Code associated with our paper "Graph2Speak: Improving Speaker Identification with Network Knowledge in Criminal Conversational Data".
https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.02093
Abstract:
Criminal investigations mostly rely on the collection of speech conversational data in order to identify speakers and build or enrich an existing criminal network. Social network analysis tools are then applied to identify the most central characters and the different communities within the network. We introduce two candidate datasets for criminal conversational data, Crime Scene Investigation (CSI), a television show, and the ROXANNE simulated data. We also introduce the metric of conversation accuracy in the context of criminal investigations. By re-ranking candidate speakers based on the frequency of previous interactions, we improve the speaker identification baseline by 1.2% absolute (1.3% relative), and the conversation accuracy by 2.6% absolute (3.4% relative) on CSI data, and by 1.1% absolute (1.2% relative), and 2% absolute (2.5% relative) respectively on the ROXANNE simulated data.
Note: In this repo, you will only find data related to CSI, since ROXANNE simulated data are not open-source. Also, this repo will be migrated to IDIAP's account in a few months.
- A notebook that goes through the data preparation
- A notebook that goes through Graph2Speak in a few steps
- The needed
requirements - The
srccode that contains:- The CSI dataset, in the
datafolder:- WAV files of some episodes
- Transcripts, with timestamps, from the University of Edinburgh
- The code to prepare the data (
data_processing.py) - The code to run the Graph2Speak re-ranking model (
graph2speak.py) - The
speaker_id_inputis a folder that contains our output of an X-vector speaker id baseline, ran in Kaldi (recipes provided), but can be replaced by any output of your choice
- The CSI dataset, in the
The rest of the folders are created automatically.
To run it, you can:
- run
python src/data_processing.py - run your Speaker Identification from the data folder and the prepared output (our output is also provided as a benchmark)
- run
python src/graph2speak.py s01e07to run it on season 1 episode 7 of CSI
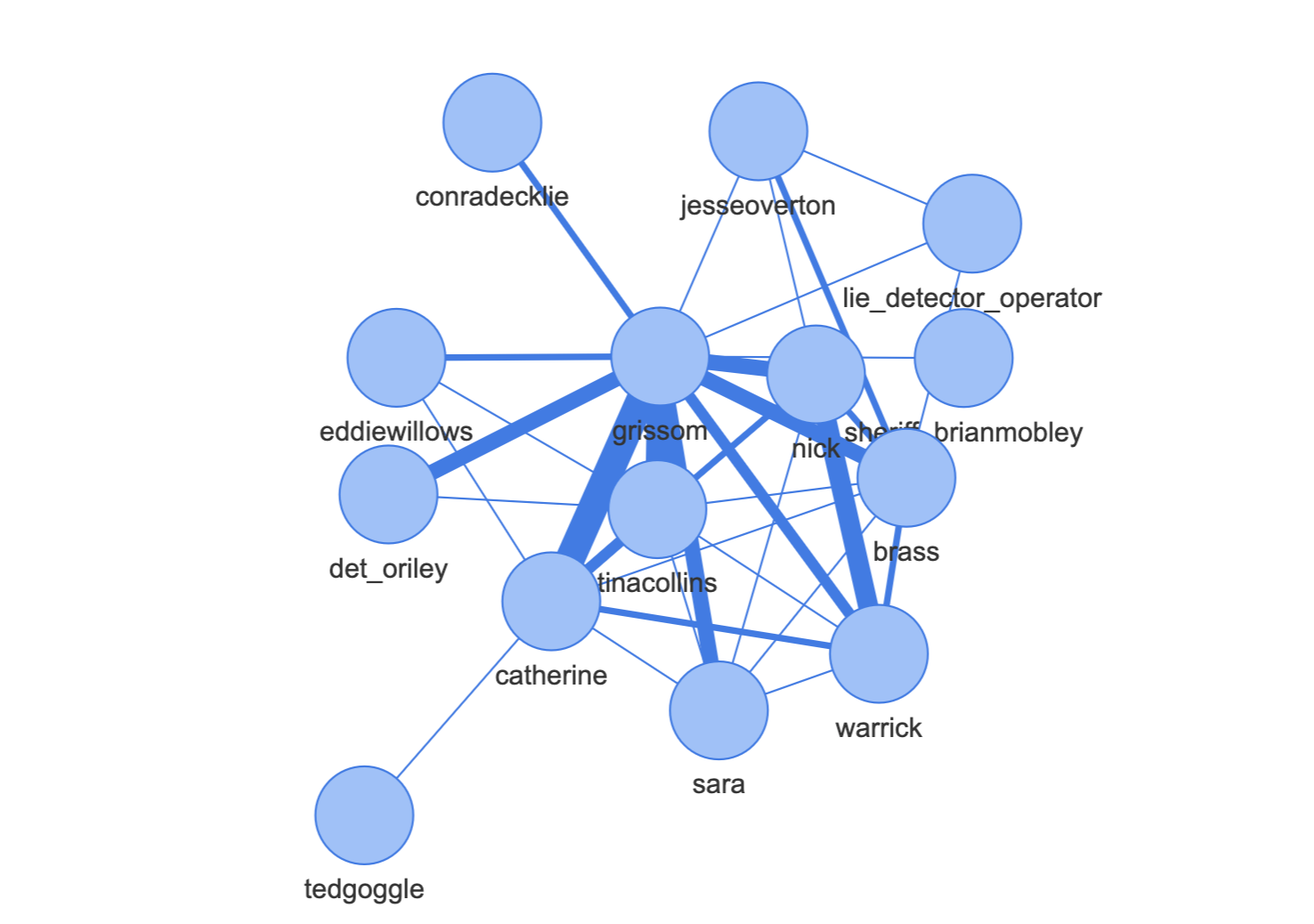
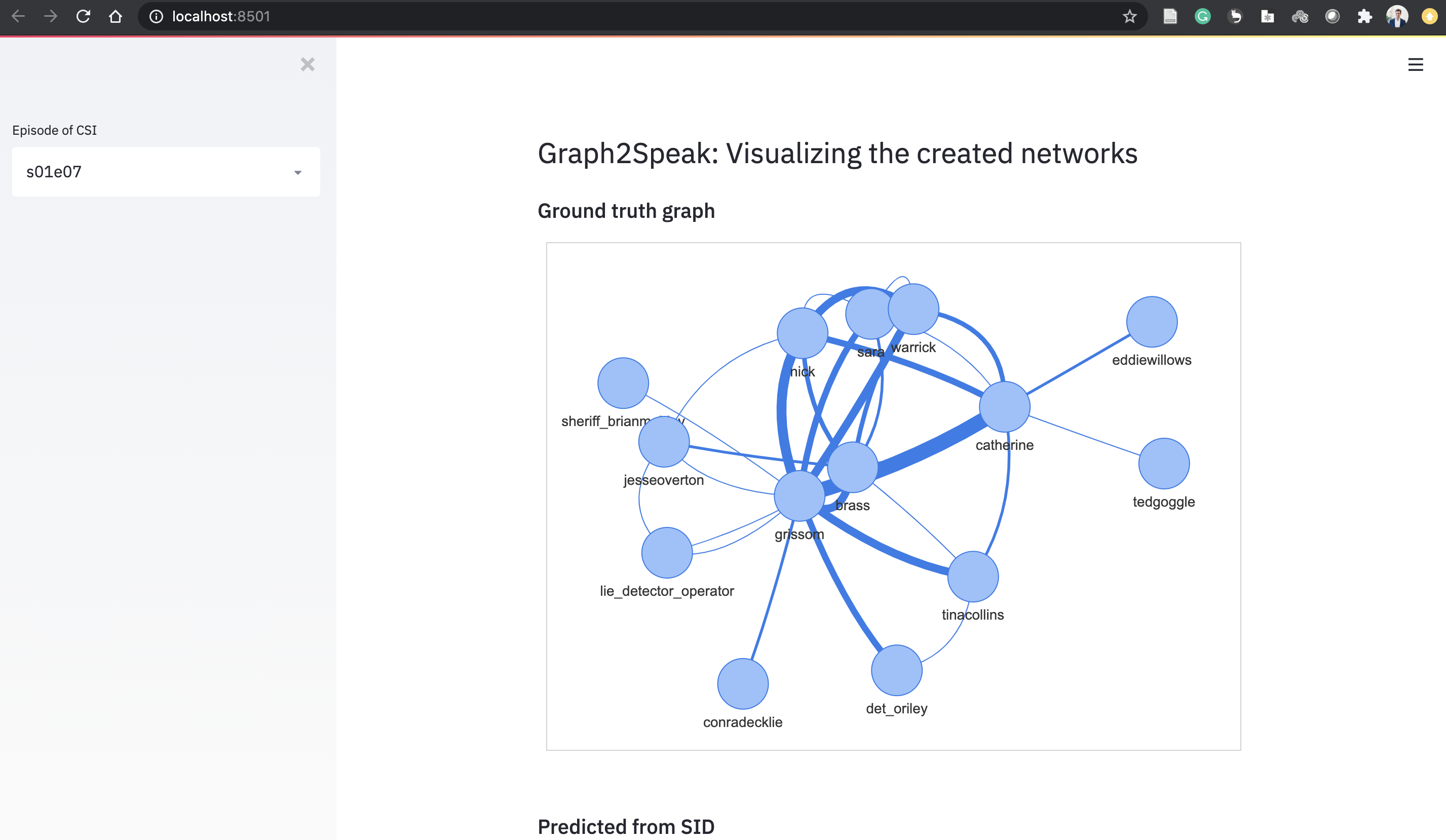
In the output folder generated_graph, the output graphs are stored as HTML files. They were built with PyVis for network visualization.
We also provide a streamlit web application to visualize the differences between the graphs. First run the pipeline mentioned above, or use the pre-computed graphs we provide. To run it, simply type
streamlit run app.py and open http://localhost:8501/.
Graph2Speak improves speaker identification in conversational data for which a graph can be built. We report below the performances of Graph2Speak on several episodes:
| Episode | Speaker acc. baseline (%) | Speaker acc. G2S (%) | Conv. acc. baseline (%) | Conv. acc. G2S (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S01E07 | 91.6 | 92.7 | 84.4 | 88.8 |
| S01E08 | 91.9 | 95.3 | 80.6 | 88.8 |
| S02E01 | 88.0 | 88.0 | 71.4 | 73.5 |
| S02E04 | 88.1 | 89.0 | 76.1 | 76.1 |
| S02E06 | 86.2 | 88.6 | 70.9 | 74.5 |
| S02E09 | 92.3 | 91.3 | 81.4 | 79.1 |
| CSI Average | 89.6 | 90.8 | 77.5 | 80.1 |
Network visualization relies on PyVis, and the framework for the interactive web application is Streamlit.
To cite this work, please mention:
@article{fabien_improving_2020,
title = {Improving {Speaker} {Identification} using {Network} {Knowledge} in {Criminal} {Conversational} {Data}},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/2006.02093},
urldate = {2020-06-11},
journal = {arXiv:2006.02093 [cs, eess]},
author = {Fabien, Mael and Sarfjoo, Seyyed Saeed and Motlicek, Petr and Madikeri, Srikanth},
month = jun,
year = {2020},
note = {arXiv: 2006.02093},
keywords = {Computer Science - Sound, Electrical Engineering and Systems Science - Audio and Speech Processing, Computer Science - Social and Information Networks},
}