This repository contains an unofficial implementation of the paper "Prevalence of Neural Collapse During the Terminal Phase of Deep Learning Training" by Papyan, V., et al. (2020), published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(40), 24652-24663.
Neural Collapse (NC) refers to a phenomenon observed in deep learning where neural network last-layer classifiers and features align during the final stages of training. Reproducing this effect accurately requires careful adjustment of training parameters, including a class-balanced dataset, appropriate (or absence of) augmentation, learning rate scheduling, and specific network architectures. Different papers use various metrics to estimate NC, which may lead to different conclusions, especially in non-ideal collapse conditions.
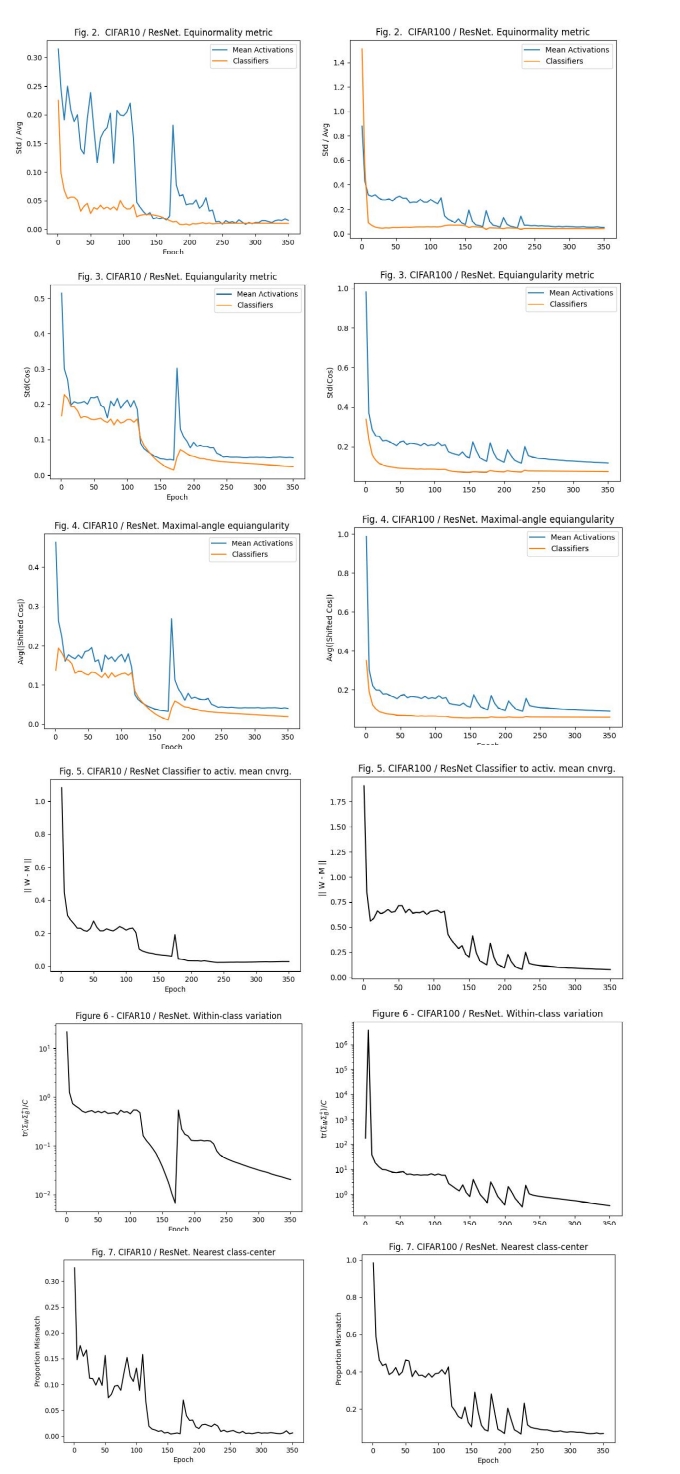
This code accurately reproduces the experiments from the original paper on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets using ResNet-18 and ResNet-50 architectures, respectively, as suggested by the authors. It replicates Figures 2 through 7 from the paper.
This code has been tested under the following environment:
torch==1.13.1torchvision==0.14.1
Ensure these dependencies are installed before running the code.
To train the network and log checkpoints for NC estimation, run the following commands:
For CIFAR-10:
python train.py --dataset CIFAR10For CIFAR-100:
python train.py --dataset CIFAR100Once the network is trained, you can estimate the neural collapse metrics using the following commands:
For CIFAR-10:
python validate_nc.py --dataset CIFAR10For CIFAR-100:
python validate_nc.py --dataset CIFAR100Plots showing the collapse metrics, analogous to Figures 2 through 7 from the original paper, are saved in the CIFAR10_plots/ and CIFAR100_plots/ directories.
- Original Paper: "Prevalence of Neural Collapse During the Terminal Phase of Deep Learning Training" by Papyan, V., et al. (2020)