Or monorepo in monorepo.
Video (YouTube) example:
Requirements:
- Node.js
- Yarn Workspaces
- Install all deps:
yarn install
- Go to the
examples/monorepo/appand start dev:
cd examples/monorepo/app
yarn dev
-
Change something visible in the
examples/monorepo/modules/module-a.- It should update the app during development.
-
Then try to change something in the
packages/package-a.- It should update the app during development.
Basically it's just spreading of the inner monorepos workspaces into workspaces of the outer monorepo.
That means that root package.json contains array of workspaces for all workspaces.
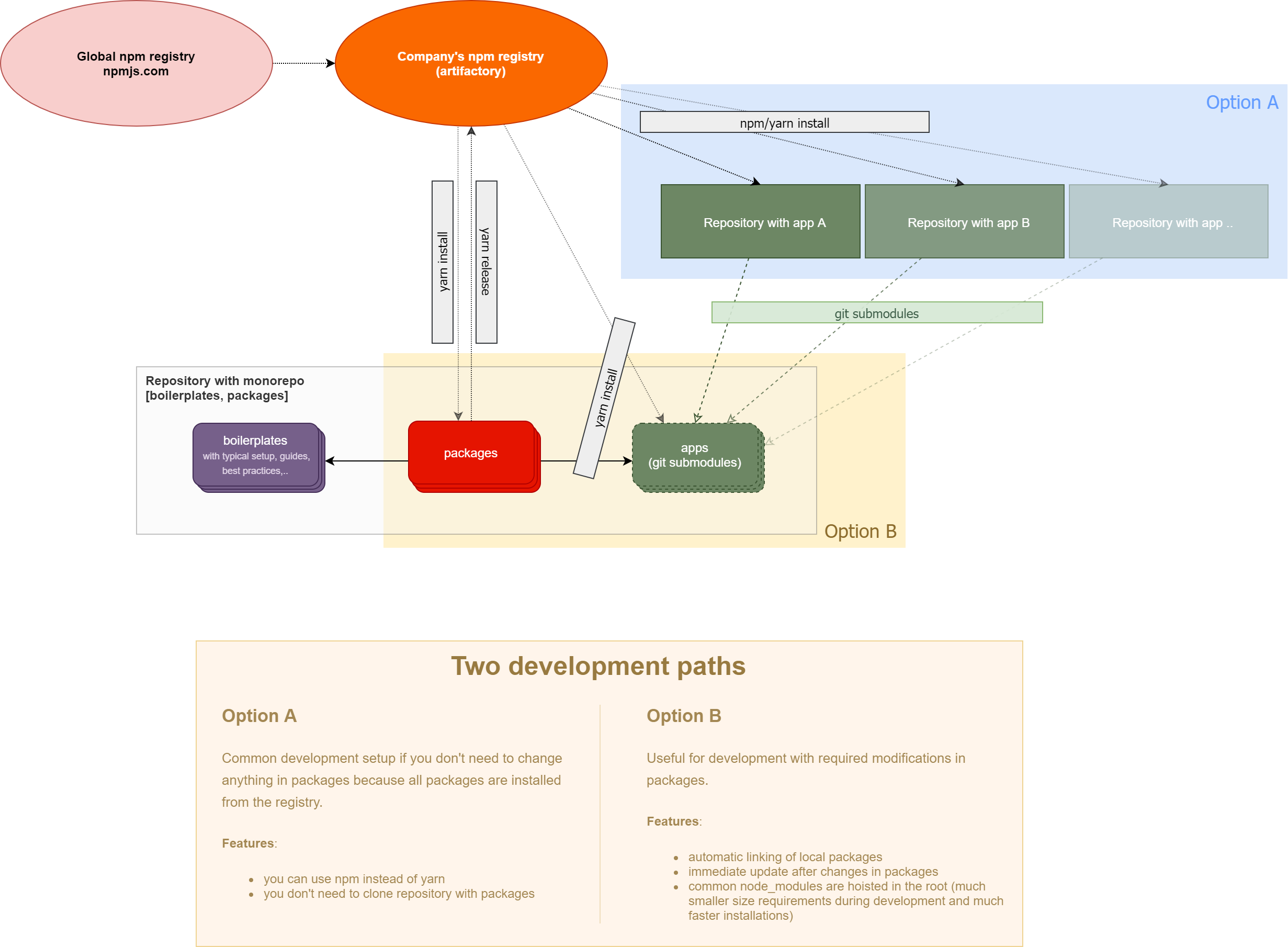
This allows to create libs and apps with one tool - Vite.js v2 which supports watching of linked packages so if we use git submodules then we can prepare setup in monorepo with published packages where you can automatically link these packages inside of other repositories which are cloned as git submodules. And because of that you can skip interbuilds of packages and immediately develop application in submodule which depends on these packages and if you change something in these packages then these changes are immediately visible in developed application!
This example represents monorepo with packages which are published. These packages are in the folder ./packages. Next to this folder is ./examples folder which can be think of as the folder with git submodules. These submodules could be frontend applications which use some of these packages from ./packages folder. Yarn Workspaces are used for automatic linking between workspaces which are packages and applications and anything else which is written inside of the pkg.workspaces array - it allows to use external packages which are not published yet! And application can be another monorepo.