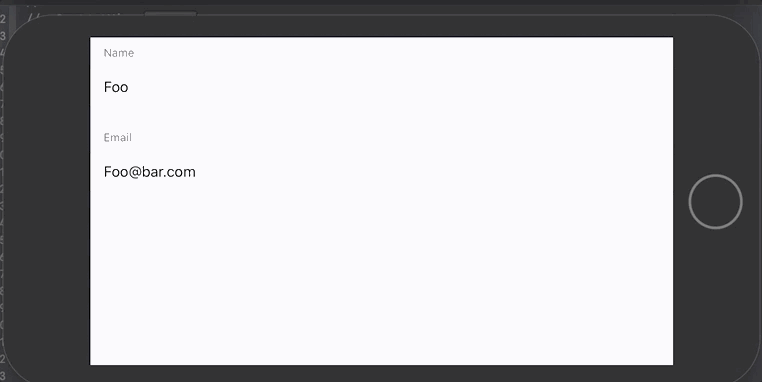
// Error texts would be `["Required: not empty", "Required: at least 5 characters"]`
ValidatingTextField("Name", text: $nameText, validator: .prefix("Required: ", !.empty && .count(5...)))
}
Section(header: Text("Email")) {
// Hook in and create custom error view, only showing the first error.
//
// Error texts would be `["Required", "invalid email"]`
ValidatingTextField("Email", text: $emailText, validator: .custom("Required", !.empty) && .email) { errors in
Group {
// Only show the first error.
if errors.first != nil {
Text(errors.first!.capitalized)
.modifier(ErrorTextModifier())
// add default style, font = .callout, foregroundColor = .red
}
}
}
}
}
}
}The errorModifier is an extension on View and will add the ability for any view to be validated. There are several ways to create add an error modifier to a view, below is just one example of using a key path on Validators to derive the validation from.
struct MyValidatableView: View {
// control when the error is evaluated.
@State private var shouldEvaluate: Bool = true
@State private var value: String = ""
var body: some View {
Form {
// display the error in the section header.
Section(header: errorView) {
TextField("Value", text: $value)
}
}
}
private var errorView: some View {
Text("")
.errorModifier(value: $value, shouldEvaluate: $shouldEvaluate, validator: !.empty)
}
// You can also hook into and customize the error view used.
private var errorView2: some View {
Text("")
.errorModifier(value: $value, shouldEvaluate: $shouldEvaluate, validator: !.empty && .email) { errors in
Group {
// Only show the first error.
if errors.first != nil {
Text(errors.first!.capitalized)
.modifier(ErrorTextModifier())
}
}
}
}
}Validator is a type that can validate a Binding value on a view.
A validator holds the text to be displayed and the validation method. A validator also has the ability to be combined with other validators, making a chain of error messages that will be displayed, depending on the result.
The default validator error messages are generic (and lowercased), as they expect to have a prefix or custom wrapper around
them.
/// Set a custom error, this will replace all errors with the custom error,
/// so should typically just be used to wrap a single validator.
let notEmpty: Validator<String> = .custom("Required", !.empty)
do {
try notEmpty.validate("")
} catch validationError as ValidationError {
assert(validationError.first! == "Required")
}
/// Set an error prefix, this will prefix all errors with the custom error prefix,
/// so should typically just be used to wrap a single validator.
let prefixedNotEmpty: Validator<String> = .prefix("Required: ", !.empty)
do {
try prefixedNotEmpty.validate("")
} catch validationError as ValidationError {
assert(validationError.first! == "Required: not empty")
}Validators can be combined with the following operators &&, ||, and ! .
&&: Combine two validators together usingAND||: Combine two validators together usingOR!: Use the inverse of a validator usingNOT
See the Documentation for available validators.