This is the repository of ml4iiot a framework to implement Machine Learning methods for time series data.
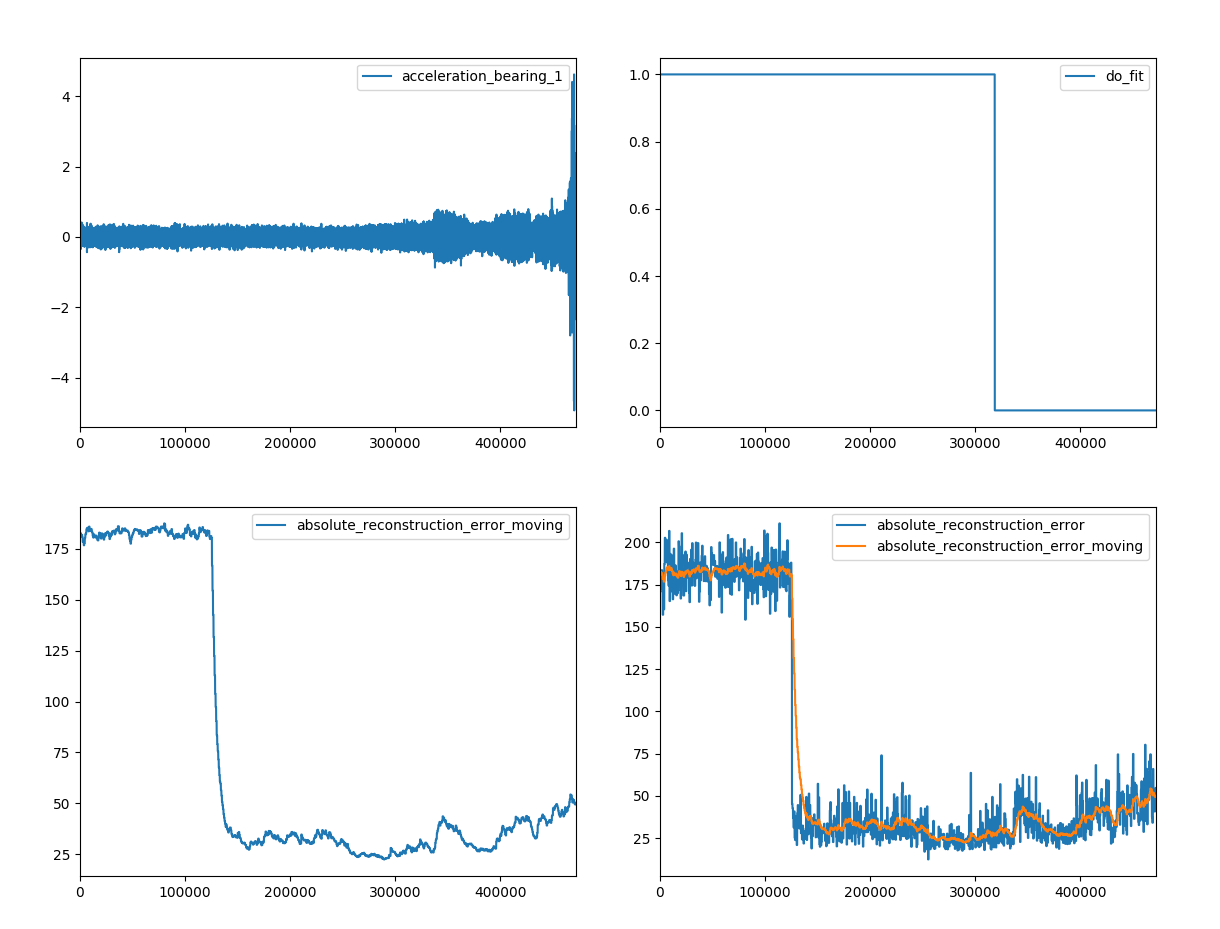
This example shows an autoencoder being trained on the Fast Fourier transform
of the acceleration of bearing 1 of the IMS Bearing Data Set.
The configuration of this experiment can be found in config/ims_bearing_data_set_autoencoder.yaml.
The autoencoder learns (adjusts its weights) and predicts until the 2004-02-17 and after that does only predictions anymore (see do_fit).
The results show that the upcoming crash shows up in an increasing reconstruction error of the autoencoder.
- Run IMS Bearing Data Set Autoencoder example:
python ml4iiot/cli_runner.py -c config/ims_bearing_data_set_autoencoder.yaml - Plot acceleration of bearing 1:
python ml4iiot/plot_csv.py -p out/YYYY_MM_DD/ims_bearing_data_set/HH_MM_SS_csv_output.csv -itime acceleration_bearing_1 - Plot reconstruction error:
python ml4iiot/plot_csv.py -p out/YYYY_MM_DD/ims_bearing_data_set/HH_MM_SS_csv_output.csv -itime absolute_reconstruction_error_moving
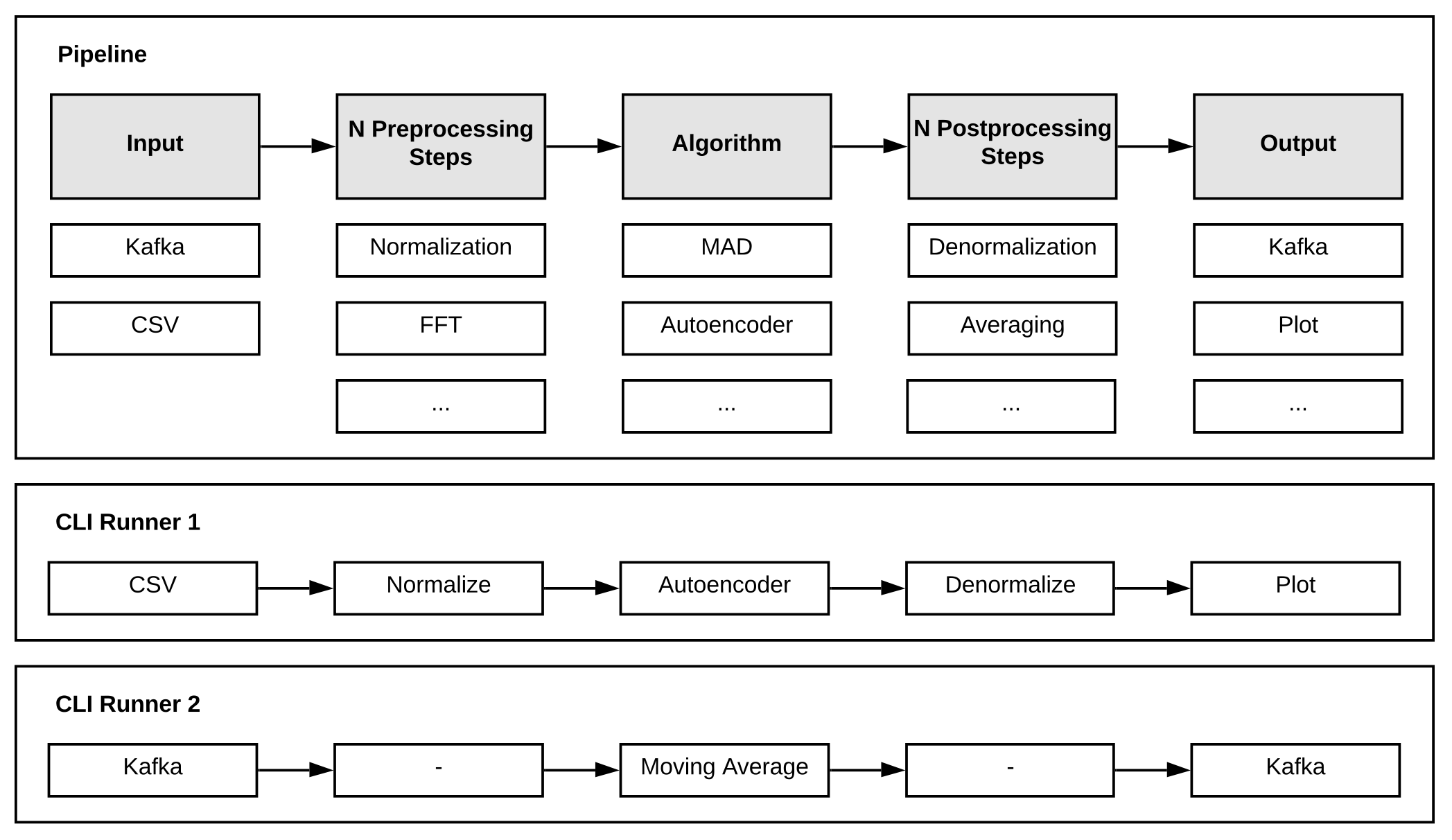
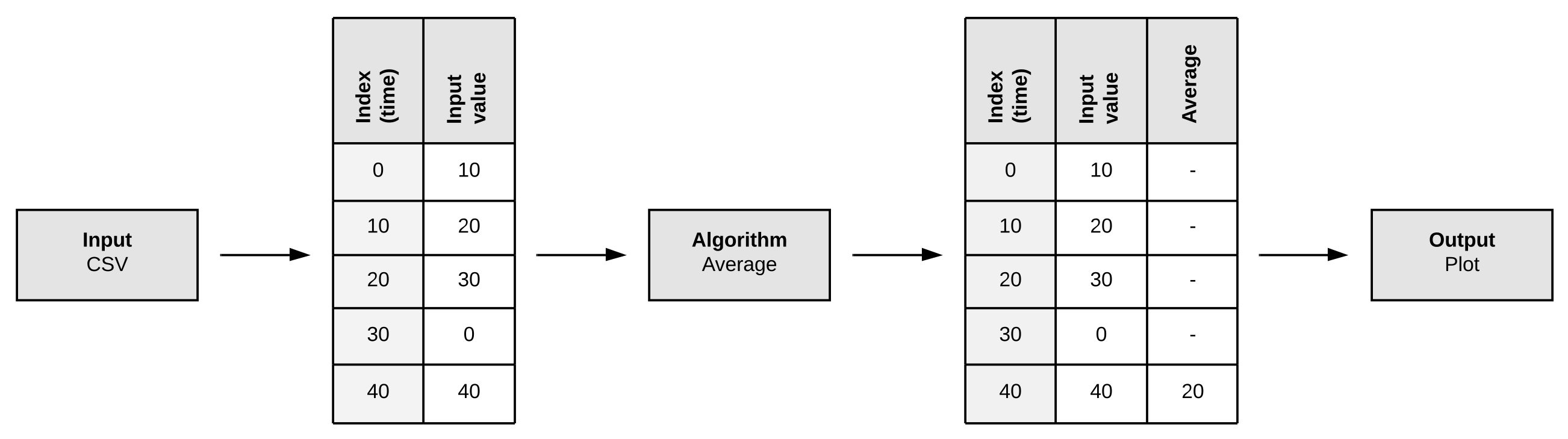
We abstract the entire process into a pipeline consisting of different processing steps. Each pipeline must have an input, an algorithm and an output step. Before and after the algorithm step there can be any number of pre- or post-processing steps.
A pipeline can configured using YAML or JSON files and can be started with the CLI runner.
The main abstraction between individual pipeline steps are pandas DataFrames. Each step can add additional columns to the dataframe but should not alter existing columns.
pip install virtualenv;
python -m virtualenv env;
source env/bin/activate;
pip install -r requirements.txt;
pip install -e .;
Run unit tests with: python -m unittest discover tests/*
deactivate
python ml4iiot/cli_runner.py -c config/your_config.yaml
Resample the training data in advance and use integer timestamps instead of formatted date strings to speed up trainings. Use the following commands to profile your code:
python -m cProfile -o out/cli_runner.profile ml4iiot/cli_runner.py -c config/your_config.yaml
snakeviz out/cli_runner.profile
version: '3'
services:
ml4iiot:
image: still/to/be/published
volumes:
- ./ml4iiot/config:/usr/src/ml4iiot/configA pipeline always consists of an input adapter, an output adapter as well as an algorithm in between.
pipeline:
input:
class: ml4iiot.input.csv.CsvInput
config:
windowing_strategy:
class: ml4iiot.input.windowing.CountBasedWindowingStrategy
config:
window_size: 100
stride_size: 100
batch_size: 20000
delimiter: ','
csv_file: /path/to/your/data.csv
index_column: time
columns:
time:
type: datetime
datetime_format: timestamp
sensor_value: float
algorithm:
class: ml4iiot.algorithm.stochastic.average.ExponentialWeightedMovingAverage
config:
column_mapping:
sensor_value: sensor_value_average
output:
class: ml4iiot.output.compound.CompoundOutput
config:
output_adapters:
- class: ml4iiot.output.std.StdOutput
config:
show_columns_progress:
- column: index
- column: sensor_value
- column: sensor_value_average
- class: ml4iiot.output.plot.PlotOutput
config:
show_plots: True
figures:
plots:
- column: sensor_value
color: blue
- column: sensor_value_average
color: redml4iiot.input.csv.CsvInputml4iiot.input.kafka.KafkaInput
ml4iiot.input.windowing.TimeBasedWindowingStrategyml4iiot.input.windowing.CountBasedWindowingStrategy
ml4iiot.algorithm.stochastic.average.ExponentialWeightedMovingAverageml4iiot.algorithm.stochastic.average.ExponentialWeightedMovingMinMaxAverageml4iiot.algorithm.stochastic.mad.Madml4iiot.algorithm.stochastic.zscore.ModifiedZScoreml4iiot.algorithm.clustering.dbscan.DBSCANml4iiot.algorithm.autoencoder.fullyconnected.FullyConnectedAutoencoderml4iiot.algorithm.autoencoder.cnn.CNNAutoencoderml4iiot.algorithm.autoencoder.cnn.BottleneckCNNAutoencoderml4iiot.algorithm.autoencoder.lstm.ReconstructionLSTMAutoencoderml4iiot.algorithm.autoencoder.lstm.PredictionLSTMAutoencoderml4iiot.algorithm.autoencoder.variational.VariationalAutoencoder
ml4iiot.processing.normalization.MinMaxScalerml4iiot.processing.smoothing.MovingExponentialSmoothingml4iiot.processing.transform.Averageml4iiot.processing.transform.StandardDeviationml4iiot.processing.transform.Minimumml4iiot.processing.transform.Maximumml4iiot.processing.transform.FastFourierTransformml4iiot.processing.control.SkipDataFrame
ml4iiot.output.compound.CompoundOutputml4iiot.output.std.StdOutputml4iiot.output.plot.PlotOutputml4iiot.output.csv.CsvOutputml4iiot.output.kafka.KafkaOutputml4iiot.output.config.ConfigOutput