Previously I wrote (https://github.com/maksimpiriyev/Search-As-You-Type-Index-master) about fast prefix search for ~10,000 key-value pairs designed for mobile.Now,Eli-Index designed to handle more than 1,000,000 key-value pairs,make fast prefix search on them,and furthermore bring the most ranked one from index.It stores index and data at the same time on external memory not in RAM (caches the nodes while it needs)
Most of the prefix search indices are designed for server side use,they store index in the RAM so that has intialization latency which prenvents opening application more faster in mobile(using threads also slows down the main thread).Eli-Index is designed to overcome this problem. Eli-Index is designed over AVL Tree,Segmented Tree and with Heap.Its nodes has the features of both AVL Tree and Segmented Tree.It makes prefix search over AVL Tree ,and gets the result list in sorted order while iterating on the nodes of segmented tree with the help of heap. It might also be the first AVL Tree implemented for string prefix search as I couldn't find any paper or implementation that use AVL Tree for string Prefix Search. Eli-Index has preferred to use AVL Tree instead of Trie Index because if Trie Index is implemented in External Memory,Either it is fast and uses more memory or it is slower because of more random file access.
class TreeIndex{
public:
TreeIndex(const string fileName);
void save();
long size();
vector<tuple<long, wstring,long > > search(wstring txt, int maxCount = 100);
vector<wstring> searchOnlyString(wstring txt, int maxCount = 100);
tuple<long, wstring,long >* find(wstring txt);
void add(wstring txt, long statCount = 1/*rank*/,long value = 0);
void loadNgram(string fileName, int ngram);
void loadTopWords(string fileName,int maxCount=-1);
bool isExist(wstring s);
void setText(Node* n, wstring txt);
void clearCache();
int cacheSize();
int treeHeight();
};Its usage :
TreeIndex xx("index_en.tf");
cout << xx.treeHeight() << endl;
xx.add(L"pretend");
xx.add(L"predict",1);
xx.add(L"prediction",2,1);
auto xff = xx.search(L"pre",100);
for (size_t j = 0; j < xff.size(); j++)
{
wcout << std::get<1>(xff[j]) << endl;
}
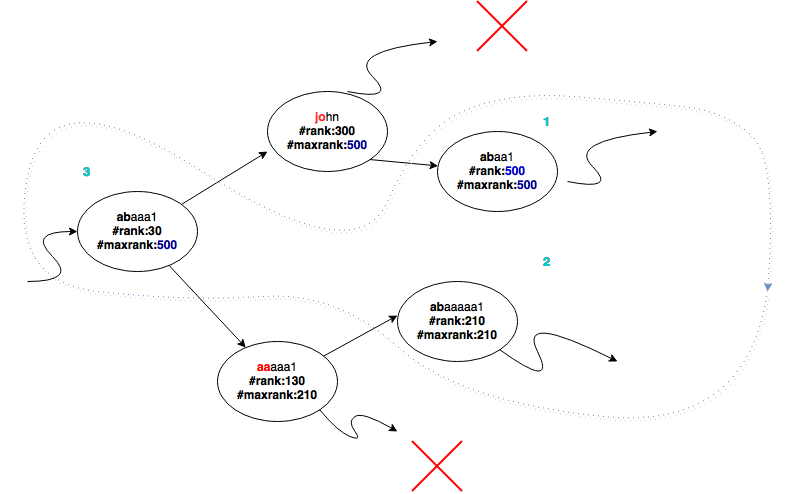
Note that AVL Tree is the same as it was with same operations,but Prefix Search on AVL Tree is little bit different than the regular search on AVL Tree.Lets say we are searching the prefix P.We always compare the prefix of the text in the node with length |P|.
- If node N is greater than the prefix then its right nodes do not contain that prefix.
- If node N is smaller than the prefix then its left nodes do not contain that prefix.
- The case that left node is smaller than P and right node is greater than P might exists only at the node itself or (either in left subtree or in right subtree),but not left and right subtree at the same time.This is why the complexity is logN not 2^N
Segmented Tree is well known structure to find the min-max values in any tree. Eli-Index iterates between top min-max values using heap.
Insert complexity is as same as the AVL tree O(logN)
Segmented Tree has the O(logN) complexity for finding the node with maximum rank value,using heap and finding next K-1 complexity brings extra O(lgK*lglgN) overhead.
Total Complexity: O(K* lgK* lgN* lglgN) .
It is written in C++11.
g++ -Ofast -std=c++11 -o prog main.cpp TreeFile.cpp
Note that nowadays most of the databases have prefix search with their full-text search functionality.Lets say you have more than 1,000,000 words and 100,000 of them starts with "a*" and you want search all of them ordered by their rank.This time Eli-Index and SQL will have very similar performance results.But If you search top 10 ranked(user-defined) results from these 100,000 words then Eli-Index will drammatically beat SQL,because SQL is abstract it retrieves and then sorts for column and gets top results, instead El-Index finds top nodes first by default
Some Operating Systems has the policy to cache whole file at first acess before you do any operation on it (OS-wide first access),and it brings extra latency in the first operation,but meanwhile makes faster the other operations.But, you can use fadvise,fcntrl etc to disable cache or tell the read pattern is random.
Typing auto-complete for mac : http://elithetyper.com
by Maksim Piriyev