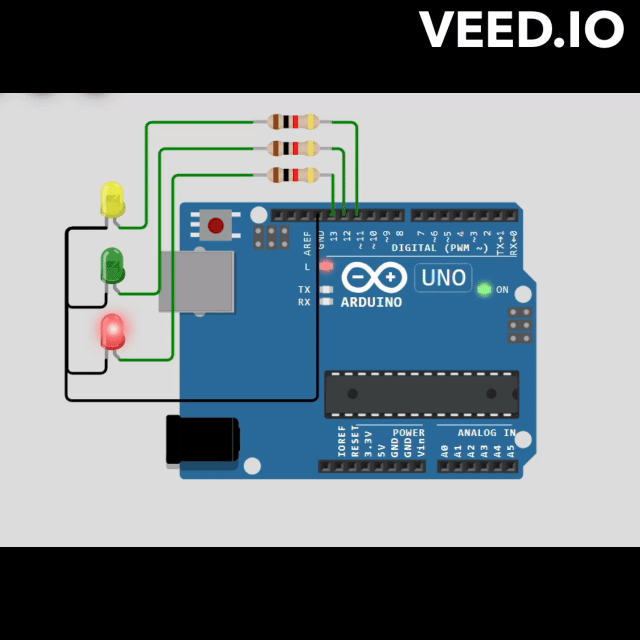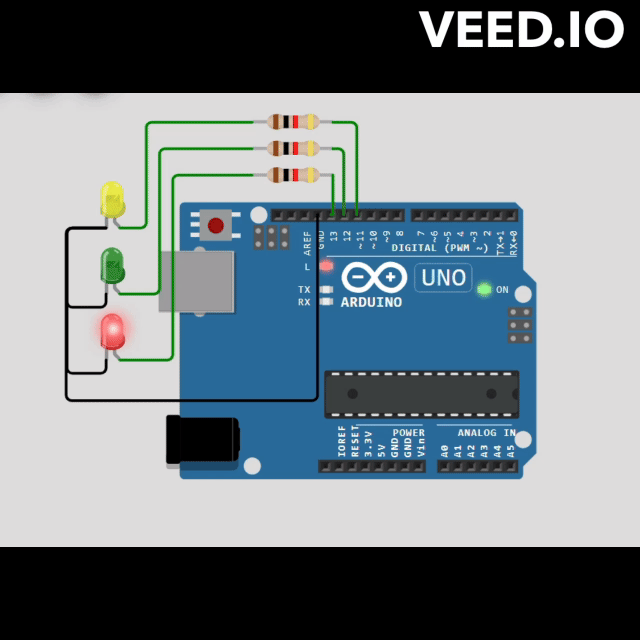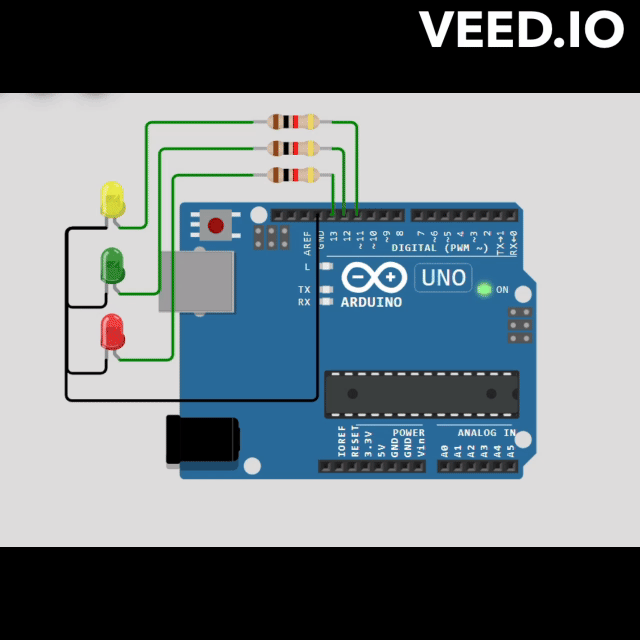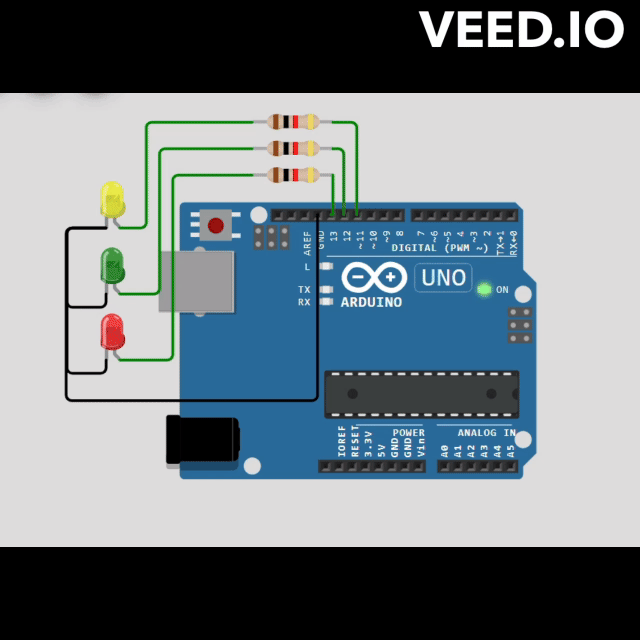
MAGX_FSM is a lightweight and versatile Finite State Machine library designed for Arduino and ESP32 platforms. It provides an intuitive way to manage complex control flows by dividing them into discrete states and transitions. With MAGX_FSM, developers can streamline their code, enhance readability, and facilitate maintainability.
-
Modular Design: MAGX_FSM implements a modular design, allowing developers to define custom states and logic tailored to their application requirements.
-
Flexible State Handling: The library offers a flexible mechanism for defining state transitions and executing custom logic associated with each state.
-
Minimal Resource Consumption: MAGX_FSM is designed to minimize resource consumption, making it suitable for resource-constrained environments like Arduino and ESP32 platforms.
-
Reduced Compile Time Dependency: By using forward declaration and template classes, MAGX_FSM reduces compile time dependencies and breaks circular dependencies, resulting in faster compilation times.
- Sequential State Transitions: Currently, MAGX_FSM initiates state transitions based on the current state. This limitation can affect scenarios where a user wants to suspend a specific task/state, as all subsequent states will not execute. However, ongoing development aims to address this limitation by introducing more flexible transition mechanisms.
-
Include the Library: Include the
magx_fsm.hheader file in your Arduino or ESP32 sketch. -
Define States and Logic: Define custom states by extending the
Stateclass and implementing thehandleStatemethod. Optionally, create concrete state classes with custom state logic using theConcreteStatetemplate class. -
Instantiate StateMachine: Instantiate a
StateMachineobject in your sketch. -
Set Initial State: Set the initial state of the StateMachine using the
setStateWithLogicmethod, providing the state name and corresponding state logic. -
Run the StateMachine: Call the
runmethod within the main loop of your sketch to execute the current state's logic. -
Handle State Transitions: Implement state transitions and associated logic within the state handling methods.
#include <magx_fsm.h>
//blink LED_BUILTIN by using magx_fsm library
//define state function prototypes
void led_off_state(StateMachine &fsm);
void led_on_state(StateMachine &fsm);
//define state transition callback for on_state
void on_state_callback(StateMachine &fsm){
fsm.setStateWithLogic("ON_STATE",led_on_state);
}
//define state transition callbacks for off_state
void off_state_callback(StateMachine &fsm){
fsm.setStateWithLogic("OFF_STATE",led_off_state);
}
// Define states, in the context of this example, there are two states
// ON state and OFF state
void led_off_state(StateMachine &fsm){
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN,LOW);
uint32_t OFF_DURATION =1000;
fsm.waitUntilElapsed(OFF_DURATION, on_state_callback, fsm);
}
void led_on_state(StateMachine &fsm){
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN,HIGH);
uint32_t ON_DURATION =1000;
fsm.waitUntilElapsed(ON_DURATION, off_state_callback, fsm);
}
StateMachine fsm;
void setup() {
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN,OUTPUT);
//initialize state manually... this can also be trriggered by event or condition
fsm.setStateWithLogic("ON_STATE", led_on_state);
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
fsm.run();
}#include <magx_fsm.h>
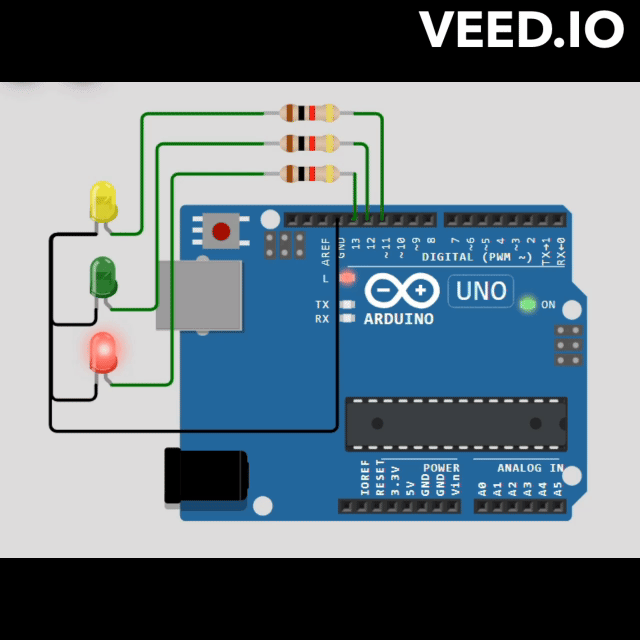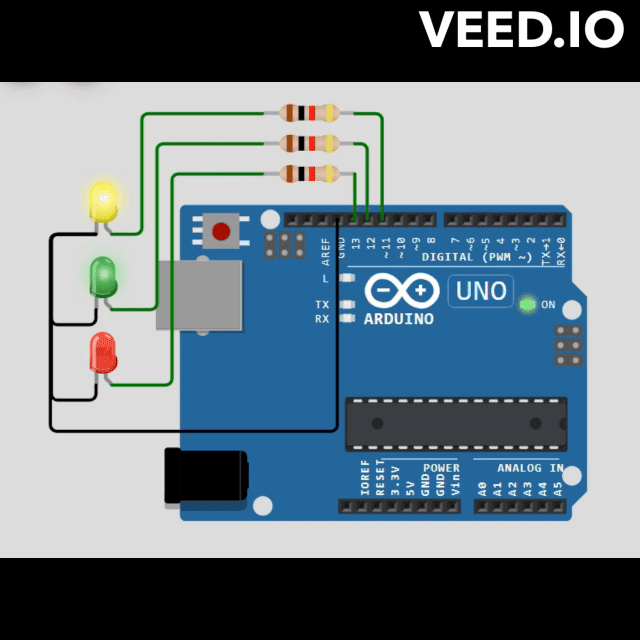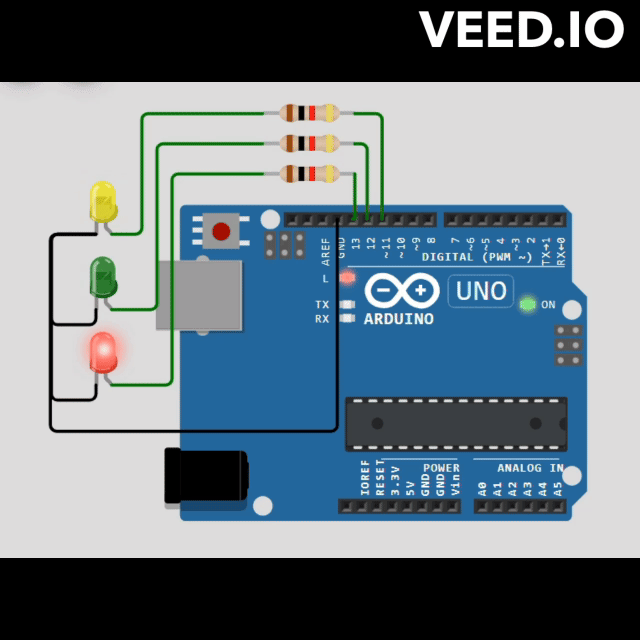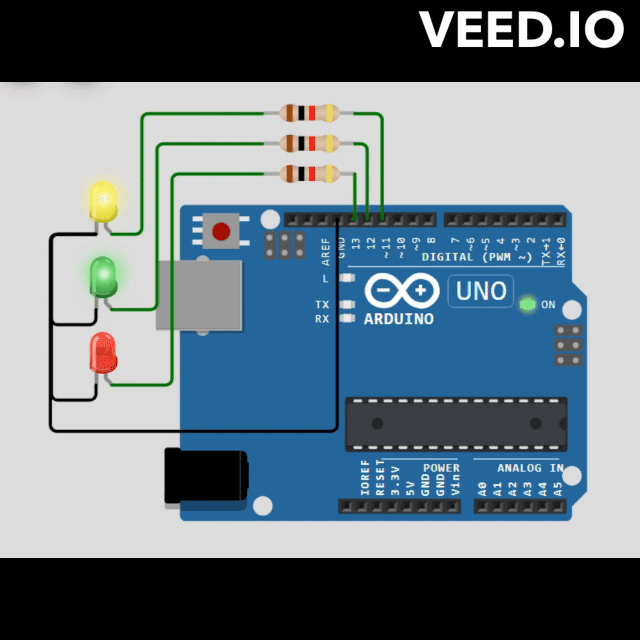
// Define pin numbers for LEDs
const int RED_PIN = 13;
const int GREEN_PIN = 12;
const int YELLOW_PIN = 11;
// Define durations for each state in milliseconds
const int RED_DURATION = 1500; // 1.5 seconds
const int GREEN_DURATION = 1000; // 1 seconds
const int YELLOW_DURATION = 600; // 0.6 seconds
// Function prototypes for state logic
void redStateLogic(StateMachine &fsm);
void greenStateLogic(StateMachine &fsm);
void yellowStateLogic(StateMachine &fsm);
// State transition callback functions
void greenStateCallback(StateMachine &fsm) {
fsm.setStateWithLogic("GREEN_STATE", greenStateLogic);
}
void yellowStateCallback(StateMachine &fsm) {
fsm.setStateWithLogic("YELLOW_STATE", yellowStateLogic);
}
void redStateCallback(StateMachine &fsm) {
fsm.setStateWithLogic("RED_STATE", redStateLogic);
}
void redStateLogic(StateMachine &fsm) {
// Set red light ON, green and yellow OFF
digitalWrite(RED_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(GREEN_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(YELLOW_PIN, LOW);
fsm.waitUntilElapsed(RED_DURATION, greenStateCallback, fsm);
}
void greenStateLogic(StateMachine &fsm) {
// Set green light ON, red and yellow OFF
digitalWrite(RED_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(GREEN_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(YELLOW_PIN, LOW);
// Wait in this state for some time
fsm.waitUntilElapsed(GREEN_DURATION, yellowStateCallback, fsm);
}
void yellowStateLogic(StateMachine &fsm) {
// Set yellow light ON, red and green OFF
digitalWrite(RED_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(GREEN_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(YELLOW_PIN, HIGH);
// Wait in this state for some time
fsm.waitUntilElapsed(YELLOW_DURATION, redStateCallback, fsm);
}
StateMachine fsm;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(RED_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(GREEN_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(YELLOW_PIN, OUTPUT);
// Start with RedState
fsm.setStateWithLogic("RED_STATE", redStateLogic);
}
void loop() {
fsm.run(); // Start traffic light operation
}-
Code Organization: MAGX_FSM promotes a structured approach to code organization by encapsulating state logic within discrete state objects.
-
Enhanced Readability: By abstracting state transitions and logic, MagX FSM enhances code readability, making it easier to understand and maintain.
-
Scalability: MAGX_FSM facilitates the scalability of Arduino and ESP32 projects by providing a scalable mechanism for managing increasingly complex control flows.
-
Resource Optimization: With minimal resource overhead, MAGX_FSM allows developers to maximize the efficiency of their code, ensuring optimal performance on resource-constrained platforms.
MAGX_FSM offers a powerful yet lightweight solution for managing control flows in Arduino and ESP32 projects. By leveraging the library's modular design and flexible state handling capabilities, developers can simplify code complexity, improve code organization, and enhance overall project maintainability.