26416083, Computer Graphics, Using OpenGL (GLUT)
- Visual Studio 2015 (v140 platform toolset)
- Target Platform Version 8.1
- #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
- Vector
- Matrix deprecated
- Matrix2 (07 Oct, 2018)
- Transformation
- Quadric
- Hierarchy
- RGBColor
- Face
- Mesh
- Light
- Material
- Camera
- Download projects
.zipfile or by using git
git clone https://github.com/MadeYoga/Computer-Graphics.git
-
Copy all files inside
Classesfolder and paste it to your project folder -
include these lines of code into your main.cpp file project
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// you should declare `glut.h` or glut header before including `Header.h`
// it doesn't always looks like this to declare `glut.h`,
// it depends on how you install `glut.h`.
#include "GL Libraries\GL\glut.h"
#include "Header.h"#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "GL Libraries\GL\glut.h"
#include "Header.h"
#define WINDOW_SIZE 600
// Define World and Camera(Eye)
World world;
Camera cam;
void idle() {
glutPostRedisplay();
}
void initWorld() {
glOrtho(-WINDOW_SIZE, WINDOW_SIZE, -WINDOW_SIZE, WINDOW_SIZE, -WINDOW_SIZE, WINDOW_SIZE);
glClearColor(0, 0, 0, 0);
// Define Objects
Mesh teapot_mesh, cube_mesh;
// load .obj file
teapot_mesh.loadObject_poly("teko.txt");
cube_mesh.loadObject_square("kubus.txt");
// add Objects to world
world.add_mesh(teapot_mesh);
world.add_mesh(cube_mesh)
}
void test() {
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glRotatef(1, 1, 1, 1);
glPointSize(2);
/*~magics happens here~*/
world.draw(cam);
glDisable(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
glutSwapBuffers();
}
void main(int argc, char **argv) {
// INIT
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGBA);
glutInitWindowSize(WINDOW_SIZE, WINDOW_SIZE);
glutCreateWindow("test 2!");
glutIdleFunc(idle);
glutDisplayFunc(test);
initWorld();
glutMainLoop();
}Camera cam;
void keyPressed(unsigned char key, int x, int y) {
if (key == 'p') {
cam.change_view_y(-20);
}
else if (key == 'a') {
cam.change_view_x(20);
}
else if (key == 'l') {
cam.change_view_y(20);
}
else if (key == 'd') {
cam.change_view_x(-20);
}
else if (key == 'w') {
cam.change_view_z(-20);
}
else if (key == 's') {
cam.change_view_z(20);
}
else if (key == 'h') {
cam.rotate(Vector(1, 0, 0, 1), 10);
}
else if (key == 'j') {
cam.rotate(Vector(-1, 0, 0, 1), 10);
}
else if (key == 'q') {
cam.rotate(Vector(0, 1, 0, 1), 10);
}
else if (key == 'e') {
cam.rotate(Vector(0, -1, 0, 1), 10);
}
else if (key == 'k') {
cam.rotate(Vector(0, 0, 1, 1), 10);
}
else if (key == 'i') {
cam.rotate(Vector(0, 0, -1, 1), 10);
}
}
void test() {
// Display something.
}
void main(int argc, char **argv) {
// INIT
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGBA);
glutInitWindowSize(WINDOW_SIZE, WINDOW_SIZE);
glutCreateWindow("GRAFKOM GG!");
glutIdleFunc(idle);
glutDisplayFunc(test);
initWorld();
glutKeyboardFunc(keyPressed); //
glutMainLoop();
}// Load obj file
bed_mesh.loadObject_square("bed.obj");
// scale
bed_mesh.matrix_transform = Transformation().scale(Vector(2, 2, 2, 1));
// translate, this will force .matrix_transform value to change.
bed_mesh.matrix_transform.translate(Vector(400, 137, -400, 1));
// rotate x
bed_mesh.matrix_transform = bed_mesh.matrix_transform.multiplies(Transformation().rotate_x(-1.575));
// set color to white. default: green
bed_mesh.set_color(RGBColor(1, 1, 1));i, provide a small set of Examples in the Other Directory. its messy, gonna clean it later.
The basics of computer graphics is MATH, so, i'm not going to explain every single detail about these math thing
i'm only going to explain how these classes works.
// Declare Vector object named `v`
Vector v(x, y, z, 1);
v.showVectorOnConsole();
// to change the declared Vector object value, use `set_value` method
v.set_value(new_x, new_y, new_z); // doesn't include `w`, w value is constant (integer 1).make sure you had identity.txt(with matrix identity value in it) inside your project directory
// Declare Matrix2 object. by default, it will declare an identity matrix.
Matrix2 matrix;
matrix.showMatrixOnConsole();
// Other method to declare Matrix2 object. this will declare a 4x4 matrix with value 0 on each indexes.
// theres a bug on it, can declare only with 4 max row and 4 max cols. gonna fix it later.
Matrix2 matrix0(4, 4);Matrix2 values is using a 2 dimensional array and its public, so, to get Matrix2 values, use Matrix2._matrix
// DECLARE matrix identity 4x4
Matrix2 dummy_matrix;
// get matrix's value at row 0 and col 0
dummy_matrix._matrix[0][0];
dummy_matrix._matrix[1][0];
.
.
dummy_matrix._matrix[3][3];
// returns a 2d array with 4x4 row and col
dummy_matrix._matrix;Matrix can be multiplied by/with a matrix. In order to multiply two matrices, A and B, the number of columns in A must equal the number of rows in B. Thus, if A is an m x n matrix and B is an r x s matrix, n = r.
// this is how you multiplies a matrix.
matrix.multiplies(matrix0);
// `multiplies` method returns a `multiplies result value` instead of changin the original `matrix` values
// so, do it like this.
matrix = matrix.multiplies(matrix0);
// Matrix can also multiplied by a `Vector` and the result would be a Vector, so, `multiplies` method gonna returns a Vector object instead of Matrix2
// still, `multiplies` method doesn't change their matrix original value, it would only returns a multiplies result.
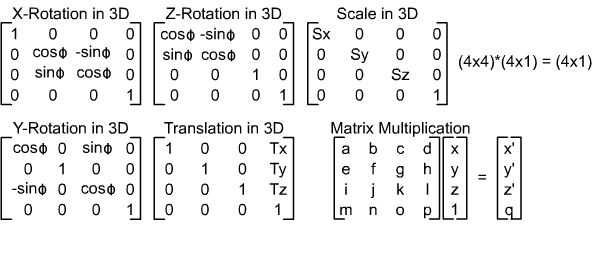
Vector v = matrix.multiplies(Vector(x, y, z, w));Transformation class provides you to get a transformation matrix value from a given Vector. Matrix Such as Translation, Scaling, Rotation. this class will return matrix as shown below.
Transformation transformation();
Vector vector(50, 50, 50, 1);
transformation.scale(vector);
transformation.translate(vector);
float theta = 60;
// returns X-ROTATION 3D matrix
transformation.rotate_x(theta);
// returns Y-ROTATION 3D matrix
transformation.rotate_y(theta);
// returns Z-ROTATION 3D matrix
transformation.rotate_z(theta);Vector vector(50, 50, 50, 1);
Transformation transformation();
Matrix2 matrix(); // Matrix that we want to transform
Matrix2 transformation_matrix = transformation.translate(vector);
// to transform a Matrix, we need to multiplies it with th transformation matrix
matrix = matrix.multiplies( transformation_matrix );