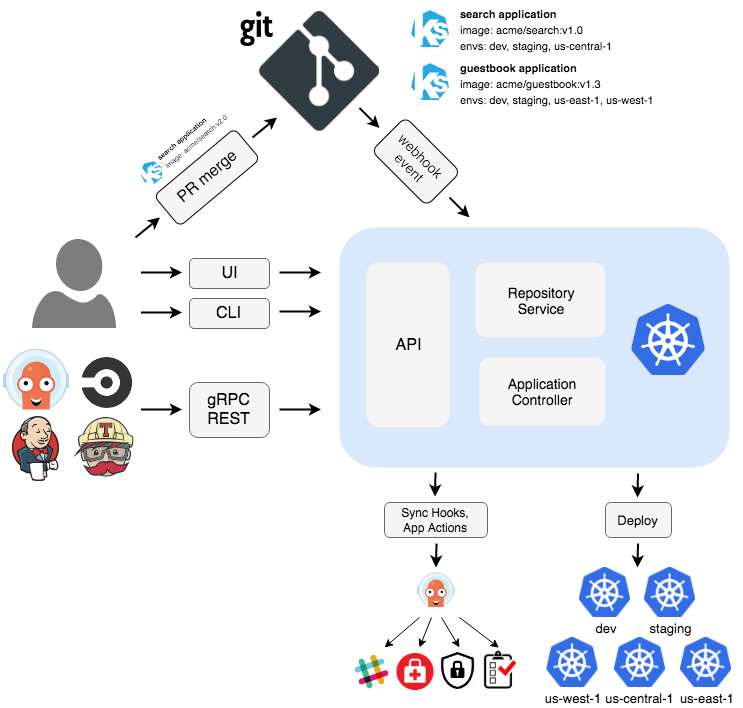
Argo CD is a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes.
GitOps is an operational framework that takes DevOps best practices used for application development such as version control, collaboration, compliance, and CI/CD tooling, and applies them to infrastructure automation.
GitOps is used to automate the process of provisioning infrastructure. Similar to how teams use application source code, operations teams that adopt GitOps use configuration files stored as code (infrastructure as code). GitOps configuration files generate the same infrastructure environment every time it’s deployed, just as application source code generates the same application binaries every time it’s built.
Argo CD follows the GitOps pattern of using Git repositories as the source of truth for defining the desired application state. Kubernetes manifests can be specified in several ways:
- kustomize applications
- helm charts
- jsonnet files
- Plain directory of YAML/json manifests
- Any custom config management tool configured as a config management plugin
Argo CD automates the deployment of the desired application states in the specified target environments. Application deployments can track updates to branches, tags, or pinned to a specific version of manifests at a Git commit.
Argo CD is implemented as a kubernetes controller which continuously monitors running applications and compares the current, live state against the desired target state (as specified in the Git repo). A deployed application whose live state deviates from the target state is considered OutOfSync. Argo CD reports & visualizes the differences, while providing facilities to automatically or manually sync the live state back to the desired target state. Any modifications made to the desired target state in the Git repo can be automatically applied and reflected in the specified target environments.
in this demo we are going to install ArgoCD in a K8s cluster, configure it with Application CRD and then test our setup by updating the Deployment file
- Clone this git repository: https://github.com/mahdibouaziz/argoCD-demo
- You need to have a K8s cluster
Create a new namespace, argocd, where Argo CD services and application resources will live.
kubectl create namespace argocd
This will create a lot of Pods and Services
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
To access The ArgoCD UI, you need to:
kubectl patch svc argocd-server -n argocd -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'
OR
kubectl port-forward -n argocd svc/argocd-server 8080:443
The initial password for the admin account is auto-generated and stored as clear text in the field password in a secret named argocd-initial-admin-secret in your Argo CD installation namespace. You can simply retrieve this password using kubectl:
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d; echo
Let's write a configuration file for argoCD to connect it to the git repository where the config files are hosted
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: myapp-argo-application
namespace: argocd
spec:
#Every application belongs to a signle project and you can group multiple application into a project
project: default
# Git Repository that argocd will connect to and sync it
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/mahdibouaziz/argoCD-demo.git
targetRevision: HEAD
path: dev # The folder in the repository
# K8s Cluster where argocd will apply the manifest files in the git repository
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc # the default service name of K8s
namespace: myapp
syncPolicy:
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true #to tell K8s to automatically create a namespace if it doesn't exists
automated: #enable automated sync (self healing & pruning)
selfHeal: true
prune: truewe need now to apply this configuration to configure argoCD with this logic
kubectl apply -f application.yaml
this is gonna be the only kubectl apply that we need to do in this project, because after that everything shoud be auto synchronized
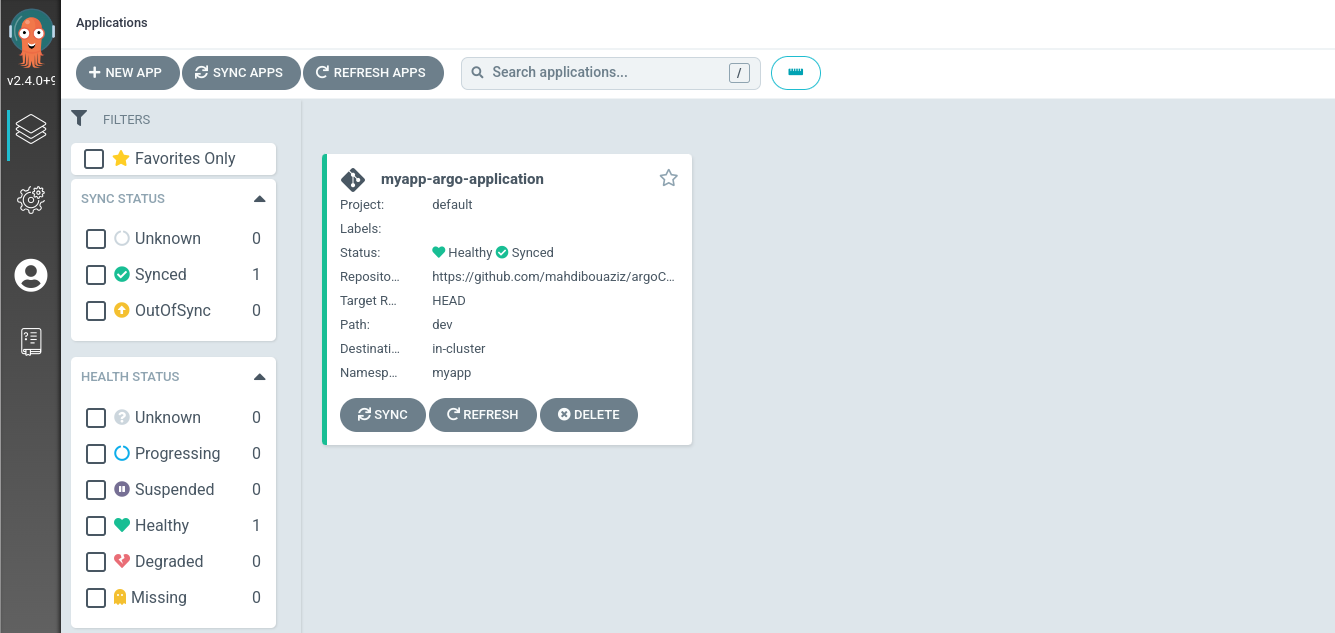
If we go to the argoCD UI we will see:
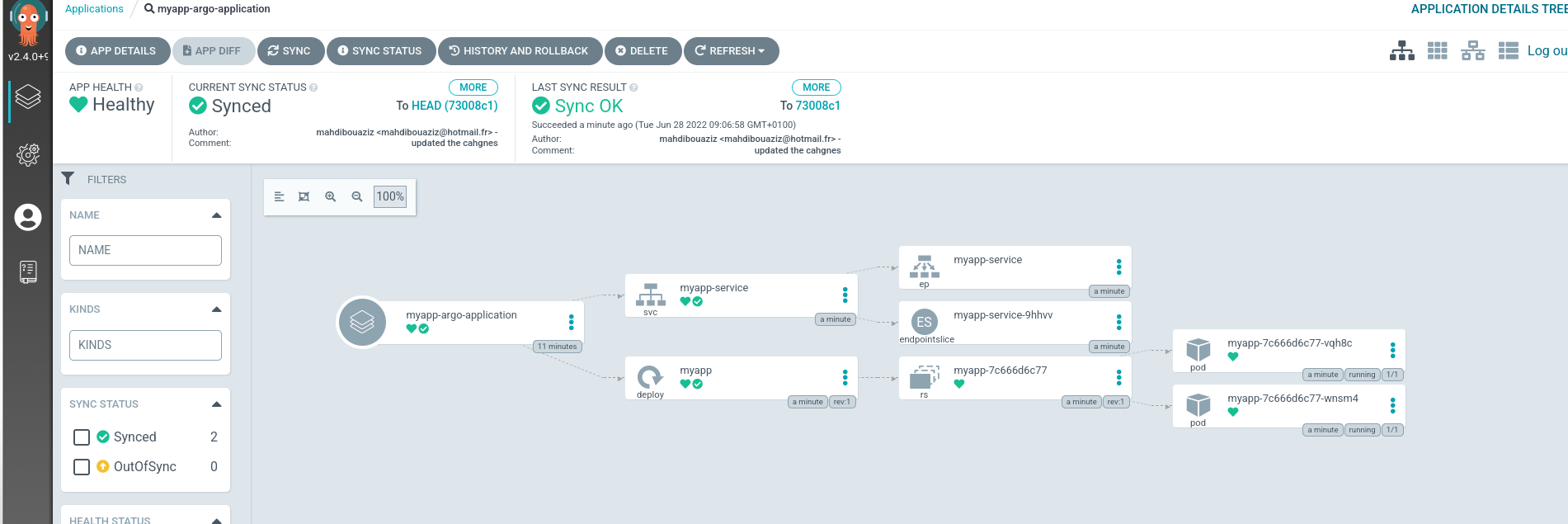
And you can see the pods are created
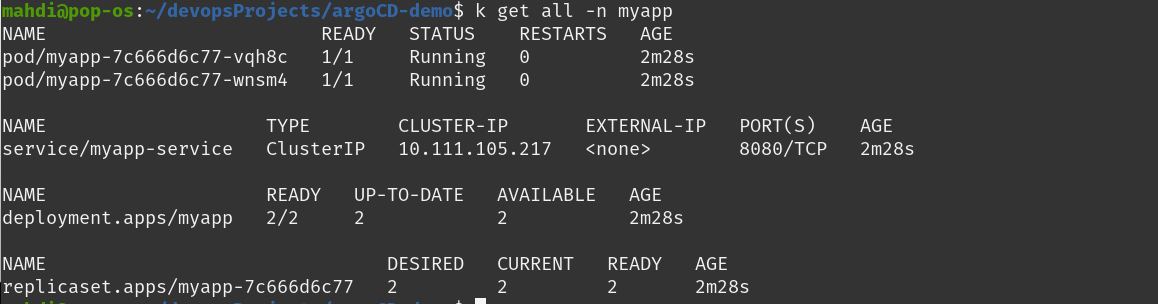
update the image version for example in the deployment file to 1.1 or 1.2. Commit and push your updates and after a certain period of time you will see the update.