Donkeybot is an end-to-end Question Answering system. It utilizes multiple data sources, an FAQ table and transfer-learning language models like BERT to answer Rucio support questions.
The aim of the project under GSoC 2020 is to use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to develop an intelligent bot prototype able to provide satisfying answers to Rucio users and handle support requests up to a certain level of complexity, forwarding only the remaining ones to the experts.
Donkeybot can be expanded and applied as a Question-Answering system for your needs. Changes in the code are required to use Donkeybot for your specific use case and data. Current implementation applies to Rucio specific data sources.
-
Data storage : A data storage holding Rucio domain-specific data. The module's current implementation is in SQLite for the fast prototyping it provides. Data sources include secure and anonymous support emails from Rucio users, Rucio GitHub issues and Rucio documentation.
-
Question detection : A module for question detection and extraction from any given text. This is being used to extract past questions from the support emails and GitHub issues by utilizing regular expressions. These questions are archived as documents and used by the other modules.
-
Document Retrieval : A search engine module that uses BM25 algorithm for the retrieval of the top-n most similar documents ( previously asked questions or Rucio documentation ) to be used as context by the answer detection module.
-
Answer Detection : The Answer detection module which follows both a transfer-learning approach and a supervised approach.
- Using pre-trained transformer models, such as BERT from Hugginface transformers, to provide the user with the top-k best answers based on the retrieved documents.
- FAQ-based supervised approach which helps handle more specific and/or frequent questions with a higher confidence.
Additional Features include :
-
FAQ creation GUI : User can use a provided GUI as an interface to interact with the data storage, insert FAQ questions, re-index the search engine and expand Donkeybot's knowledge base.
-
Name hashing : A script that uses Stanford's NER tagger to detect private user information from support emails and hash them. Thus, following CERN's privacy guidelines and keeping all data anonymized.
See the full documentation for examples, operational details and other information.
See FAQ : GSoC for a detailed timeline, student information, problems faced, future improvement suggestions, a reading list and more.
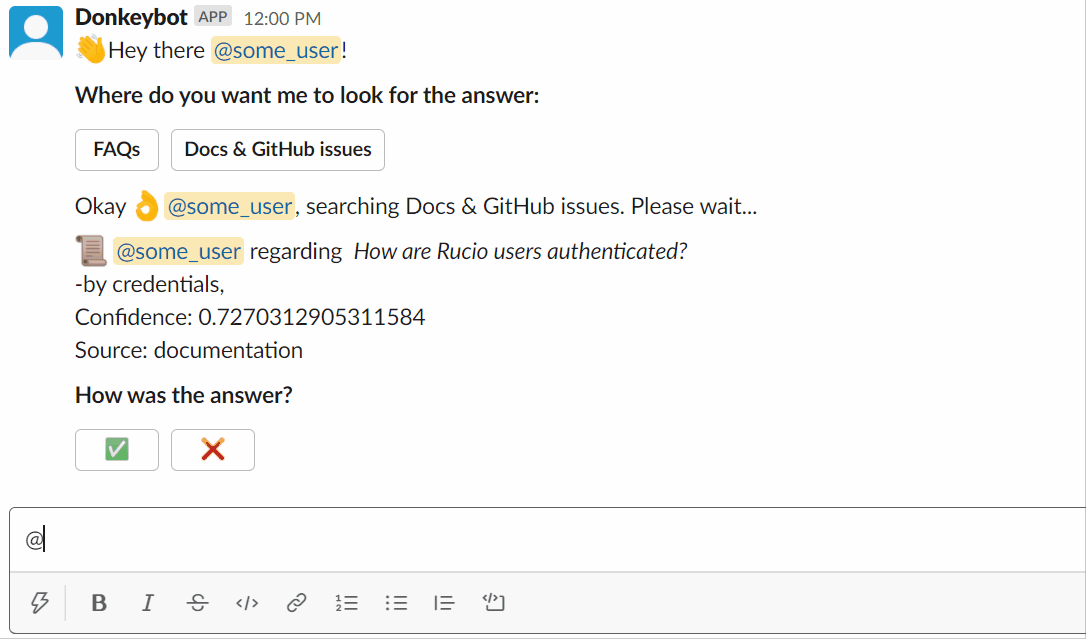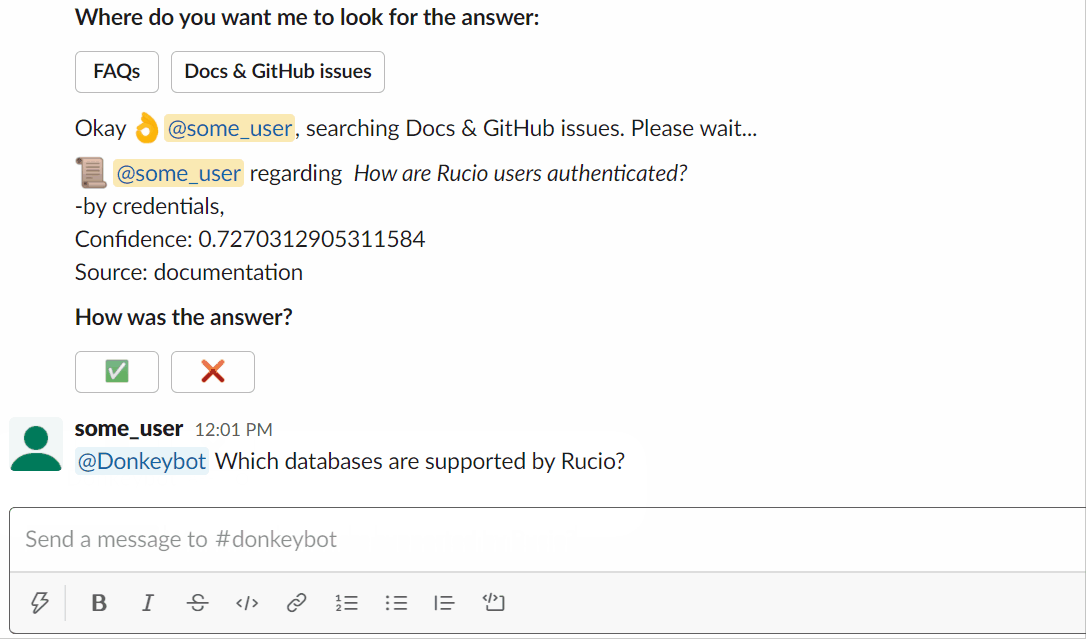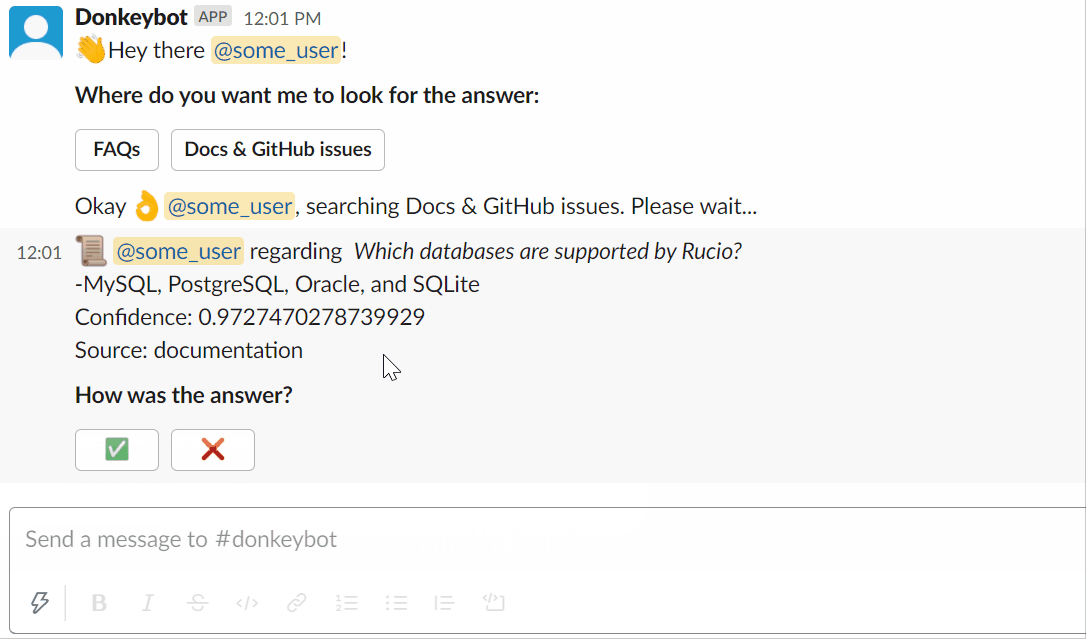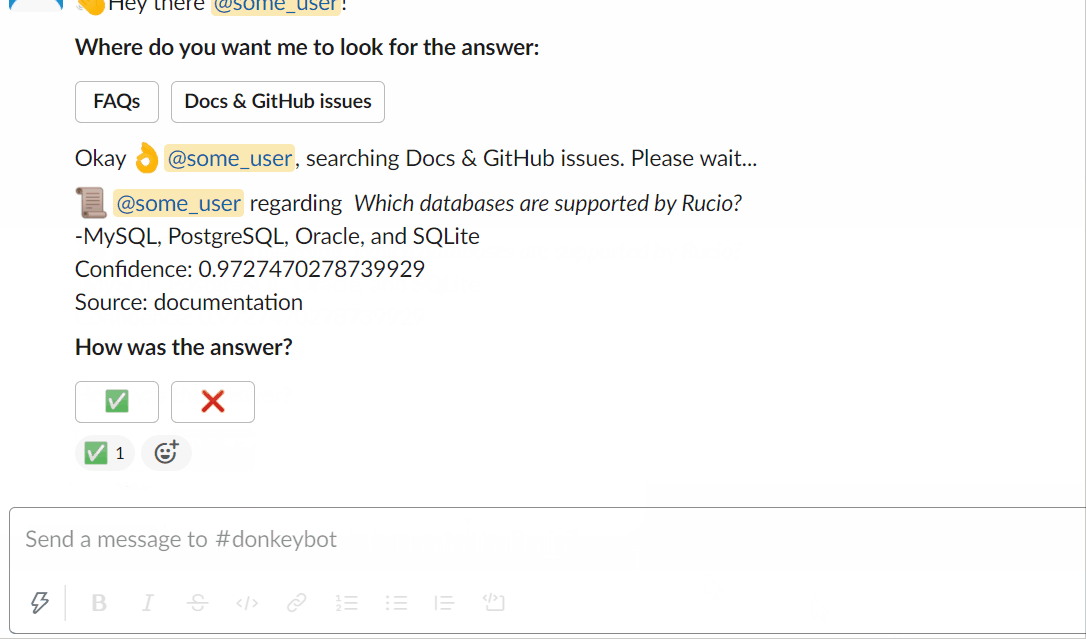
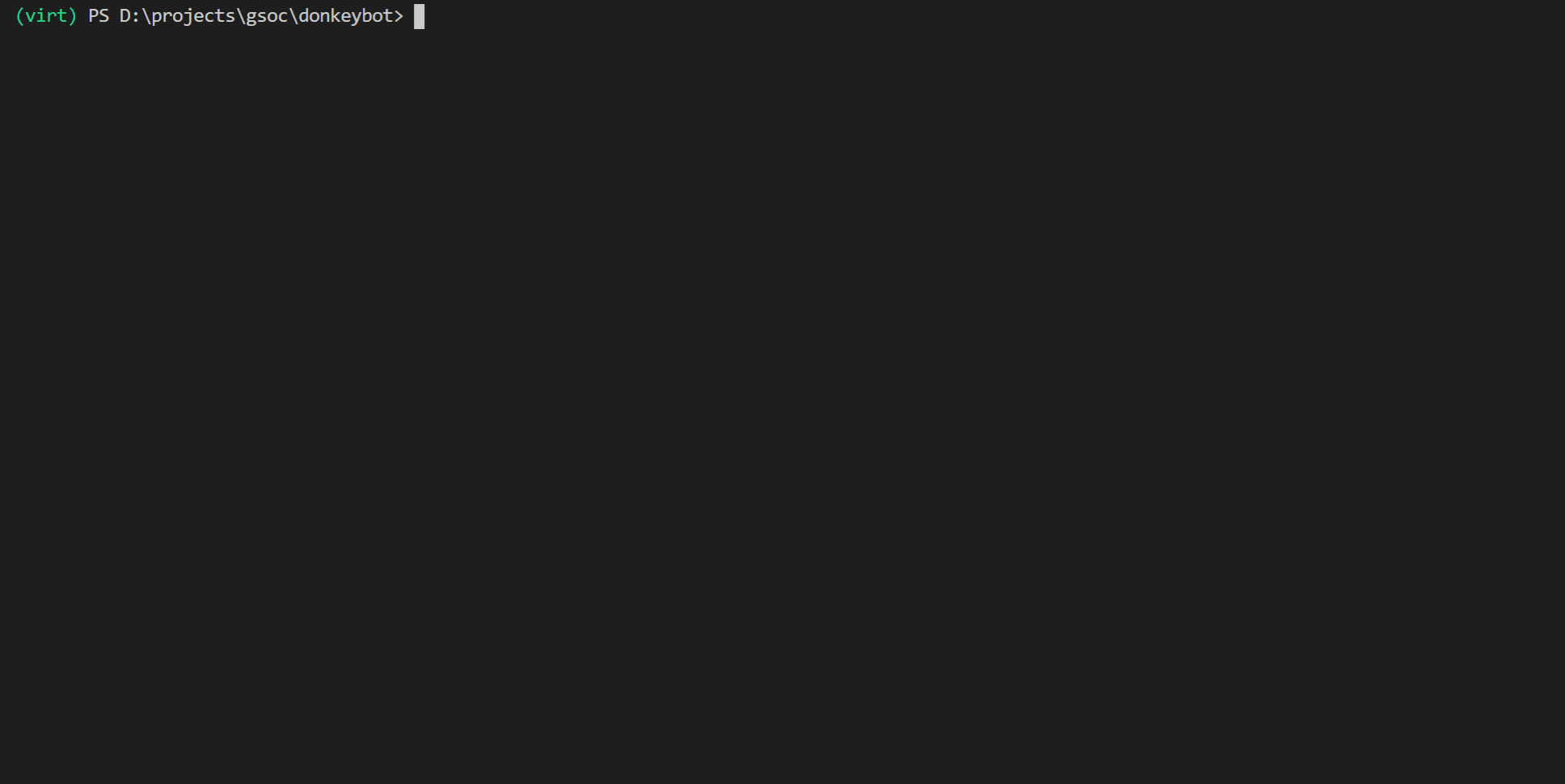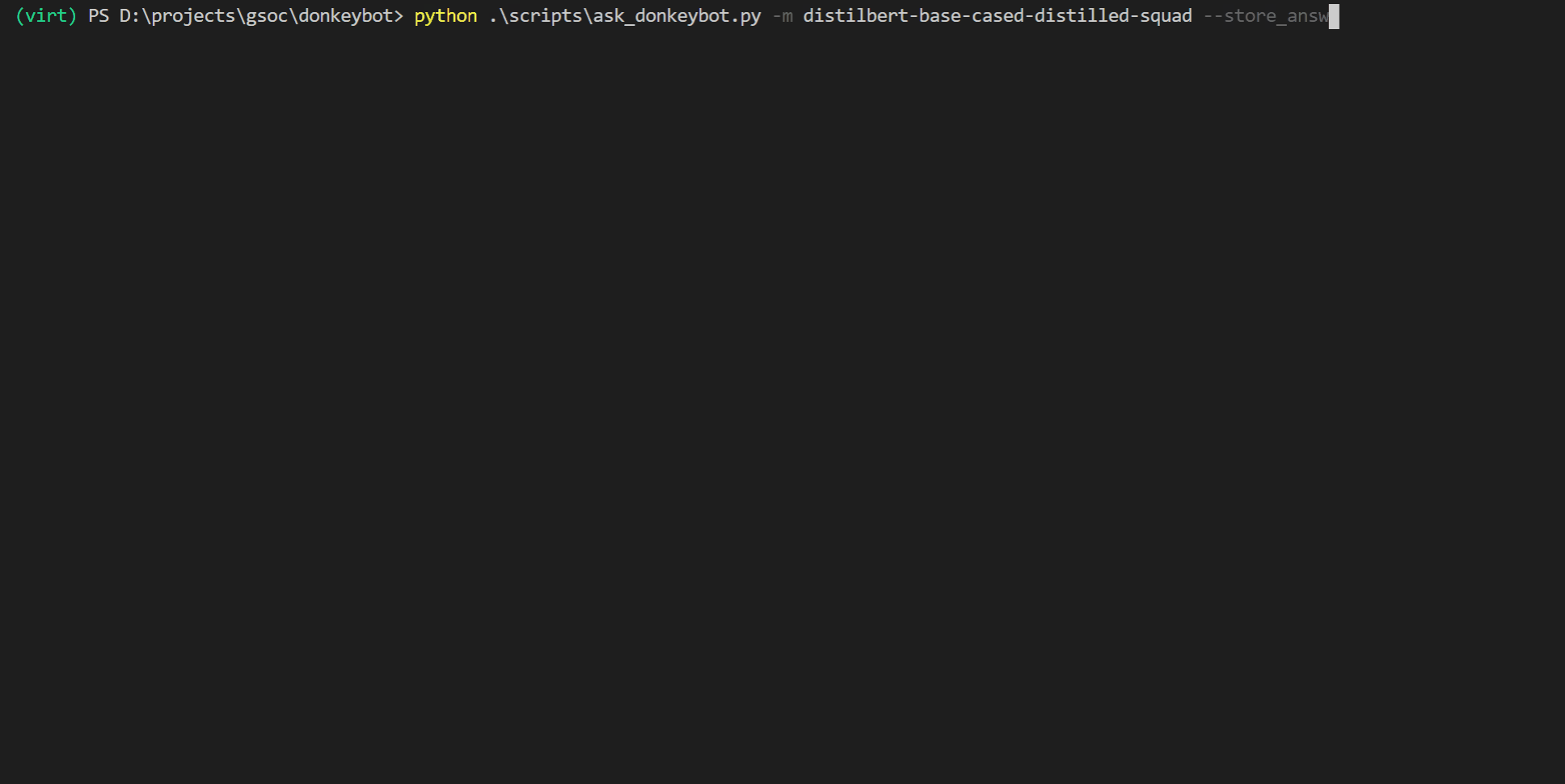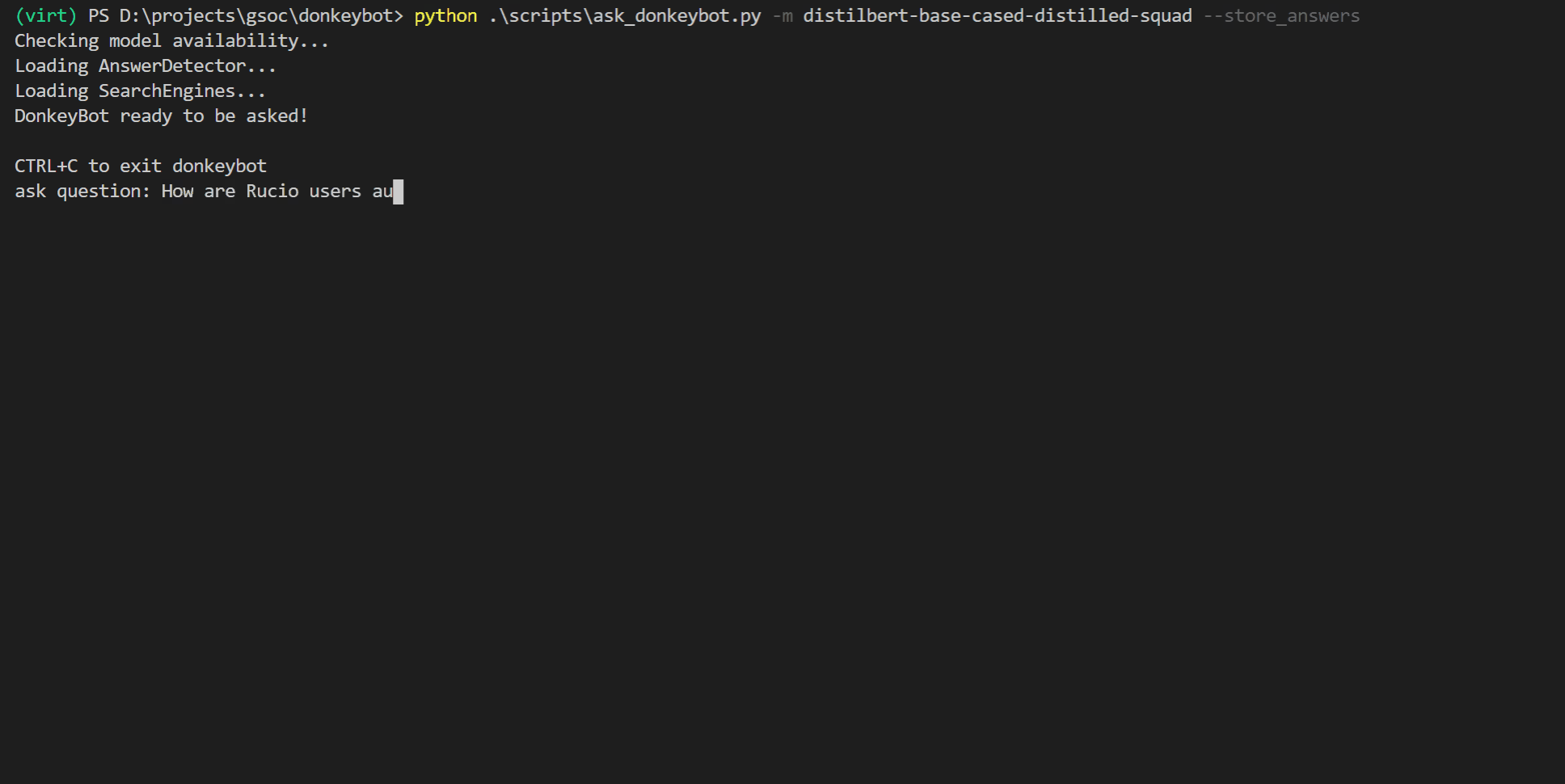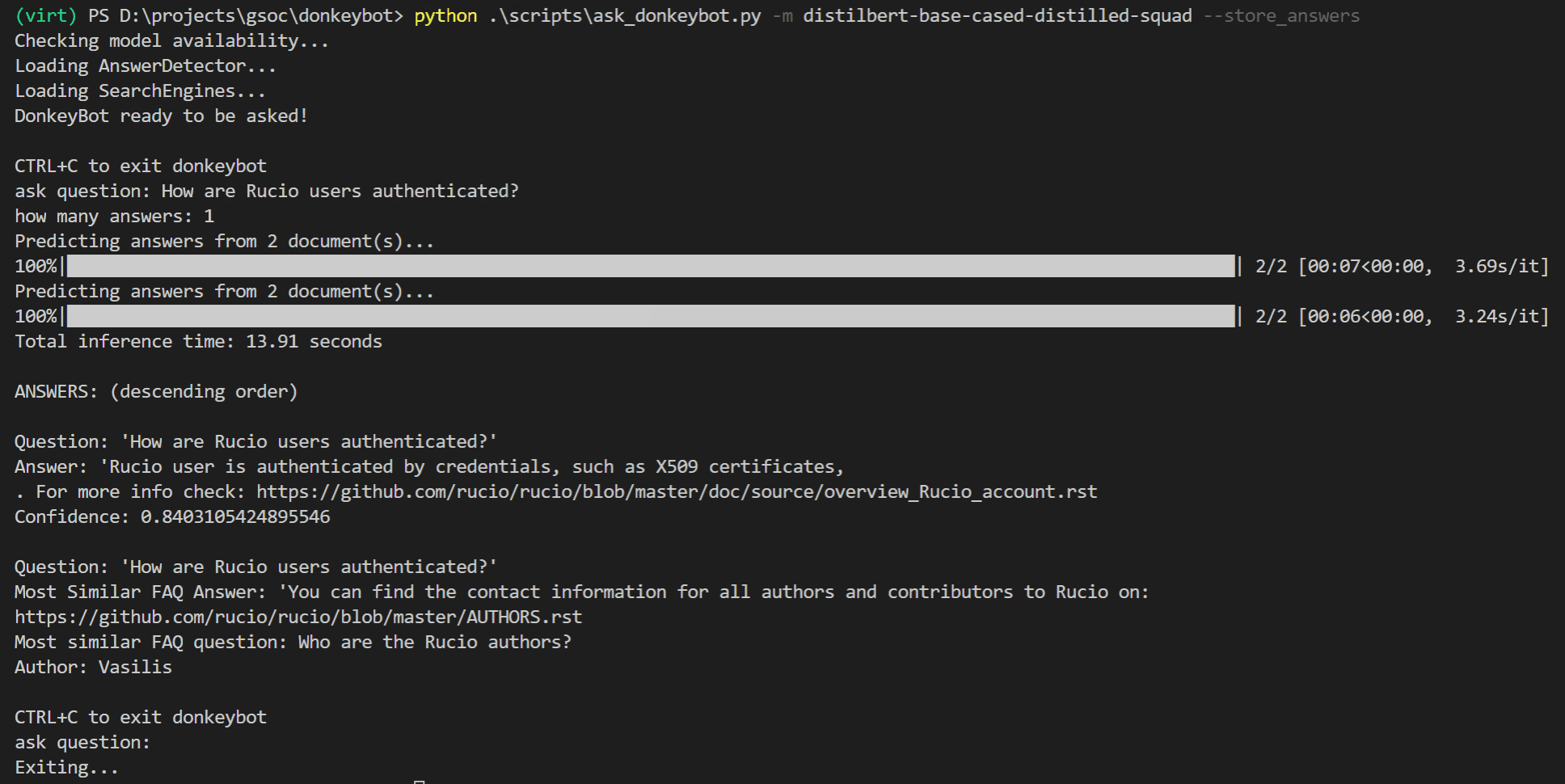
You can try asking Donkeybot yourself!
Using the slackbot :
Or you can use the CLI:
$ python .\scripts\ask_donkeybot.pyMore examples and information can be found in the How To Use section.
Step 1: A 64 bit Python 3.x installation is required by PyTorch.
Step 2: To install PyTorch head over to https://pytorch.org/ and follow the quick start guide based on your operating system.
# versions used in development
torch==1.6.0 --find-links https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html
torchvision==0.7.0 --find-links https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.htmlStep 3: Clone the repository to your development machine.
$ git clone https://github.com/rucio/donkeybot.git
$ cd donkeybotStep 4: For additional requirements run.
$ pip install -r requirements.txtStep 5: Build and populate Donkeybot's data storage.
$ python scripts/build_donkeybot -t <GITHUB_API_TOKEN>- To generate a GitHub token visit Personal Access Tokens and follow Creating a Personal Access Token.
See the Getting Started page for more details on contributing, initiating the developer mode and testing.
For bugs, questions and discussions please use the GitHub Issues or contact the student @mageirakos.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0;