Behavioral Cloning
Behavioral Cloning Project
The goals / steps of this project are the following:
- Use the simulator to collect data of good driving behavior
- Build, a convolution neural network in Keras that predicts steering angles from images
- Train and validate the model with a training and validation set
- Test that the model successfully drives around track one without leaving the road
- Summarize the results with a written report
Rubric Points
Here I will consider the rubric points individually and describe how I addressed each point in my implementation.
Files Submitted & Code Quality
1. Submission includes all required files and can be used to run the simulator in autonomous mode
My project includes the following files:
- helpers/prepare_data.py read data from csv files and combine them into one csv
- helpers/load_data.py add images into numpy array + streeing angle
- network_models/MobileNet.py contain the model should be used for this project
- model.py containing the script to create and train the model
- drive.py for driving the car in autonomous mode
- MobileNet.h5 containing a trained convolution neural network
- README.md summarizing the results
- video.mp4 video output
2. Submission includes functional code
Using the Udacity provided simulator and my drive.py file, the car can be driven autonomously around the track by executing
python drive.py MobileNet.h5
3. Submission code is usable and readable
The model.py file contains the code for training and saving the convolution neural network. The file shows the pipeline I used for training and validating the model, and it contains comments to explain how the code works.
Model Architecture and Training Strategy
1. An appropriate model architecture has been employed
I have implemented few models (look at network_models folder for more details) in order to exam how each model behave.However, Since I have a limited resources of GPU hardware, first I ran (network_models/Basic.py) which did not give any good result. After that I implemented LeNet architecture, which it gave a better performance, but still the car did not stay on the track. Next, I implemented NVIDIA architecture, which provided by Udacity during the class.
However, after many testing with NVIDIA model I realized that I need to collect more data, in order to train the model, so I generate more than 100 K data, by using my own generated data + udacity + the right and left images + flipping each image too. In fact, it help the model to give a lower loss rate, but the car was not moving smooth and safe on the track. I guessed that the issue was most of the images extracted from the simulator were similar so the model was kind of training with same images over and over.
When I reached to this point, I started exploring pretrain models such as InceptionV3, VGG16, VGG19 and MobileNet, (which are defined on network_models folder). Nevertheless, because of memory allocation error (ResourceExhaustedError) while running InceptionV3, VGG16, VGG19 on g2.4(1 GPU, 4 GB memory) instance on Amazon Web Server, I upgrade the instance to 8 GB memory (g3.4). Training VGG models take very long time (almost an hour four few epochs); therefore, I used MobileNet which was faster to train epically when I freeze the pretrain layers.
The final model I use is MobileNet, therefore run python driver.py MobileNet.h5
I removed the fully connected layers from MobileNet, and I added new three fully connected layers. Also, the model includes RELU layers to introduce nonlinearity (network_models/MobileNet.py #28), and the data is normalized in the model using a Keras lambda layer (network_models/MobileNet.py #10).
2. Attempts to reduce overfitting in the model
The model contains dropout layer in order to reduce overfitting (network_models/MobileNet.py #30)
Also, I used regularization by penalizing the weight on the first fully connected layer, because the steering angle does not only depend on images, speed has an effect by how much the steering should shift.
The model was trained and validated on different data sets to ensure that the model was not overfitting (model.py #62). The model was tested by running it through the simulator and ensuring that the vehicle could stay on the track.
3. Model parameter tuning
The model used an adam optimizer, so the learning rate was not tuned manually (model.py # 25).
4. Appropriate training data
Training data was chosen to keep the vehicle driving on the road. I used a combination of center lane driving, recovering from the left and right sides of the road and also I flipped the images (by using cv2.flip) and negate the steering angle
For details about how I created the training data, see the next section.
Model Architecture and Training Strategy
1. Solution Design Approach
In deed, first I used NVIDIA model in order to find other issue with training rather than the model itself. For example, I have trained images with following: region of interest: (helpers/load_data.py #27)
number of samples: 10k-100k (10K was chosen)
number of epochs: 10-70 (50 was chosen)
left and right images: (I used left and right images in the end)
Using gray images: I found it has no big difference whether I trained with gray image or RGB images.
After selected the best combination I trained MobileNet model with freezing the pre-train layer because it learn fast and the model works (network_model/MobileNet.py #25)
At the end of the process, the vehicle is able to drive autonomously around the track without leaving the road.
2. Final Model Architecture
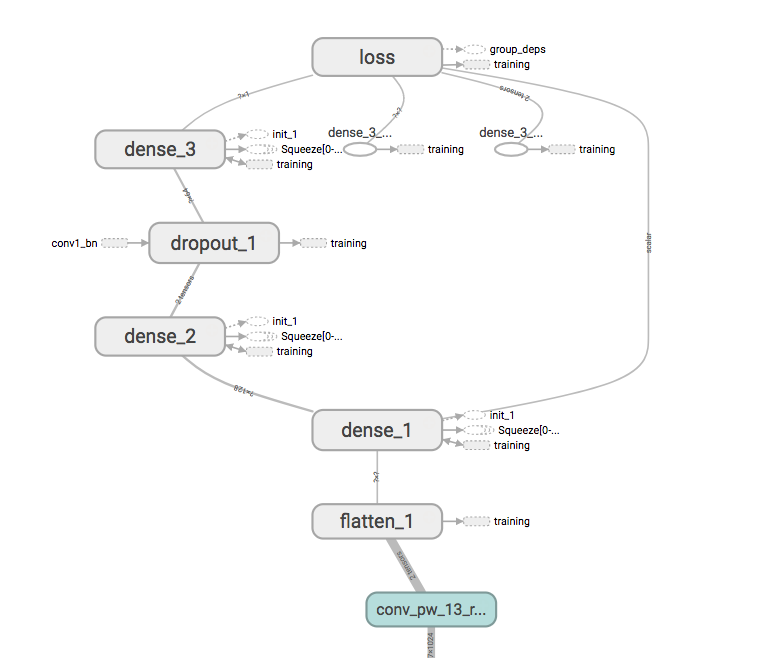
The final model architecture (network_model/MobileNet.py) consisted of a MobileNet architecture excluding the top layers + adding 3 fully connect layers
Here is a visualization of the architecture
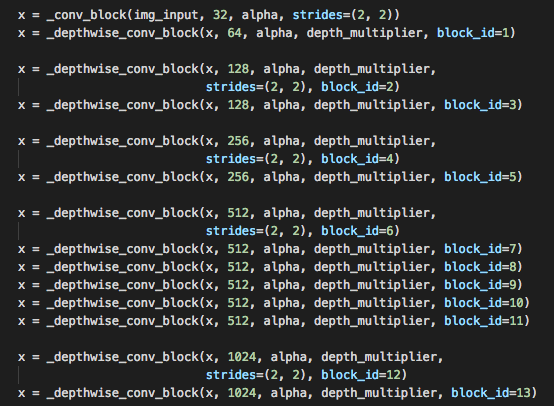
Here is the an screenshot of the implementation fo MobileNet model in Keras.
3. Creation of the Training Set & Training Process
To capture good driving behavior, I first recorded one lap on track one using center lane driving. Here is an example image of center lane driving:
I then recorded the vehicle recovering from the left side and right sides of the road back to center so that the vehicle would learn to turn when it close to the edge of the road. These images show what a recovery looks like starting from left,right and flipped center :
Then I repeated this process on track two in order to get more data points but I never used the data.
To augment the data sat, I also flipped images (center, left and right) and angles thinking that this would help the model to see different images. For example, here is an image that has then been flipped:
As well, I resized the images to the shape (224,224,3) which is require for MobileNet model.
I finally randomly shuffled the data set and put Y% of the data into a validation set.
I used this training data for training the model. The validation set helped determine if the model was over or under fitting. The ideal number of epochs was 50 as evidenced by ...
Also, I used an adam optimizer so that manually training the learning rate wasn't necessary.
My References
These references has nothing to do with the project.