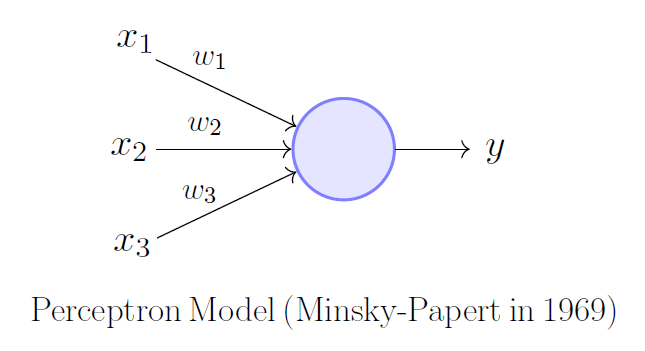
Modelling the perceptron model from scratch.
Urine specimens were analyzed in an effort to determine if certain physical characteristics of the urine might be related to the formation of calcium oxalate crystals.
This data frame contains the following columns:
- r - Indicator of the presence of calcium oxalate crystals.
- gravity - The specific gravity of the urine.
- ph - The pH reading of the urine.
- osmo - The osmolarity of the urine. Osmolarity is proportional to the concentration of molecules in solution.
- cond - The conductivity of the urine. Conductivity is proportional to the concentration of charged ions in solution.
- urea - The urea concentration in millimoles per litre.
- calc - The calcium concentration in millimoles per litre.
Source - The data were obtained from Andrews, D.F. and Herzberg, A.M. (1985) Data: A Collection of Problems from Many Fields for the Student and Research Worker. Springer-Verlag.
References - Davison, A.C. and Hinkley, D.V. (1997) Bootstrap Methods and Their Application. Cambridge University Press.
The perceptron model, proposed by Minsky-Papert, is a more general computational model than McCulloch-Pitts neuron. It overcomes some of the limitations of the M-P neuron by introducing the concept of numerical weights (a measure of importance) for inputs, and a mechanism for learning those weights. Inputs are no longer limited to boolean values like in the case of an M-P neuron, it supports real inputs as well which makes it more useful and generalized.
In this repository we are going to make our perceptron Model from scratch and then use it to determine the presence of calcium oxalate crystals in the given urine sample.
Accuracy of 83% was acheived using this model.