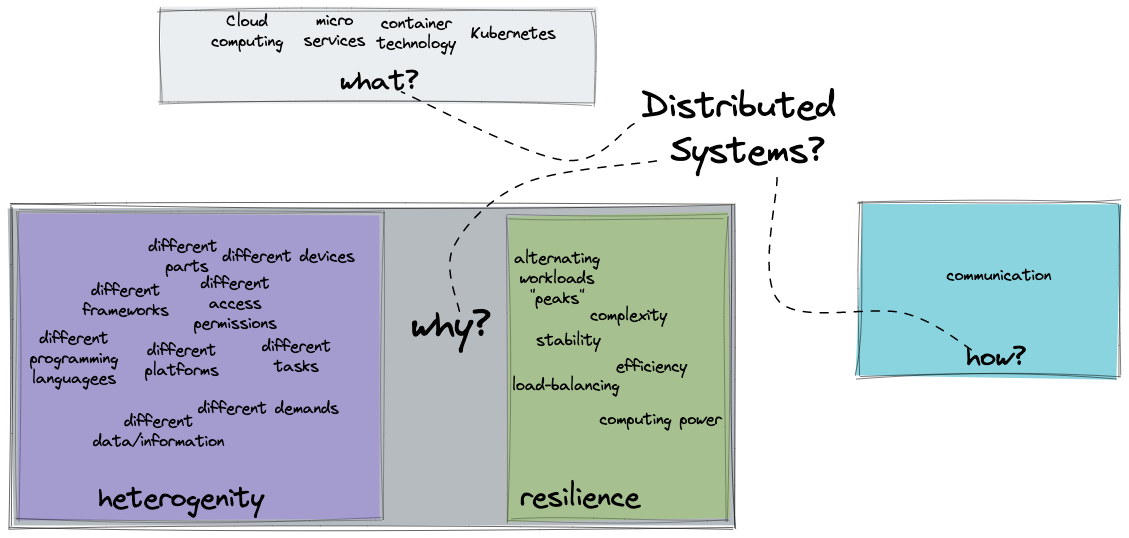
- Which technologies or what do you have in mind in general if you think about "distributed systems"?
- the "WHY" - Why would people use and implement a distributed systems architecture?
- Why distributed systems?
- What is Cloud Computing? Encounters in everyday life and history
- Characteristic, advantages & challenges
- Terminology - public, private, hybrid, dedicated
- Abstraction layers - IaaS, PaaS, FaaS, SaaS
- Overview - Hypervisors, virtual machines, containers and orchestration
The student is able to describe the reasons for distributed systems and cloud computing in own words and list examples for offerings, topologies and technologies. Includes ability to differentiate between different abstraction layers and knowledge how those layers and according technologies interact with each other. No exercises in this module
- https://landscape.cncf.io/
- https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-145/final
- https://spring.io/tools
- https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/
- https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/java/java-tutorial
- https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=Pivotal.vscode-boot-dev-pack
- https://www.gitpod.io
- "WHY" Cloud? Explain advantages (and disadvantages) IN YOUR OWN WORDS!
- Sketch a Cloud abstraction layer diagram and provide technology/provider samples for each
- "aas" - Explain the term service as opposed to a product (in the context of cloud)
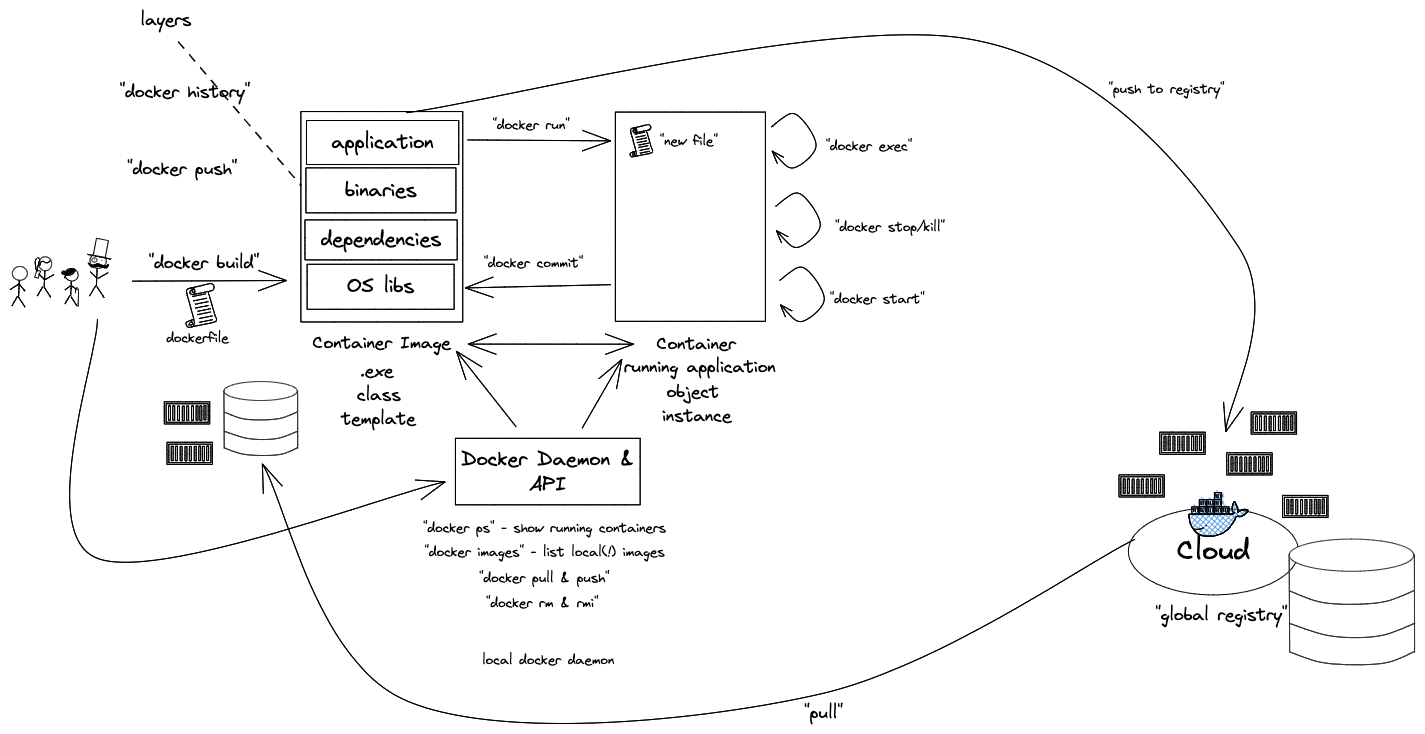
- What are containers and how do they work?
- Containers vs. VMs
- History of containers and rise of Docker
- Docker concepts: daemon, hub, dockerfile, CLI
- Running containers with various options
The student understands the concepts and use cases of container technology and is able to describe them. The first exercise is to pull sample images from an image registry (e.g. Docker Hub) and interact with them (run, expose port, execute shell, cleanup etc). After that the student can show how to build a custom image via Dockerfile and push it to a registry for others to access. Complete the exercises handed out via URL.
- Create or get yourself a Docker Id (https://www.docker.com)
- Do the container lab given at: https://hfthse.trainings.nvtc.io/
- "WHY" Containers? List advantages/disadvantages ..
- What is the difference between a container and a VM? List 3 criteria
- Which technologies led to the evolution of docker (and why)?
- What is the difference between a docker daemon and the docker hub?
- What is the difference between docker run, docker pull and docker start?
- Which command transitions from a container instance to an image?
- What are the Docker components and describe them?
- What does docker exec do? Provide a pseudo-code example and explain what it does
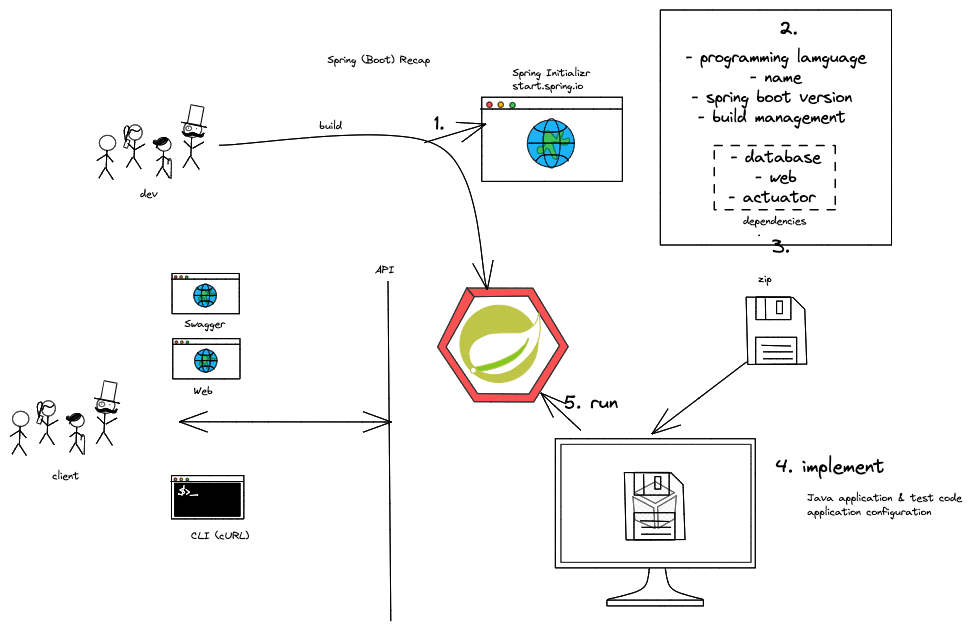
- Background: Spring Framework - History & components
- Spring ← → Spring Boot
- Spring Initializr (start.spring.io) & starter dependencies
- Basic project structure (folders, configuration ..)
- "Hello, World!" example explained
- Using Actuator
The student is able to build and configure an own Spring Boot application from scratch with the IDE of choice. The exercise is to build an own "Hello, World!" application that exposes various - endpoints and is able to execute CRUD operations on the state of the application. Optional: Add logging and testing, configure Actuator.
- Create a first project from Spring Initializr at: https://start.spring.io/
- Edit in your editor of choice.
- Optional: Try gitpod as cloud-based editor https://gitpod.io/
- Experiment with starter dependencies. Recommended: Spring Web, Actuator, DevTools
- Expose a public REST endpoint for a GET Call.
- Pass a variable to the application using the @PathVariable annotation.
- https://start.spring.io/
- https://gitpod.io/
- https://spring.io/guides/gs/rest-service/ (or basically Spring Guides in general)
- https://www.baeldung.com/spring-pathvariable (or basically all Baeldung guides)
- "WHY" Spring Boot? "WHY" Frameworks?
- What is the difference (and common aspects) between Spring and Spring Boot?
- What is the web page to start building your spring boot apps?
- What kind of things can you configure on that Initializr?
- What is the role of the Actuator?
- If you don't know the actuator list 3 other starter dependencies and explain briefly what they do?
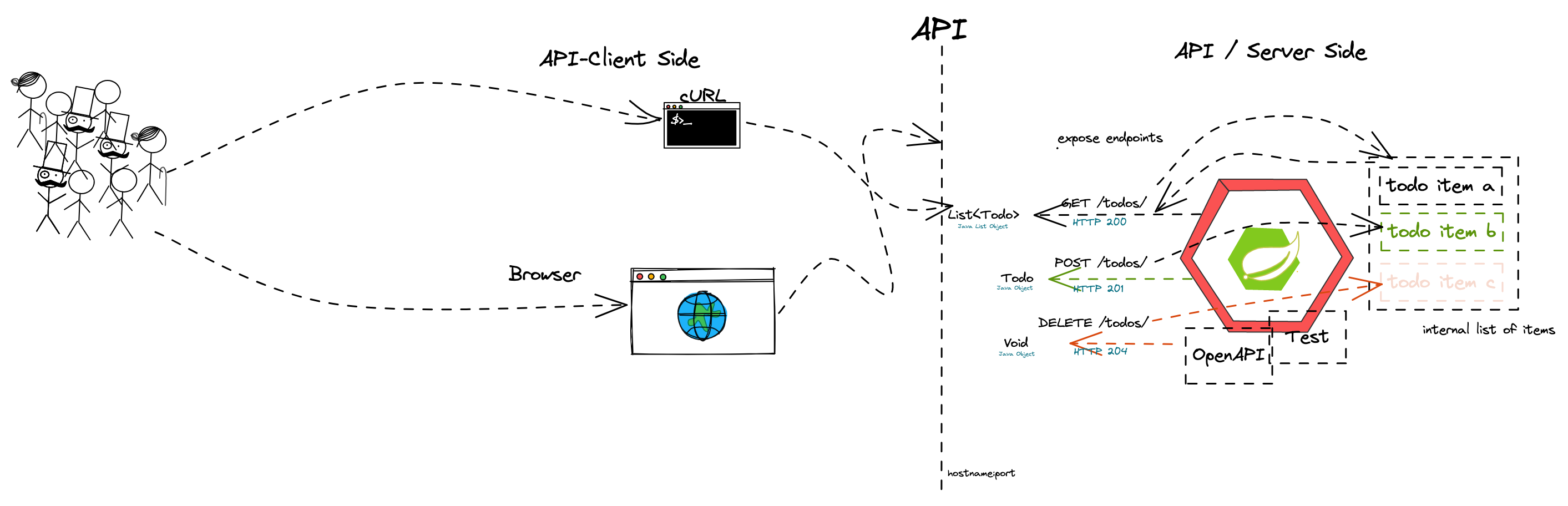
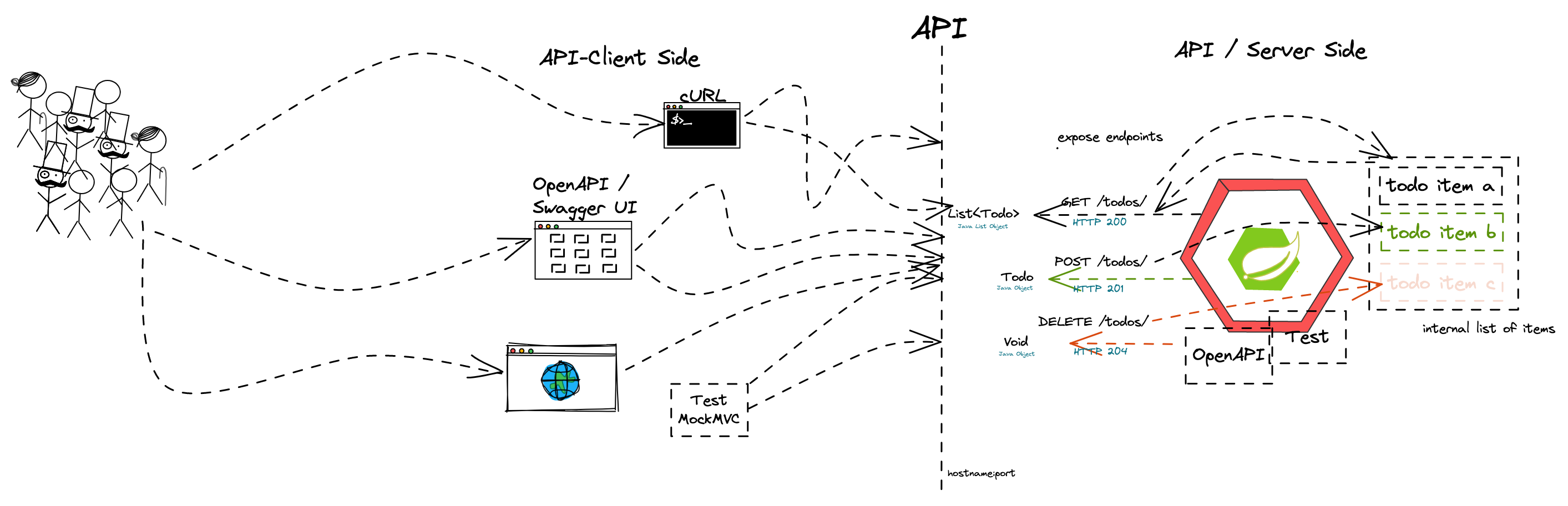
- Synchronous communication
- HTTP and REST
- Verbs, Resources, Nouns
- Evolution, Richardson Maturity Model
- CRUD Operations
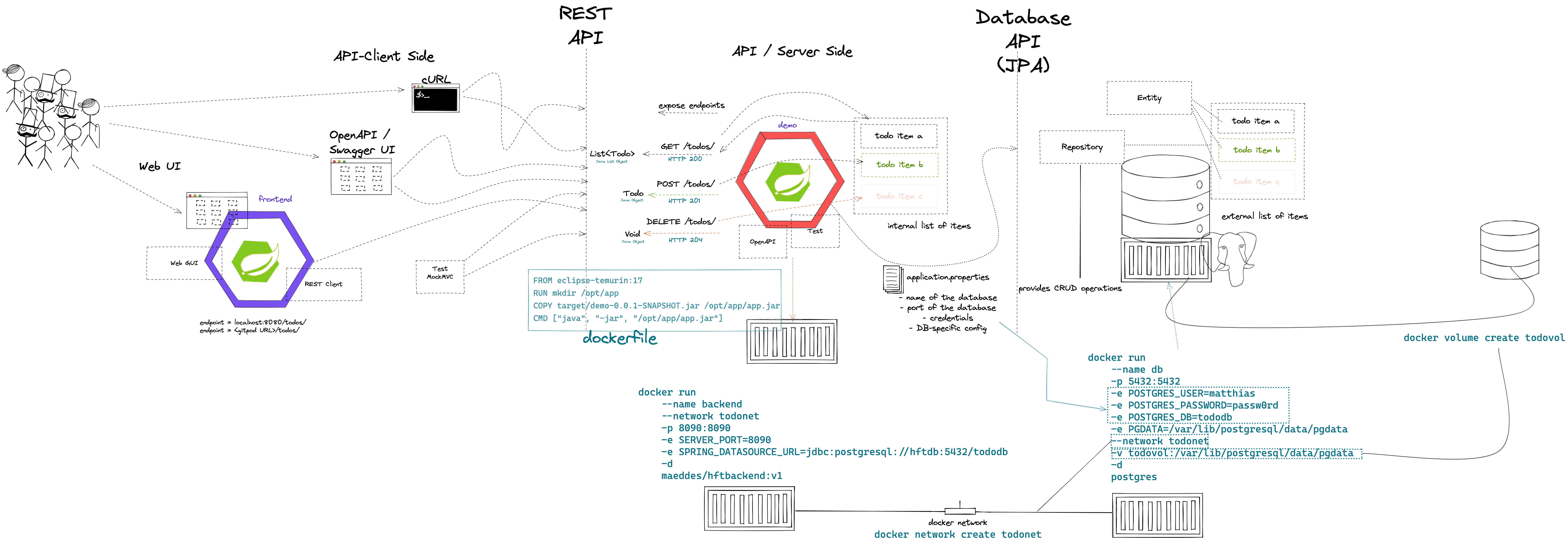
- Building a REST API with Spring (Boot)
- Building a data model with REST
The student understands the concepts of an API and synchronous communication in distributed systems and can explain it in own words.
- Create a full CRUD Rest API on your application
- The API object is a simple Java object with the following field
private String todo;
private int priority = 2;
- A RestController class is supposed to have an internal list of these objects and provide CRUD functionality.
- Starter sample is given in the git repo.
Links:
- Identify good and bad API examples and explain why
- Describe the concepts of Verbs and Nouns
- When is an invocation idempotent and safe? What does it mean? Provide examples
- Describe in your own words the mapping of REST calls to database (SQL) and CRUD calls
- Watch the video I uploaded :-)
- Exercises given there
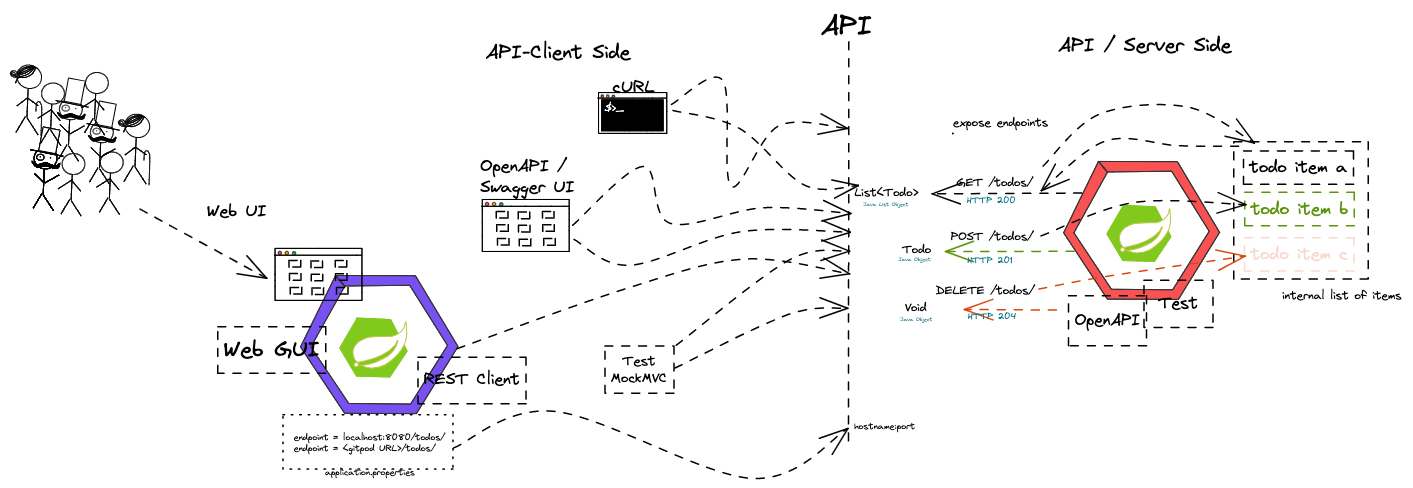
- Use WebClient as REST client within an application
- Build a graphical web UI using Thymeleaf
- CRUD operations between applications
- Connect Thymeleaf and WebClient functionality
=== Objectives and exercises The student is able to understand web UIs using Thymeleaf technologie. This includes steps like displaying dynamic content, iterating over lists and reading input from the web UI. The student understands the WebClient as default REST Client for Spring Boot applications and is able to implement CRUD operations with a REST API. In the exercise combine both technologies to provide a graphical web UI to interact with a REST API of another service.
image::pics/thymeleaf_webclient.png[Thymeleaf & WebClient]
=== Links:
- https://rieckpil.de/spring-webclient-for-restful-communication-setup-and-examples/
- https://bclozel.github.io/webflux-workshop/
- https://www.websparrow.org/spring/spring-boot-consuming-a-rest-services-with-webclient
- https://javatechonline.com/how-to-develop-a-reactive-crud-rest-api-with-spring-webflux/
- https://www.baeldung.com/spring-5-webclient
- https://www.baeldung.com/spring-controller-vs-restcontroller
- https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html
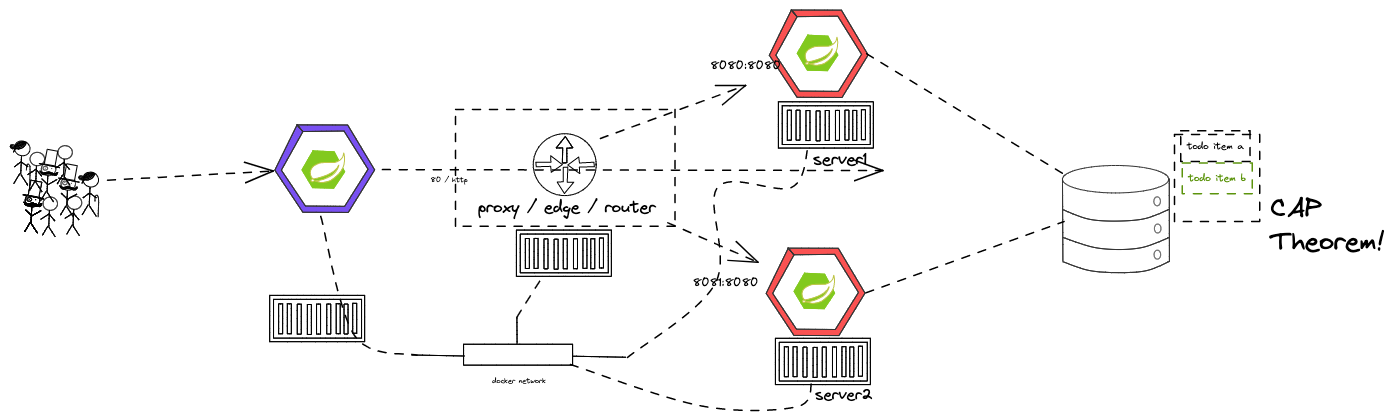
- CAP Theorem
- Conway's Law
- Fallacies of distributed computing
- Domain-Driven Design basics
- 12-factor application
- Evolution of applications and deployments: Monolithic -> Service-Oriented Architecture -> Microservices
- Introduction to serverless and FaaS terminology
The student knows about the evolution of distributed systems (and middleware) and the drivers towards state-of-the-art implementation and deployment. She/he can explain the underlying concepts and theories and put it into practical context. No dedicated exercises for this module. Recap of basics: Spring Boot, Docker, configuration, persistence and messaging.
- "WHY" Cloud-Native Software? What IS Cloud-Native Software?
- Why "evolution" from a monolithic approach to a distributed approach?
- How does the CAP Theorem/Conway's Law relate to this?
- (NO Domain-Driven Design questions)
- How do the 12-factor application "methodology" relate to the technologies that we covered in this semester? (important)
- "WHY" is external configuration important in cloud-native software?
- Where did you see aspects of external configuration in the technologies we used? Provide examples
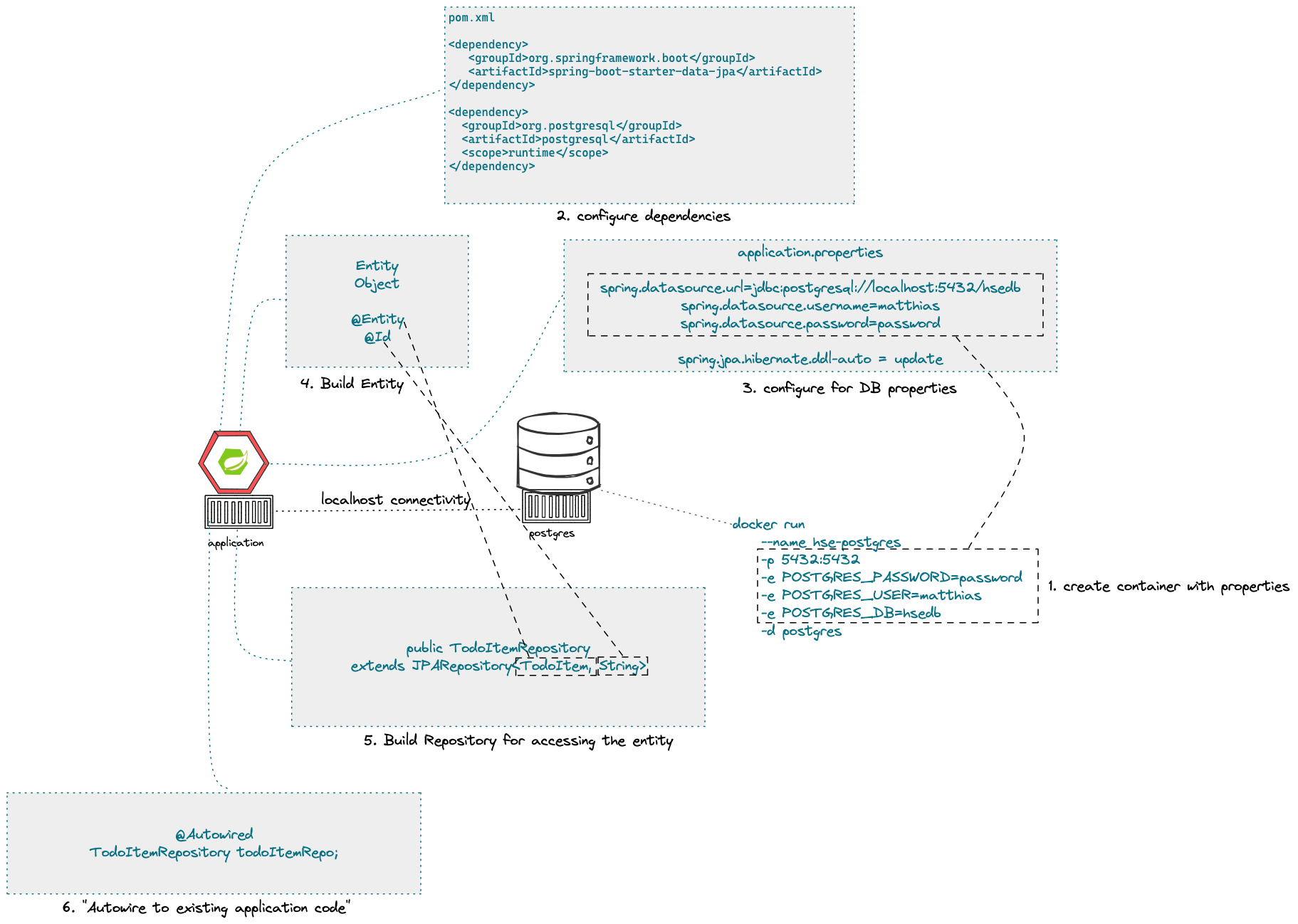
- Spring Data
- Concept of entities and repositories
- JPA and JDBC basics
- H2, PostgeSQL, MySQL - configuration via Spring Boot profiles
- Running databases as Docker images
The student is able to build a Spring Boot application (or extend an existing one) with Spring Data configuration. The exercise is to create an application, which performs CRUD operations on a database backend. The database can either be in-memory (H2) or a (containerized) PostgreSQL. Optional: Provide a docker-compose file to stand up a multi-container environment with application and database.
- "WHY" persistence? "WHY" persistence frameworks like JPA?
- Describe the necessary components to build an application with Spring Data? Potentially sketch
- What does the annotation @Entity do?
- How could docker compose help if you have a persistence-based application?
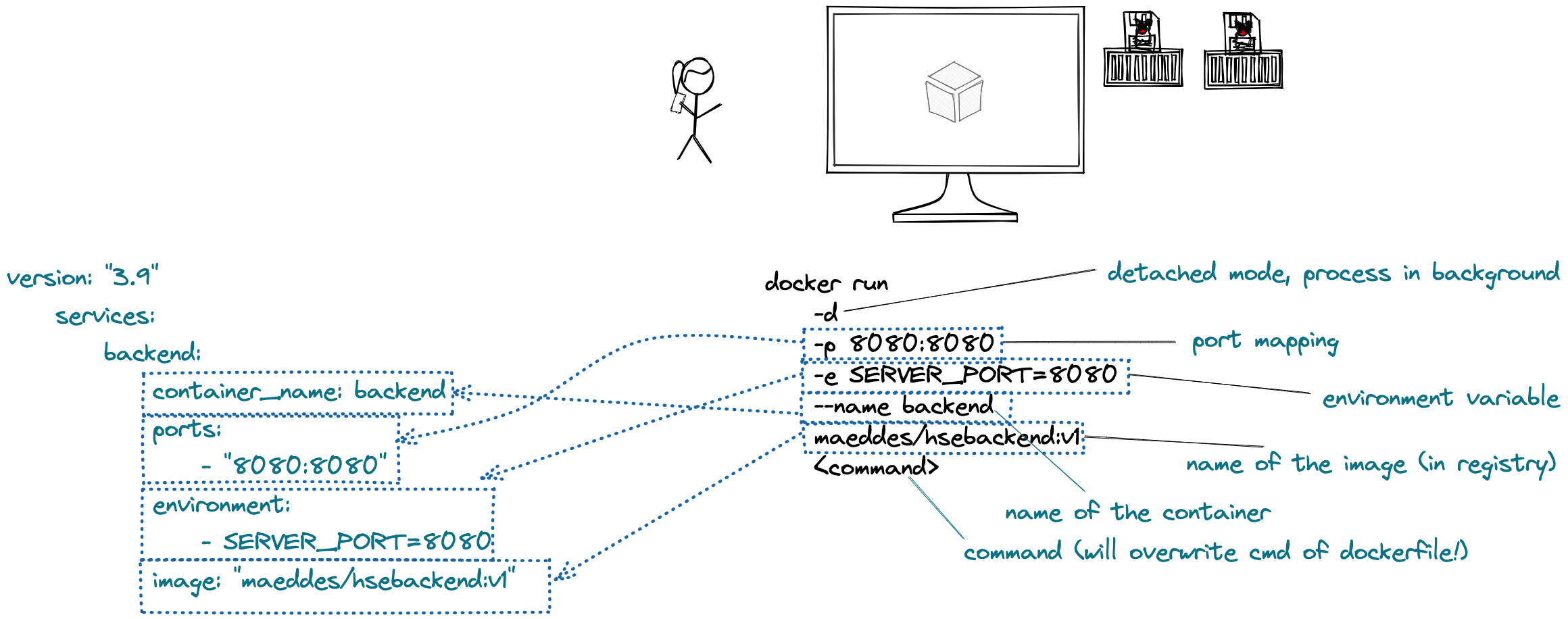
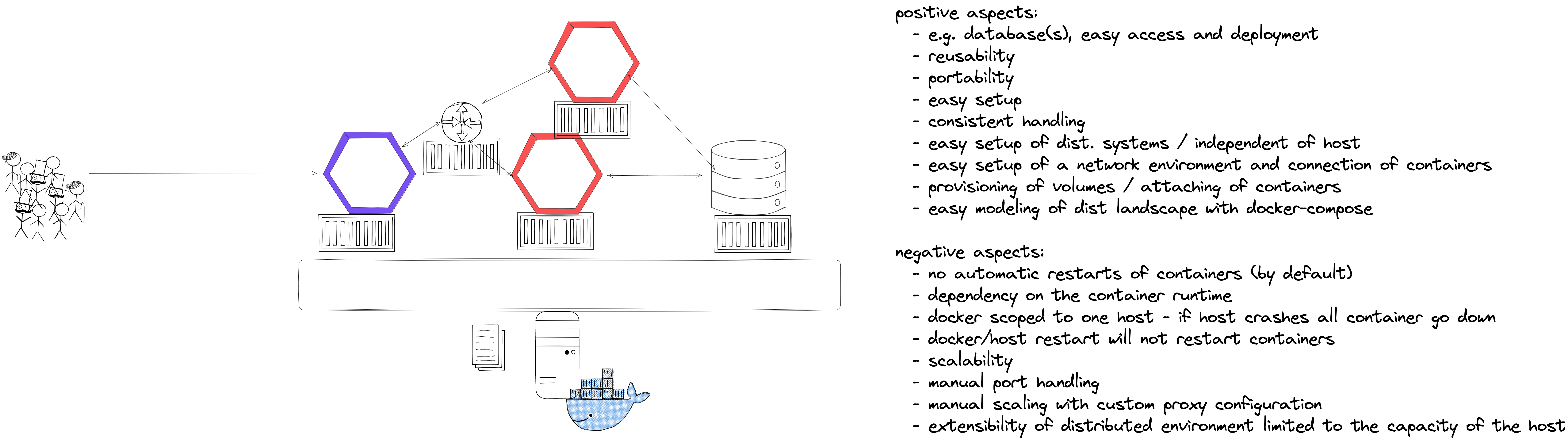
- Docker networks
- Docker volumes
- Docker-compose
The student understands the Docker functionality of networks and volumes. This includes the ability to create volumes and networks and connect them to container instances. The student is able to build container landscapes by using docker run, docker network and docker volume CLI API commands on the one hand, but also how to do equivalent things using docker-compose.
- What's the difference between docker run and docker-compose?
- Which advantages does docker-compose bring over plain docker commands?
- What's the difference in handling docker networks and docker volumes from the perspective of a running container?
- Which 12-factor aspects can you identify in the context of docker?
See previous lecture :-)
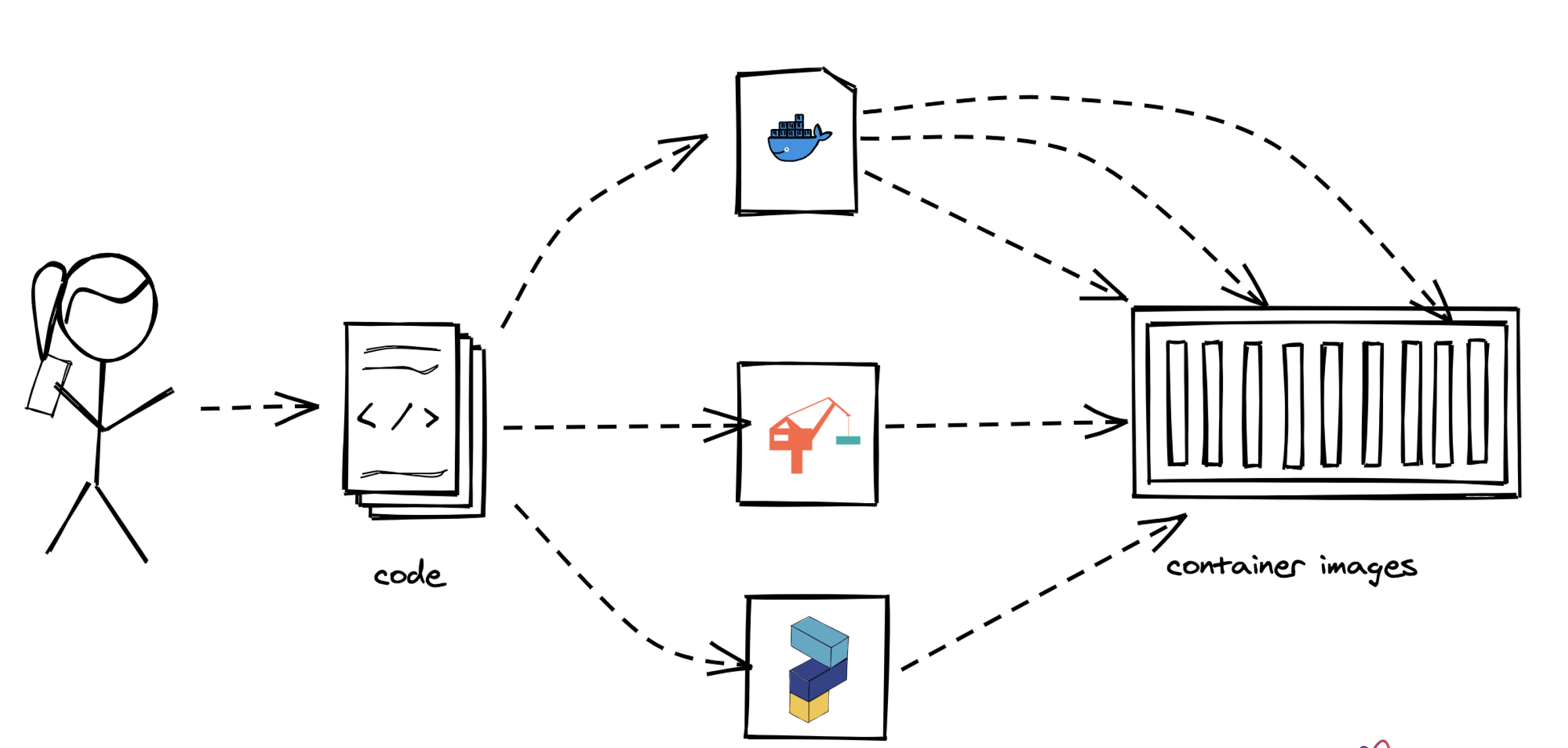
- Difference and relation between container and container images
- Concepts of image layers
- "docker commit"
- History of Dockerfile. Initial, multi-stage & BuildKit
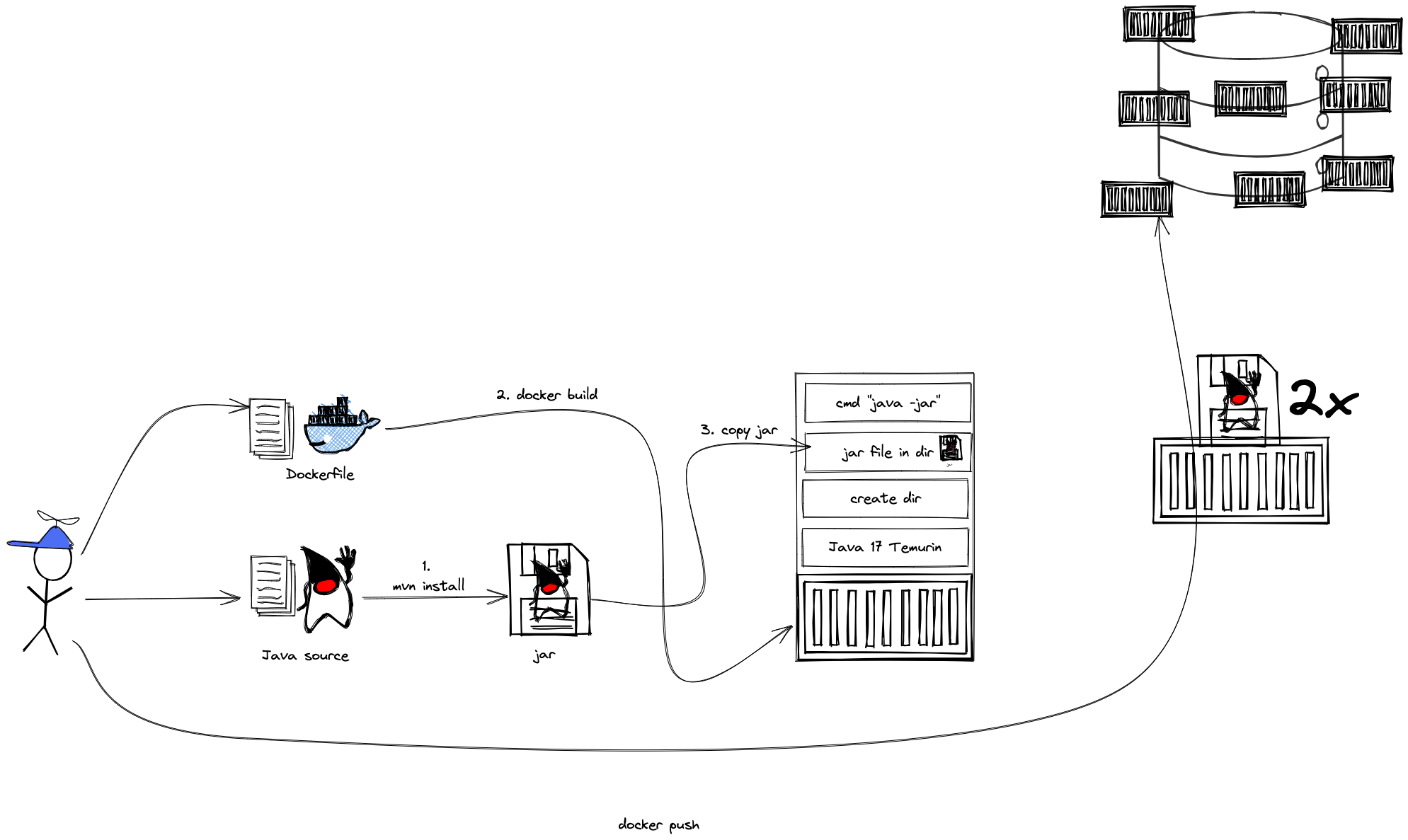
- Building container for Java apps
- Using Jib, Cloud-Native Buildpacks and Paketo
The student understands the relation between container image and container, how to instantiate a container from an image and how to commit to a new image from an existing container. The exercise is to build the previous Spring Boot application and put it into a container image using various options, e.g. different Dockerfile options, Google JIB, CND, Paketo and more ...? The student is aware and able to describe on a high-level what the different fundamentals of the various approaches are and is able to list advantages and disadvantages.
- https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/builder/
- https://buildpacks.io/
- https://paketo.io/
- https://github.com/maeddes/options-galore-container-build/blob/main/walkthrough.adoc
- https://github.com/GoogleContainerTools/jib
- List 3 different options to build a container image
- Explain docker build vs docker commit
- List 2 evolution steps of the Dockerfile and provide 1 improvement for each step
- Explain or list 1 advantage&disadvantage comparing JIB and Paketo/CNB to original Dockerfiles
- How is a container image build up internally?
- Which are criterias you can think that make image building "better"
- "WHY" do you need an enterprise architecture? What are the requirements?
- How can you solve these problems with framework or containers?
- "At which do you need more?"
- "What else do you need?"
- Which kind of limitations do you see in a docker-based environment for running high-available distributed applications?
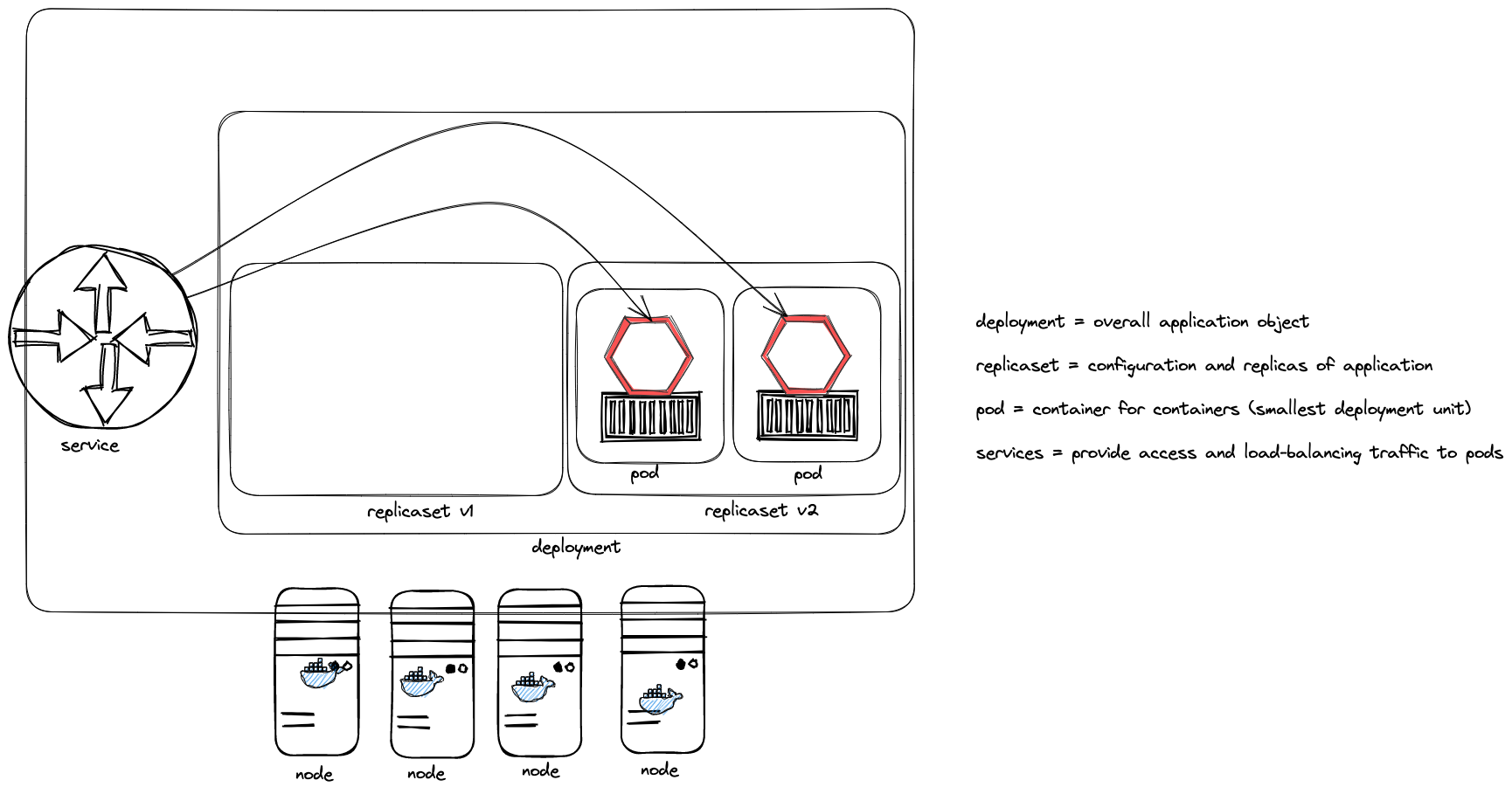
- Presentation: Cloud Platforms & Kubernetes
- Kubernetes Background
- What is CaaS?
- Cluster & Node Concept
- Behaviour scenarios of Kubernetes in Action
- Base API objects: Deployments, ReplicaSets, Pods, Services
- Intro into kubectl
The student understands the requirements and expectations towards cloud platforms and is able to list them. She/he can explain the advantages over standard container operation with Docker. The exercise is to take a sample Spring Boot application and walk through the steps to containerize and deploy to Kubernetes. The student is aware about various options for local and remote Kubernetes options.
image:images/kubernetes_overview.png[Kubernetes in a nutshell]
- Please write 100 lines of YAML Code :)
- Explain the relation of "some" of the 12 factors in relation to Kubernetes
- Explain the core principe of Kubernetes in own words. "Why" Kubernetes?
- What is pod? What is a service?
- Which kind of Kubernetes providers do you know? Can they be grouped somehow?
- https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/compose_build/
- https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-liveness-readiness-startup-probes/
- https://www.baeldung.com/spring-value-annotation
-
https://github.com/learnk8s/free-kubernetes (Overview)
-
https://www.katacoda.com/courses/kubernetes/playground (web-based)
-
https://training.play-with-kubernetes.com/ (web-based, broken?)
-
https://k3s.io/ (local)
-
https://microk8s.io/ (local)