One-click Trusted Execution Environment For TLSNotary
tlsn-tofu was born as a reference for simple and secure infra for tlsnotary to leverage secure enclaves, and to demonstrate how to use their most important (and complex) feature: remote attestation!
clone this repo; cd into it, then:
- mac:
brew update && brew install azure-cli
- linux:
curl -sL https://aka.ms/InstallAzureCLIDeb | sudo bash
az login
chmod +x ./install_tofu.sh && bash ./install_tofu.sh
- mac:
brew update && brew install ansible && ansible-galaxy collection install cloud.terraform
- debian/ubuntu linux:
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:ansible/ansible && sudo apt update && sudo apt install ansible && ansible-galaxy collection install cloud.terraform
this will create an azure resource group, a vm suitable for SGX to be the verifier, and vm to be the prover, and an SSH key:
tofu init && tofu plan && tofu apply
if all is well, tofu will ask you to confirm:
type yes and hit enter
this will configure the two vms created above:
ansible-playbook -i inventory.yml playbook.yml
tofu destroy
-
How do I generate my own MR_ENCLAVE signature, to see if it matches the signature I get back from SGX Remote Attestation?
- Follow these steps to create a local measurement without SGX: ensure you have gramine, rust, and openssl-dev on the host you are using:
git clone https://github.com/maceip/sgx-tlsn-notary-servercd sgx-tlsn-notary-servermakegramine-sgx-gen-private-keygramine-sgx-sign -v --manifest sgx-notary-server.manifest --output tlsn-tofu-test.sgxgramine-sgx-sigstruct-view sgx-notary-server.sig-
Attributes: mr_signer: 18c8a8ee1fddf6edd5251a1f9421ca6922e33fa4e3a8436e34cb6ab1349dc254 mr_enclave: 4f6e89a59d42fcb55f27ad5f3b3f4b384783a5fb3fc3b07afdcc31bff6f17e52 isv_prod_id: 0 isv_svn: 0 debug_enclave: False
-
- if you rm -rf the directory and run the steps again, the mr_enclave value will be the same
- Follow these steps to create a local measurement without SGX: ensure you have gramine, rust, and openssl-dev on the host you are using:
-
How does Remote Attestation work?
-
In this repo we are running the SGX-TLSNotary-Server repo inside the TEE, which is a repo using the vanilla TLSNotary Server with a Gramine specific manifest and loaded with the Gramine-RATLS wrapper. Gramine RATLS is a shim that is loaded in the TEE first, and sets up a modified TLS server that implements RATLS.
-
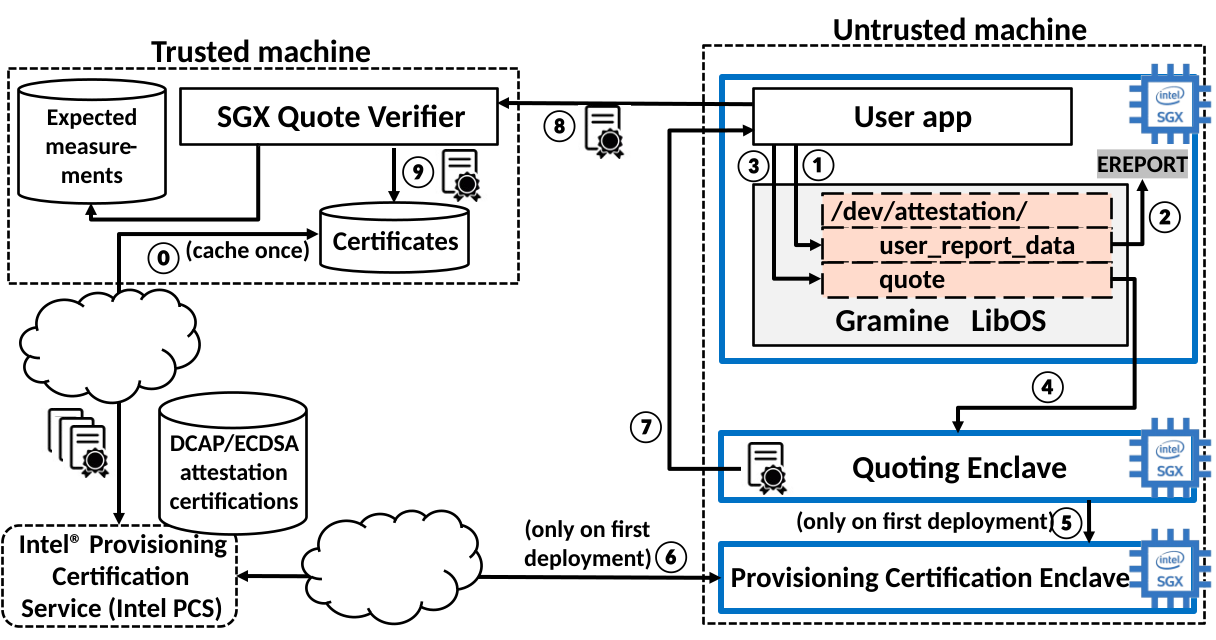
the steps are as follows:
- the enclavized user application opening the special file
/dev/attestation/user_report_datafor write - gramine uses the EREPORT hardware instruction to generate an SGX Report
- After the SGX report is generated, the application opens another special file
/dev/attestation/quotefor read - Under the hood, Gramine communicates with the Quoting Enclave to receive the SGX Quote
- Quoting Enclave talks to the Provisioning Certification Enclave (PCE)
- The PCE uses another Intel service called Intel Provisioning Certification Service (PCS) to obtain the attestation collateral. This collateral comprises attestation certificates and certificate revocation lists for the SGX machine
- When the SGX quote arrives, the user compares the certificates embedded in the quote against these cached certificates
- the enclavized user application opening the special file
-
for more information, consult the Gramine docs
-
- Azure
- Azure THIM DCAP
- PCCS
- Remote Attestation Demo
- TDX
- SEV-SNP
-
This repo utilizes open tofu to provision TEE capable hardware across various cloud providers. Currently, it only supports a single notary running inside SGX via Gramine on Azure.
-
The hardware is configured with Ansible, and sets up SGX Remote Attestation (DCAP /w ECDSA), a Provisioning Certificate Caching Service, and a development gramine key.
-
inspect the cloud configuration via:
tofu show
-
to see the ansible-host that tofu created, run:
ansible-playbook -i inventory.yml playbook.yml --list-hosts
tofu creates a ssh key in ~/.ssh/${var.resource_group_name_prefix}-sshkey.pem". This key is deleted when you use tofu destroy!
notes from call with chris
- explain gramine-ratls and how it's used in this demo
- how would someone compute an MR_ENCLAVE value on their own (with or without SGX)
- don't just print the sigstruct hash, loop in the tlsnotary extension and add a plugin that fetches the hash from the tlsnotary github repo (also add the mrenclave of the mainline notary server to the readme.md)