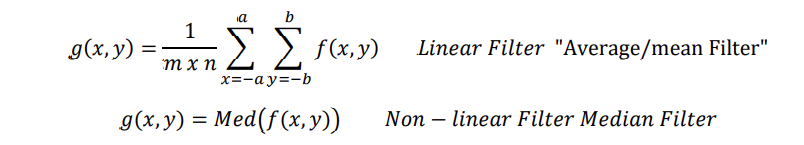The project aims to explain how the mean and median filters work and design discrete implementation of the mean and median filters on MATLAB from scratch with basic syntax and make the code operate with and respectively without padding and with padding by zero and padding by replication the user will be asked at the start of the program about padding
Image Filtering Enhancement is one of the most important processes in Digital Image processing, It is used to remove noise, sharpen the contrast, edge detection, and contours highlight, [24] by applying a specific algorithm to the image, one of the most used domain to regard the image is Spatial domain techniques that it is a spatial distribution operate directly on the pixels of the image and it categories into Gray-level transformation and Spatial Filtering, [25] we will focus on the spatial filtering which categorized to Linear Spatial filtering (Mean filter) which is widely used in digital image processing for blurring hide the small gaps in lines and curves and Non-linear spatial filtering (median filter) where it’s a very popular use for noise reduction such as impulse noise and salt and pepper noise. This paper aims to explain how the mean and median filters work and design discrete implementation of the mean and median filters on MATLAB from scratch with basic syntax and make the code operate with and respectively without padding and with padding by zero and padding by replication the user will be asked at the start of the program about padding.
As mentioned in the introduction, the spatial domine techniques operate directly on the pixels of an image, the spatial domain process discussed in references [26] [27] where the expression denoted by a mathematical equation
𝑔(𝑥, 𝑦) = 𝑇 [𝑓(𝑥, 𝑦)]
Where f (x, y) is the input image and g (x, y) is the processed image, and T is an operator of f, defined over a
specified Neighborhood. So that the image can be modified by applying a particular function to each pixel
value. The idea is to define a spatial neighborhood of the image is use a rectangle “mask\kernel” region
usually with sides of odd length 3x3 or 5x5 moved from pixel to pixel over the given image after that a new
image will be created whose pixels have grey values calculated from the grey values under the mask as
illustrated in figure 1.

The combination of mask and function is called Filter, there are two principal terms to identify operation neighborhood processing and spatial filtering. Spatial filtering is more popular, if the computations performed on pixels of neighborhoods are linear, the operation is called linear spatial filtering [28] which means if they use a linear function in the mask operator the filter is called linear filter, otherwise called a nonlinear spatial filter.
The following equations are examples of Linear and Non-linear Filters:
operation consists of multiplying each pixel in the mask by corresponding element in the neighbourhood, and adding up all these products, As showing in ref [29] the strategy of linear spatial filtering is shown in figure 31, the process consists simply of moving the centre of the filter mask from point to point in an image f,
The following equation shows the mathematical formula if linear filter: [30]

The form an be normalised be multiplying it with a factor 1 / 𝑚*𝑥
One of the most popular Smoothing spatial linear filters is Averaging\mean filter, it is widely used to remove small gabs in lines or curves” irrelevant details” in the image, the output of it is smoothed image with reduced in sharp with blur edges.
How it is Work?
- The Averaging Filter take the average of the pixels contained in the neighbourhood of the filter mask.
- The process of work could be illustrated in the following Figure 32 shows the mask, the main idea is replacing the value of every pixel in an image by the averaging of the gray level in the neighbourhood defined in the filter mask.
- The mask dimension M x N has a direct effect on the processed image when the mask dimension increases the blur in image increase that shown in following images:
- As shown in figure 33 the blurring which increased whenever the mask size increases and removing small objects with the background when the mask size increase, also we notice the black border because of padding the borders of the original image and the quality of image ins reduced.
Neighborhood operations are also used in nonlinear spatial filtering and the strategy of defining a Mask and sliding it over every pixel in image [31], However, we discussed in last section the linear filters based on linear operation such as sum of product, On the other hand, the nonlinear spatial filters is based on nonlinear operations such as taking the maximum element in the mask in Max Filters or taking the maximum element in the mask in Min Filters or taking a medium element in median filters, some books [32]called it an order-statistics filters because the response of it based on ordering (ranking) the pixels in the neighbourhood and then replacing the value of the centre pixels with the value determined by ranking result. Example of nonlinear filters: Max, Min, and Median filters.
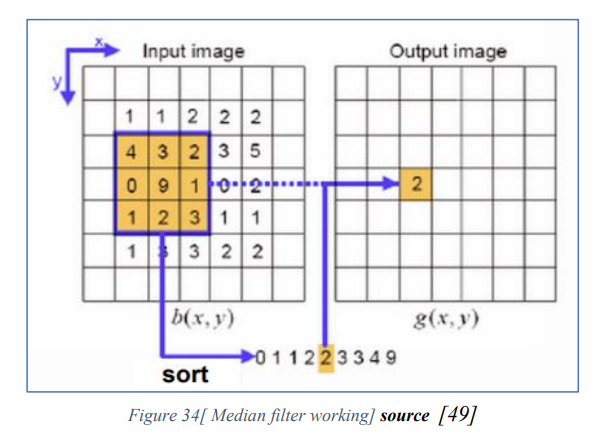
This paper we will focus on Median filter: which widely used in removing impulse noise (Salt and pepper noise), the median filter strategy [33] is sliding the mask over the image pixel by pixel replacing each value with the median(medium) value of neighbouring pixels. The median is calculated by sorting all the pixels values from the mask into numerical order and replacing the pixel being considered with the middle (Median) pixels value the figure 34 illustrate the working technique of median filter.
The effect of Median filter shows in figure 35.
The original image containing a significant amount slat & pepper noise (impulse noise), the effect of process this image by median filter illustrates in figure 35 which all noise removed while preserving edges.
When doing lineal spatial filtering [29], two crucial principles must be highlighted: the first is correlation, and the second is convolution. Figure 31 depicts the correlation process of passing the mask w via picture array f. The convolution method is the same, except that w is rotated by 180 degrees before being passed by f. the following figure 38 show the different between correlation and convolution.
The output image sometimes not the same as input image that appeared in figure 33 when we applied a average filter with big size mask the output image has a black borders, and to solve this problem we should apply Padding on processed image. As mentioned in discussion [34]The padding is the process of adding additional pixels in input image to keep the processed image size the same as input image. There are two types of padding the first one is “zero padding” which it is adding extra row & column of zeros on each side of the image, and it leads to a dark border effect, where the second
one is Replication padding which replicate the pixels value in additional row and column on each side of the image, the figure 39 shows the different types of padding.
The main aim of the paper is to design a discrete implementation of Mean and respectively median filters with mask 3x3 on MATLAB from scratch with basic syntax, and the code will be operated without padding and with zero padding and padding with replication.
- This will be made by designing a mean algorithm which will take a mask 3x3 sum all element of it and divided by 9 after that replacing the value in output image.
- Also, designing a Median Algorithm by making a sorting algorithm that collect all element in the mask and store them in array after that it will take the medium element in the array and replace it in output image.
- The program will operate in three different cases the first one applying the two algorithms mentioned on image without padding which will reduce the dimension of it, the second applying the same algorithms on image (matrix) with padded by zeros the output image will be the same size, the third one will be applying the algorithms in image(matrix) padded by replicate.
- The user will be asked at the first of program about choosing the padding option o= without padding, 1=padding by zeros, 2=padding by replicate.
The program will be able to filter the image(matrix) by mean and median filters respectively without padding and padding by zeros and padding by replicate. This section will discuss the mean and median designed algorithm and strategy of solving the problem. The Following figure 40 show the Program Flowchart and Plan.
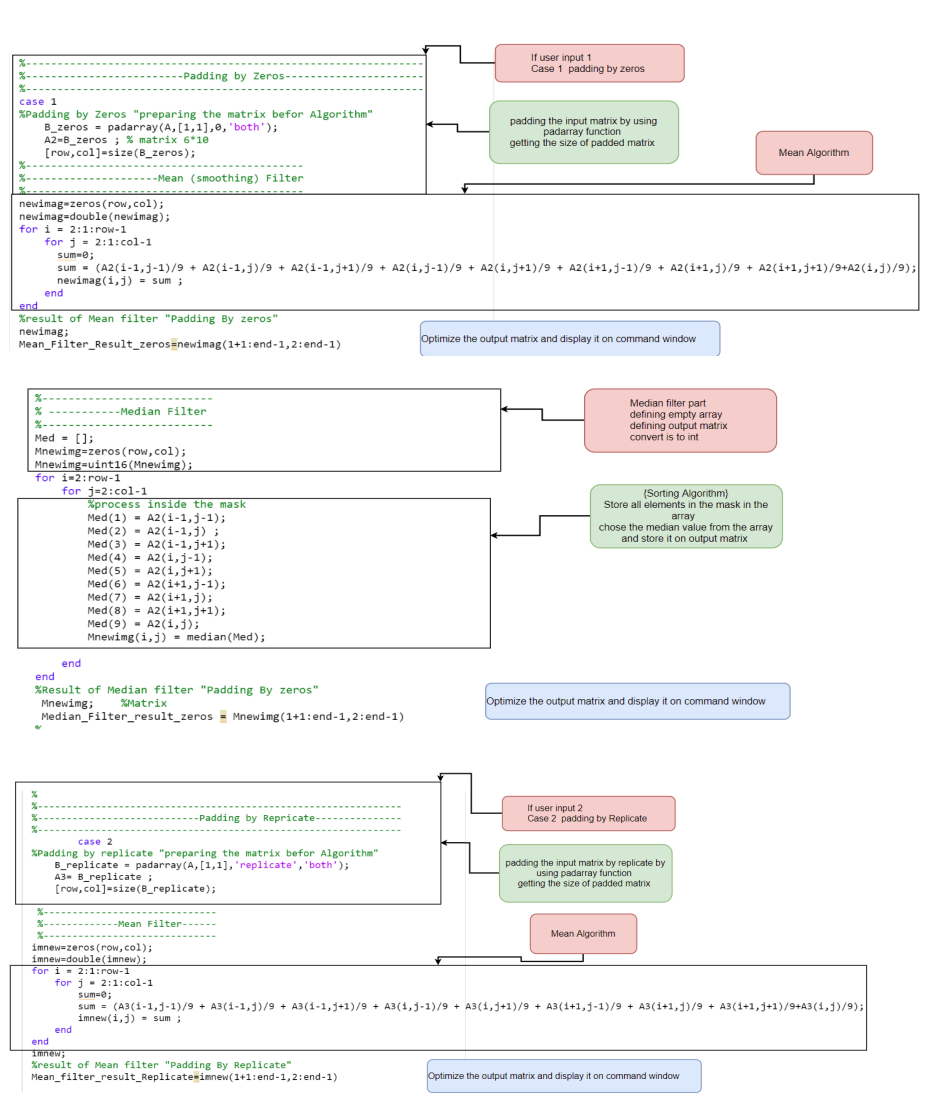
As shown in Figure 40 the program flowchart consists of three parts are common in mean algorithm and median algorithm and different in padding strategies, the following section will discuss the process of implementing Mean and median algorithms. Before we started to develop the algorithms for those filters, I took a long time in searching on internet and I found many people and websites discussed this thing here some of them [35], [36], [37], [38], [39].
- The main idea of Mean Filter is to make a mask for example (3x3) and slide this mask in every pixel in image and take the sum of all elements and divided them all by 9 and put the value in output image (matrix). the figure 41 shows the process of mean filter the right matrix is matrix without padding the black line is the matrix and the 3x3 cube line is the MASK 3x3 the mask will start from row 2 and col 2 and it will move in every pixel in the image sum all elements inside it and divided them by 9 and put the output in output matrix as shown in figure 41
- When applying mean or median filter on unpadded image such as figure 41 the output image(matrix) size decreased that’s make a border looking sharping and black this problem mentioned in background section, so to avoid this we pad the image with zeros or replicate to keep the dimension as it is. The following figure 42 illustrates the process of applying mean filter on image(matrix) padding by zeros or replicate.
To implementing MATLAB code that will make the mean filter we have two challenge the first one to make the mask slide on image(matrix) pixels and the second is to sum all elements inside the mask and replace it in output image(matrix).
For the first challenge: we will get the size of image(matrix) by function called size [40] and store the size of matrix in variables row and col (row X col) after that, we will use nested loop [41] the first one (i) will be to move the mask from row 2 till the row-1 and the second (j) to move the mask from column 2 to the col-1 this will scan the image (matrix) in every pixel starting from position (2,2) till the end depending on matrix size.
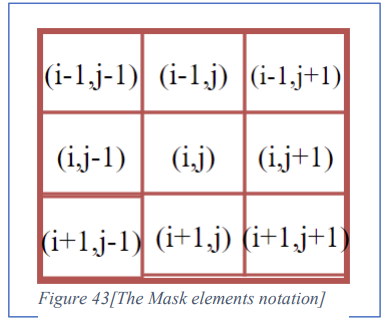
The second challenge: to sum the elements and divided them by 9 in the mask the figure 43 illustrates the mask element
notation.
The Algorithm will divide every element by 9 and sum them all and store the output pixel average mask in matrix new called imnew(i,j) and the type of it is double as shown in figure 44.
The process will repeat until the row-1 and col-1 reach zeros and loop will stop.
In case of padding by zeros and padding be replicate, at the first we will define a new matrix padded by function called arraypad [42] and will take the size of it and substitute in the mean algorithm after that rearrange the matrix and display it in command window.
- The main idea of median filter is to arrange the elements of the mask 3x3 in array and take the medium pixel in that array and substitute by it in the output image(matrix) as shown in figure 45
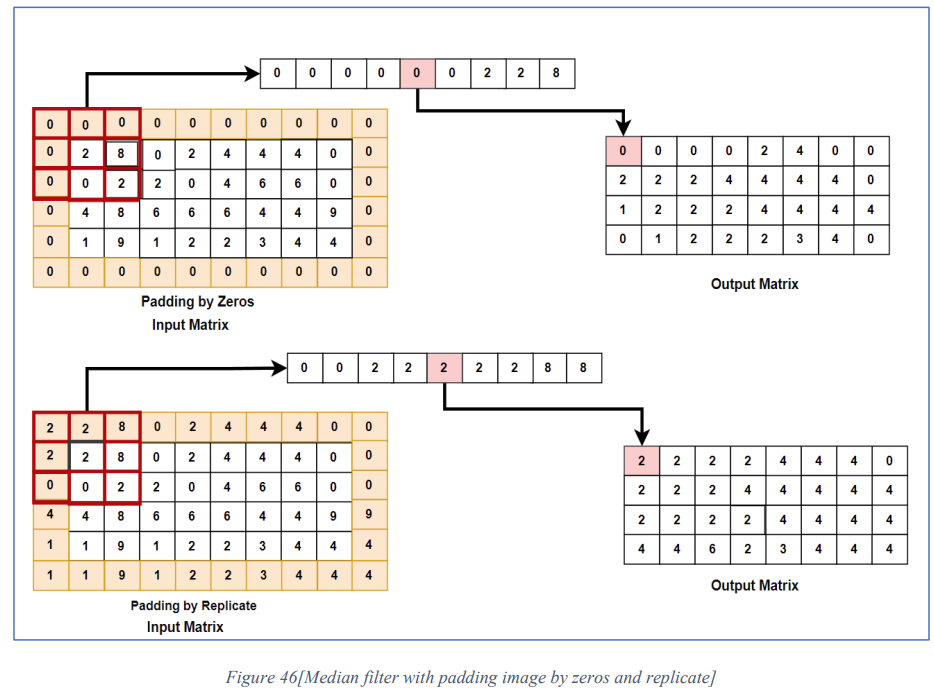
- As mean filter when applying median filter on unpadded image the size of image decrease because of the mask should cover 3x3 region that cause problem of sharping edges of the output image, that problem covered in background section, to avoid this problem we pad the input image borders by zeros or replicate and the output image will give us the same dimension of input image. That’s illustrated in figure 46.
The moving of Mask strategy will be the same as discussed in mean filter section, we will make use of size function and nested loop strategy to scan the input image (matrix) pixel by pixel from row 2 and col 2 to the end and apply median algorithm on it and substitute the output value in output image (matrix) as shown in figures 45,46.
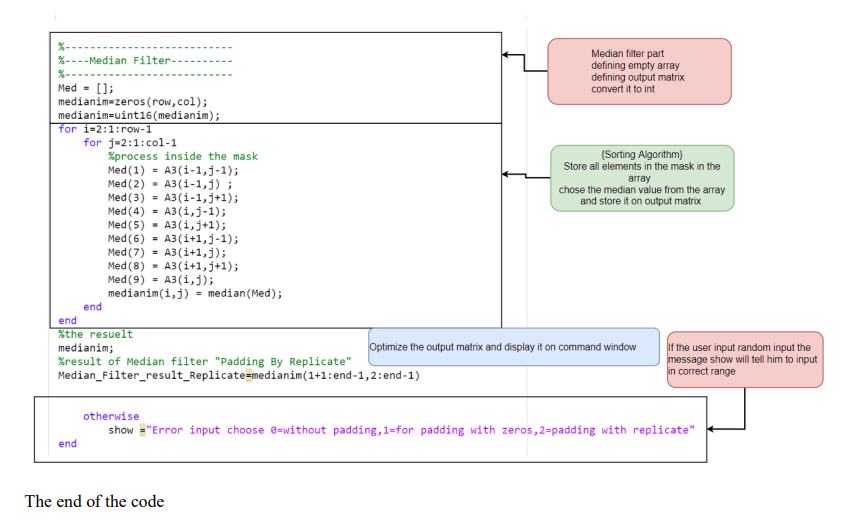
Before, we go inside the loop the empty array will be made called Med= [] and output matrix will be defined and well, Inside the loop the sorting Algorithm will store all elements in the mask inside the empty array as shown in figure 47.
After adding all elements inside the empty array, we will choose the medium element in the array by median [43] function and put the output value inside the output matrix. This process will be repeated on overall pixels on the input image(matrix).
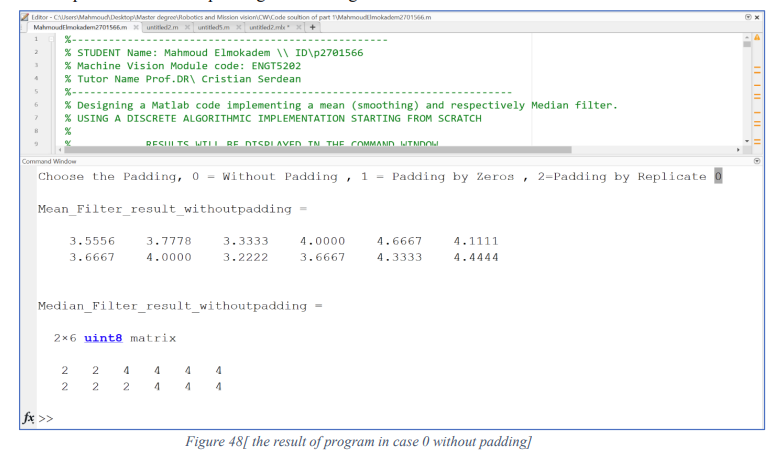
In this section the code will be tested by comparing the result of it by a ready-made function on MATLAB: The result of mean and median filters in case 0 without padding: we notice the size of output matrix is decreased because the input matrix without padding shown in figure 48
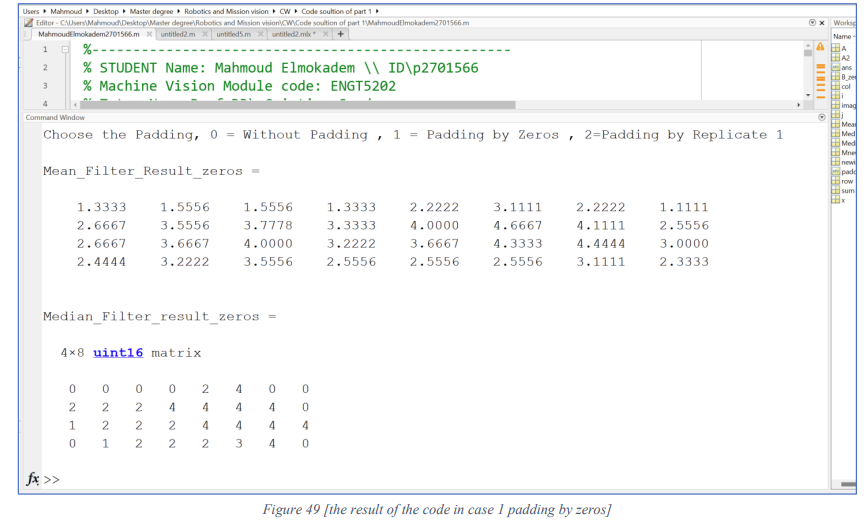
The result of Mean and Median filters in case 1 padding by zeros illustrated in Figure 49
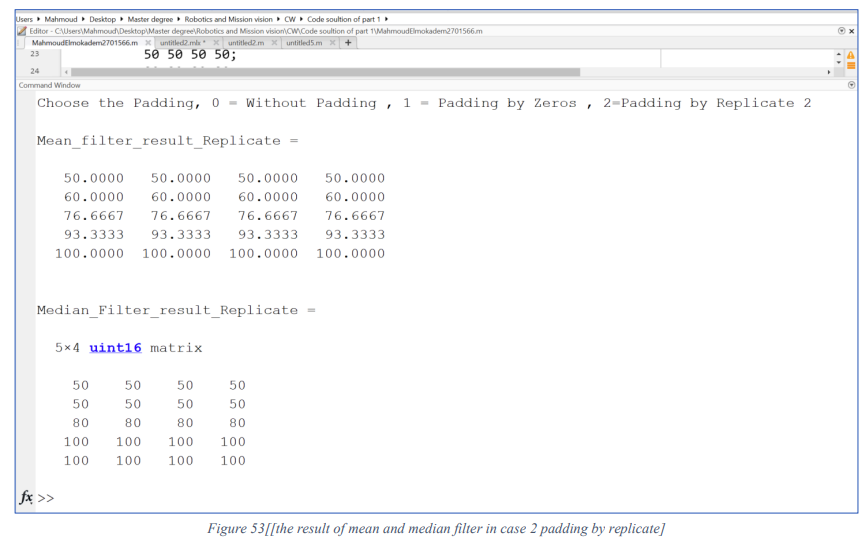
The result of Mean and Median filters in case 2 padding by replicate illustrated in Figure 50
The result of ready-made function on MATLAB shown in figure 51
The result of the code showed in figures 49 and 50 gives the same result of ready-made functions.
We will test the code w7ith another matrix:
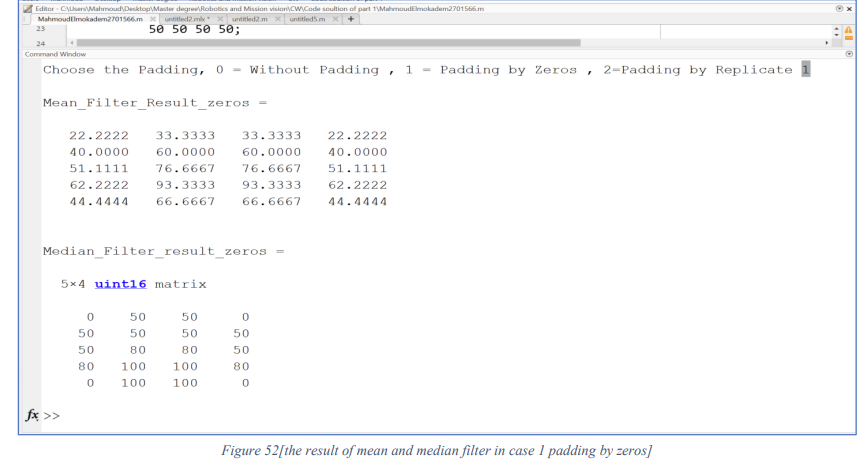
The result of Mean and Median filters in case 1 padding by zeros illustrated in Figure 52
The result of Mean and Median filters in case 2 padding by replicate illustrated in Figure 53
The result of ready-made function on MATLAB shown in figure 54
The result of code shown in figures 52 and 53 are the same output by ready-made functions in MATLAB shown in figure 54 with different matrix.
The mean (Averaging) and median filters are powerful filters widely used in digital image processing to smooth the images and remove salt and pepper noise, this paper discussed a discrete implementation of those filters with basic syntax and from scratch in MATLAB and also it considered the three different padding cases the first on applying those filters without padding and applying with padding by zeros and replicate, and also descried the code implementation and Algorithm, and tested the code on two different matrices and verified the code working by compares the out put result by ready-made functions on MATLAB
[24] Anonymous "Lecture "image filtering" ", [Online] Available from: https://www.cs.auckland.ac.nz/courses/compsci373s1c/PatricesLectures/Image%20Filtering_2up.p df . [25] Rafael C. Gonzalez, Richard E. Woods and Steven L. Eddins, Digital image processing using MATLAB® 2nd edition , . [26] Rafael C. Gonzalez, Richard E. Woods and Steven L. Eddins, Digital image processing using MATLAB® 2nd edition , . [27] Alasdair McAndrew, An introduction to digital image processing with matlab notes for SCM2511 image processing 1 semester 1, 2004 , . [28] Prof.Bebis, "Spatial filtering CS474/674 lecture note", [Online] Available from: http://www.csre.iitb.ac.in/~avikb/GNR401/DIP/Spatial_Filtering.pdf . 38 Mahmoud Elmokadem p2701566 [29] Steven L. Eddins, Richard E. Woods and Rafael C. Gonzalez, Digital image processing using MATLAB 2nd edition , . [30] Prof Cristian Serdean, Lecture 4 neighbourhood operation (1) machine/computer vision , . [31] Rafael C. Gonzalez, Richard E. Woods and Steven L. Eddins, Digital image processing using MATLAB® 2nd edition , . [32] Waseem Nahy Ibrahim, "Image processing lecture notes lec6 ", [Online] Available from: https://uotechnology.edu.iq/ce/lecture%202013n/4th%20Image%20Processing%20_Lectures/DIP_ Lecture6.pdf . [33] Anonymous "Image filtering median filter lecture ", [Online] Available from: https://www.cs.auckland.ac.nz/courses/compsci373s1c/PatricesLectures/Image%20Filtering_2up.p df . [34] Y.Ç Aktaş, "Image processing part 2", -12-23T21:18:23.644Z. [Online] Available from: https://towardsdatascience.com/image-processing-part-2-1fb84931364a [Accessed Apr 20, 2022]. [35] Anonymous "Http://Matlab.izmiran.ru/help/toolbox/images/enhan23b.html", [Online] Available from: http://matlab.izmiran.ru/help/toolbox/images/enhan23b.html . [36] Pascal Getreuer, "Image processing with matlab ", [Online] Available from: https://getreuer.info/tutorials/matlabimaging/ . [37] naik24, "Image-filters-in-MATLAB", [Online] Available from: https://github.com/naik24/Image�Filters-in-MATLAB . [38] A. Angel, "MATLAB PROGRAM : 2D MEDIAN FILTERING FOR SALT AND PEPPER NOISE WITHOUT USING medfilt2 FUNCTION", . Available from: https://www.imageeprocessing.com/2011/03/matlab-program-2d-median-filtering-for.html [Accessed Apr 23, 2022]. [39] Prof\Cristian Serdean, Ed. Lecture 4: Neighbourhood operations (I) Machine/computer vision, 16. [40] Anonymous "Array size - MATLAB size - MathWorks united kingdom", [Online] Available from: https://uk.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/size.html . [41] tutorialspoint, "MATLAB - the nested loops ", [Online] Available from: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/matlab/matlab_nested_loops.htm . [42] Mathworks, "Pad array - MATLAB padarray - MathWorks united kingdom", [Online] Available from: https://uk.mathworks.com/help/images/ref/padarray.html . [43] Mathworks, "Median value of array - MATLAB median - MathWorks united kingdom", [Online] Available from: https://uk.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/median.html . [44] Anonymous "Aibo - ROBOTS: Your guide to the world of robotics", [Online] Available from: https://robots.ieee.org/robots/aibo2018/ [Accessed Mar 24, 2022]. 39 Mahmoud Elmokadem p2701566 [45] Robert Castle Active Vision Laboratory, "Object tracking with single-camera SLAM", [Online] Available from: https://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~bob/research/research_objectslam.html . [46] Anonymous "Micro robot servo | adamant namiki precision jewel co., ltd.", [Online] Available from: https://www.ad-na.com/en/product/motor-unit/servo.html . [47] Alasdair McAndrew, An introduction to digital image processing with Matlab Notes for SCM2511 image processing 1 , 2004. [48] Alasdair McAndrew, An introduction to digital image processing with matlab notes for SCM2511 image processing 1 , 2004. [49] Prof Cristian Serdean, Neighbourhood operations (I) lecture 4 machine/ computer vision , . [50] Anonymous "Spatial filtering page 63", [Online] Available from: http://www.csre.iitb.ac.in/~avikb/GNR401/DIP/Spatial_Filtering.pdf