Research Paper: Achieving Flatness: Selecting the Honeywords from Existing User Passwords
Link to the paper »
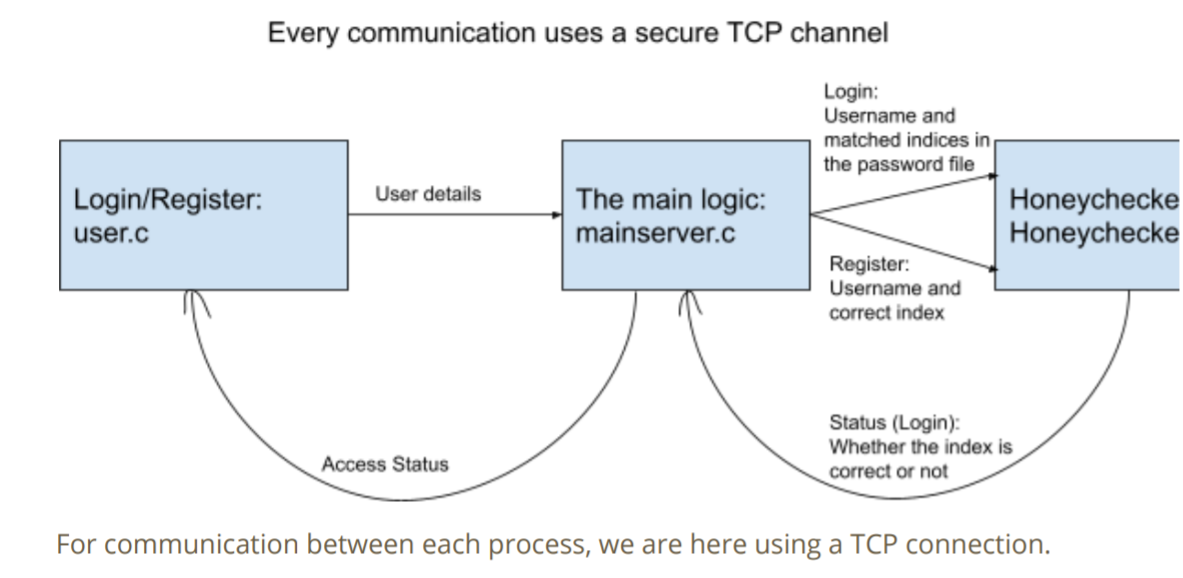
Implementation of Erguler’s honeyword based scheme. Socket programming (secure TCP channel) is used for the communication.
Here's why:
- Honeywords are a defense against stolen password files.
- Specifically, they are bogus passwords placed in the password file of an authentication server to deceive attackers.
- Honeywords resemble ordinary, user-‐selected passwords.
- C Language
- Socket Programming
- Linux
This is an example of how you may give instructions on setting up your project locally. To get a local copy up and running follow these simple example steps.
Install md5deep package.
sudo apt install md5deep- Using make file provided
make
- Run manually (Open three terminals and run the following commands)
gcc -o honeychecker honeychecker.c ./honeychecker.c gcc -o mainserver mainserver.c ./mainserver gcc -o user user.c ./user
Choose between Login (1) and Register (2)
After choosing, enter the username and password
If its a login process, the user details are sent to mainserver.c using a secure tcp channel. The main server searches for the user in f1.txt and gets all the sweet indexes. Then it searches the sweet indexes in the f2.txt and selects the indexes which match with the password provided by the user. If there is a match, then the matched index is sent to honeychecker.c using tcp channel. The honeychecker checks whether the index is correct and returns the status to mainserver which then again reverts to the user.c with the status code.
Status code:
Code Status
0 Username not found
1 Successfully Logged In
2 Password breach! Matched with a honeyword! (An alert is raised)Files details:
user.c - Used for login and registration purpose
mainserver.c - Used for the main logic (to check for the login details provided and registration process)
honeychecker.c - Stores the correct index of a user and also returns whether the provided index is a correct one or a honeypot