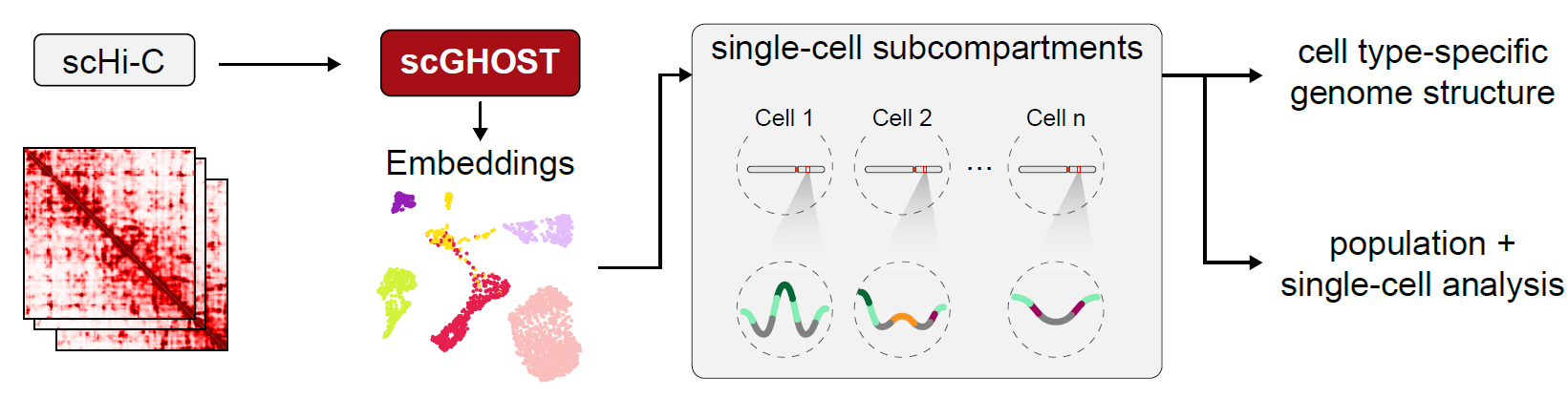
scGHOST is an unsupervised single-cell subcompartment annotation method based on graph embedding with constrained random walk sampling. scGHOST is designed to be run on a single-cell Hi-C (scHi-C) dataset which has undergone imputation by Higashi (Zhang et al. 2022). scGHOST assigns embeddings to genomic loci in the genomes of individual cells by viewing scHi-C as graphs whose vertices are genomic loci and edges are the contact frequencies among loci. While scGHOST is developed for scHi-C data, it can also identify single-cell subcompartments in single-cell genome imaging data.
scGHOST uses the outputs from Higashi as its inputs. Specifically, it requires the scHi-C imputations (hdf5 format), per-cell embeddings (numpy format), sparse raw scHi-C adjacency maps (numpy format), the scA/B scores (hdf5 format), and the label info file (pickle format) describing the cell types corresponding to each cell in the dataset.
Before installing any Python packages, we strongly recommend using Anaconda (please refer to the Anaconda webpage for conda installation instructions) to create a python 3.10 environment using the following command:
conda install --name scghost python=3.10
After creating the environment, activate it using:
conda activate scghost
- PyTorch (2.1.0) with CUDA (11.8)
- Scikit-learn (latest)
- h5py
Users can install scGHOST dependencies using the conda or pip commands following the specifications above.
Systems without a CUDA-capable GPU can also install scGHOST using the same dependencies and installing PyTorch for CPU only, but will have to modify the source code in modules/clustering.py to use SKMeans instead of KMeans under the scghost_clustering_reworked function. We may add a flag in the config file to run CPU only instead, but from our experience running scGHOST on the CPU only takes far longer than on a GPU and is not recommended.
scGHOST can use up to 40 GB of memory for a single-cell dataset of 4,238 cells. Considering operating system overhead, we recommend running scGHOST on a machine with at least 64 GB of memory to avoid poor performance or out-of-memory errors at runtime.
scGHOST was developed on a system with a 12-core 12th generation Intel CPU, an Nvidia RTX 3090 GPU with 24GB of VRAM, and 64GB of system memory. With GPU caching enabled, scGHOST uses a maximum of 15 GB of VRAM on the PFC dataset. With GPU caching disabled, VRAM becomes less of a limiting factor and scGHOST should run on any CUDA-capable GPU with at least 4 GB of VRAM.
Users can run scGHOST using the following command:
python scghost.py --config <configuration.json>
Sample JSON config files for scGHOST have been provided.
configuration is the filepath to a custom configuration file adhering to the JSON format for scGHOST. By default, scGHOST uses the included config.json file, which can be modified to the user's specifications.
Note: users may run into a RuntimeWarning after the clustering step. This is normal behavior and should not affect the accuracy of results.
scGHOST was run on a machine with a 12-core 12th generation Intel CPU and Nvidia RTX 3090 24GB GPU. From scratch, scGHOST takes about 2 hours to run on the sciHi-C GM12878 dataset and about 4 hours to run on the human prefrontal cortex dataset.
schic_directory: the directory containing Higashi-imputed single-cell Hi-C maps.label_info:label_info.picklefile following the format in Higashi.path: the file path of thelabel_info.picklefilecell_type_key: the key inlabel_info.picklewith a list of the cell types in the dataset
data_directory: the output directory of scGHOSTchromosomes: the list of chromosomes to apply scGHOST to. default: autosomeschrom_sizes: file path to the chromosome sizes file. default:data/hg38.chrom.sizeschrom_indices: file path to chrom indices if previously computed. Development flag to save time over multiple runs on the same dataset. Default:nullembeddings_path: file path to the Higashi embeddings.npyfile for each cell in the datasethigashi_scab_path: file path to Higashi scA/B scores.h5filecell_type: the cell type in the dataset to apply scGHOST on; usenullto apply scGHOST to all cell types in the dataset. default:nullrandom_walk: random walk parametersnum_walks: number of random walks per iteration. default: 50ignore_top: the top and bottom percentile to be ignored, to remove extreme values in the input matrix. default: 0.02top_percentile: the top percentiles within which random walks are performed. default: 0.25
eps: small float value to prevent dividing by zero in some functions. default: 1e-8num_clusters: number of clusters to partition chromosomes intoneighbor_contacts: determine whether to use the average of nearest neighbor contacts as the target label during node embedding.nearest_neighbor_override: use a custom numpy array to define nearest neighbors. The format should be anN x (k+1)array withNdenoting the number of cells in the dataset andkdenoting the number of nearest neighbors. Rowiin the array should contain entries denoting which cells are the nearest neighbors of celli.cluster_gpu_caching: toggle caching chromosome embeddings on the GPU prior to clustering to reduce CPU overhead converting embedding vectors to cuda variables. We recomend disabling this if your GPU memory is less than 16 GB.gpu_uniques: determine whether to use the GPU to compute unique random walk samples. On machines with higher CPU core counts, CPU processing may be faster than GPU processing.kmeans_init: then_initparameter in scikit-learn/cuML'sKMeans. We set this value at a default of 1 to reduce clustering runtime.
Please follow our tutorial notebooks in the root directory for examples on how to run scGHOST with and without first running Higashi. For a sample run of scGHOST, users can download the smaller WTC-11 dataset here. After downloading the sample data, please change the sample_configs/config_wtc.json configuration file accordingly to point to the correct paths and run the following command:
python scghost.py --config sample_configs/config_wtc.json
Please email jianma@cs.cmu.edu or raise an issue in the github repository with any questions about installation or usage or any encountered bugs.