A sample Java application to produce and consume messages in Event Streams (Apache Kafka on IBM Cloud)
IBM Event Streams for IBM Cloud is a high-throughput message bus built with Apache Kafka. To get started with Event Streams and start sending and receiving messages, you can use the Java sample. The sample shows how a producer sends messages to a consumer using a topic. The same sample program is used to consume messages and produce messages.
a. An IBM Cloud account. Register The following needs to be installed:
-> git
-> Gradle
-> Java 8 or higher
a. Log in to the IBM Cloud console.
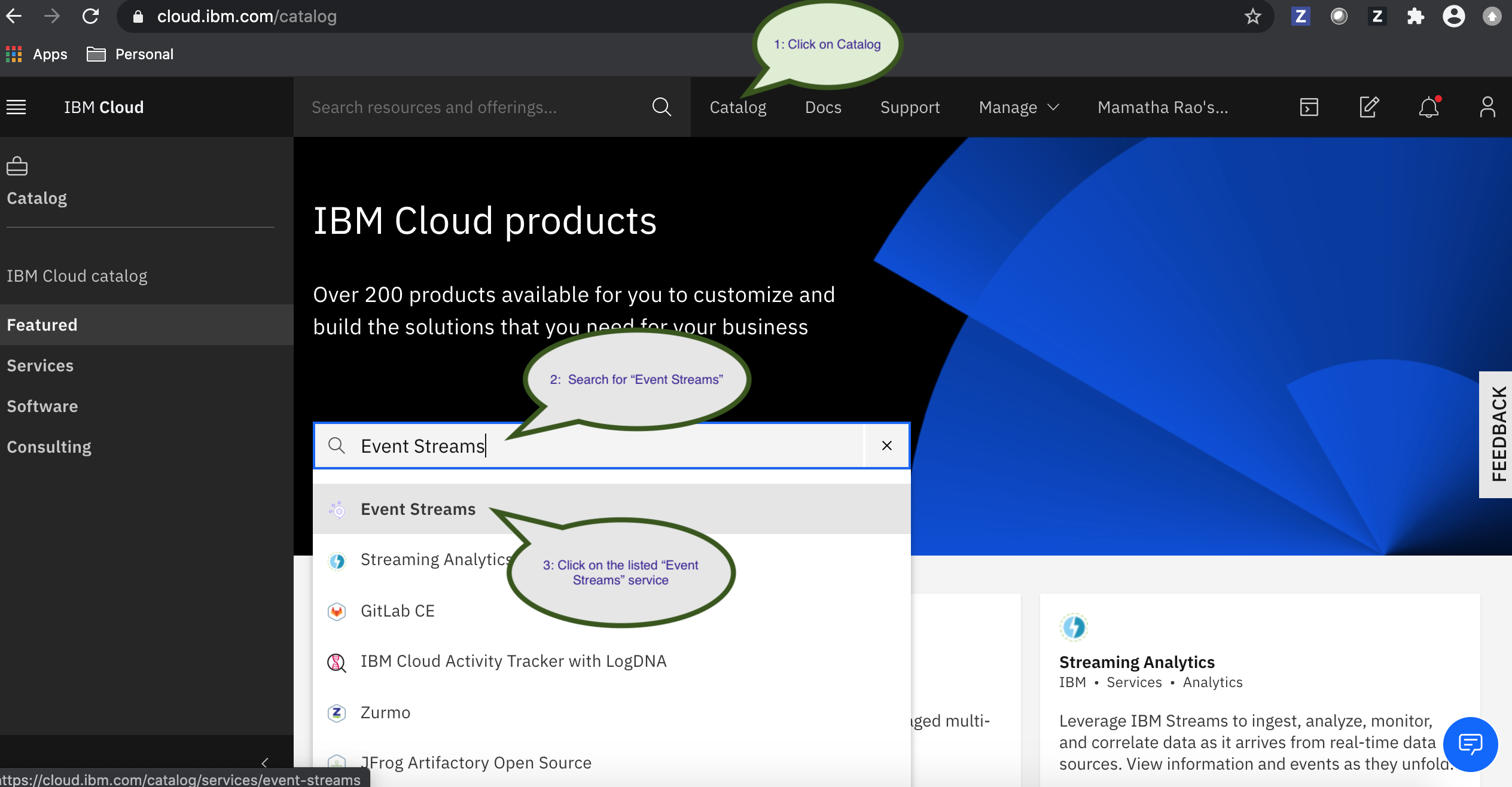
b. Click the Event Streams service in the Catalog.
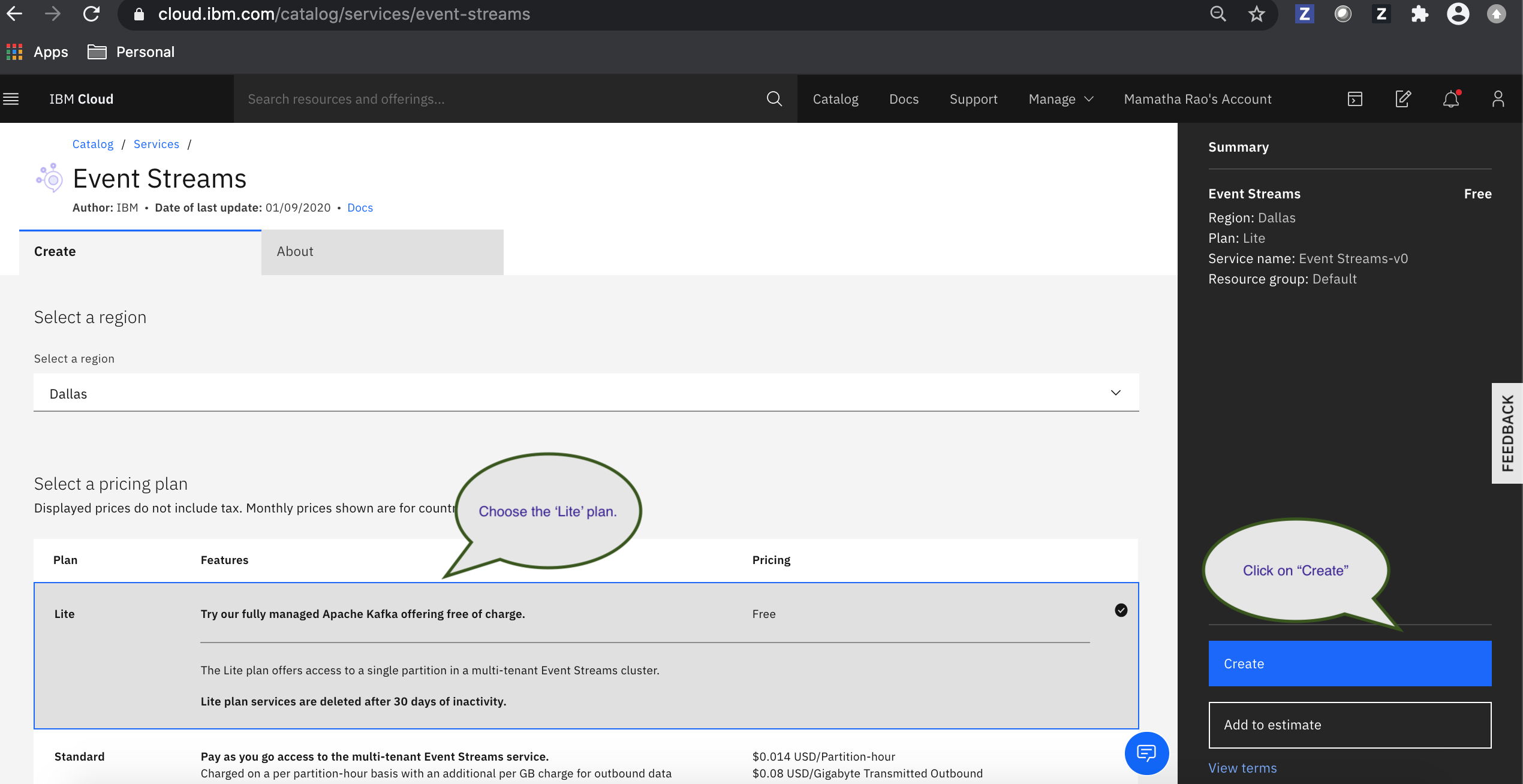
c. Select the Lite plan on the service instance page.
d. Enter a name for your service. You can use the default value.
e. Click Create. The Event Streams service instance page opens.
To allow the sample application to access your topic, we need to create some credentials for it.
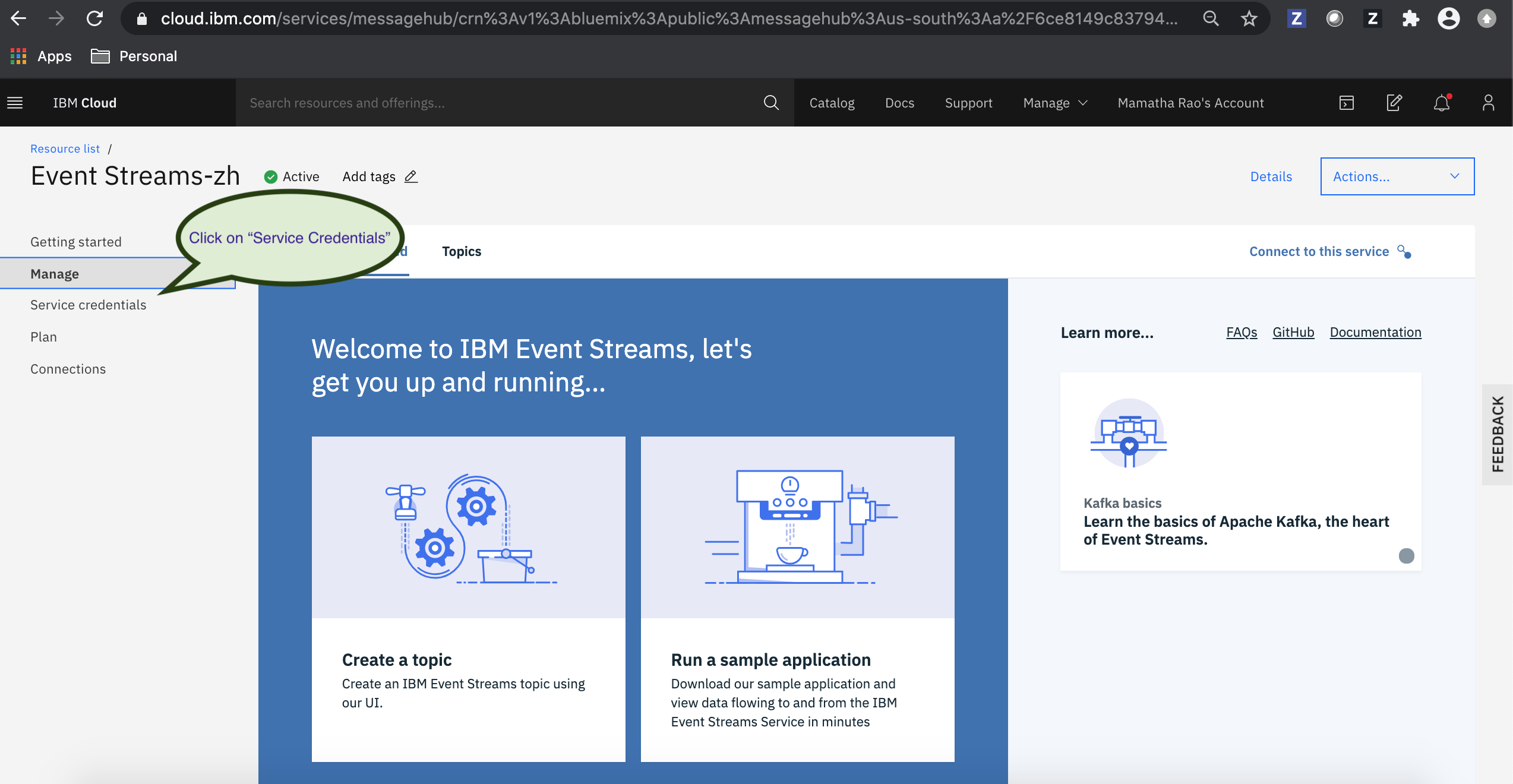
a. Go to Service credentials in the navigation pane.
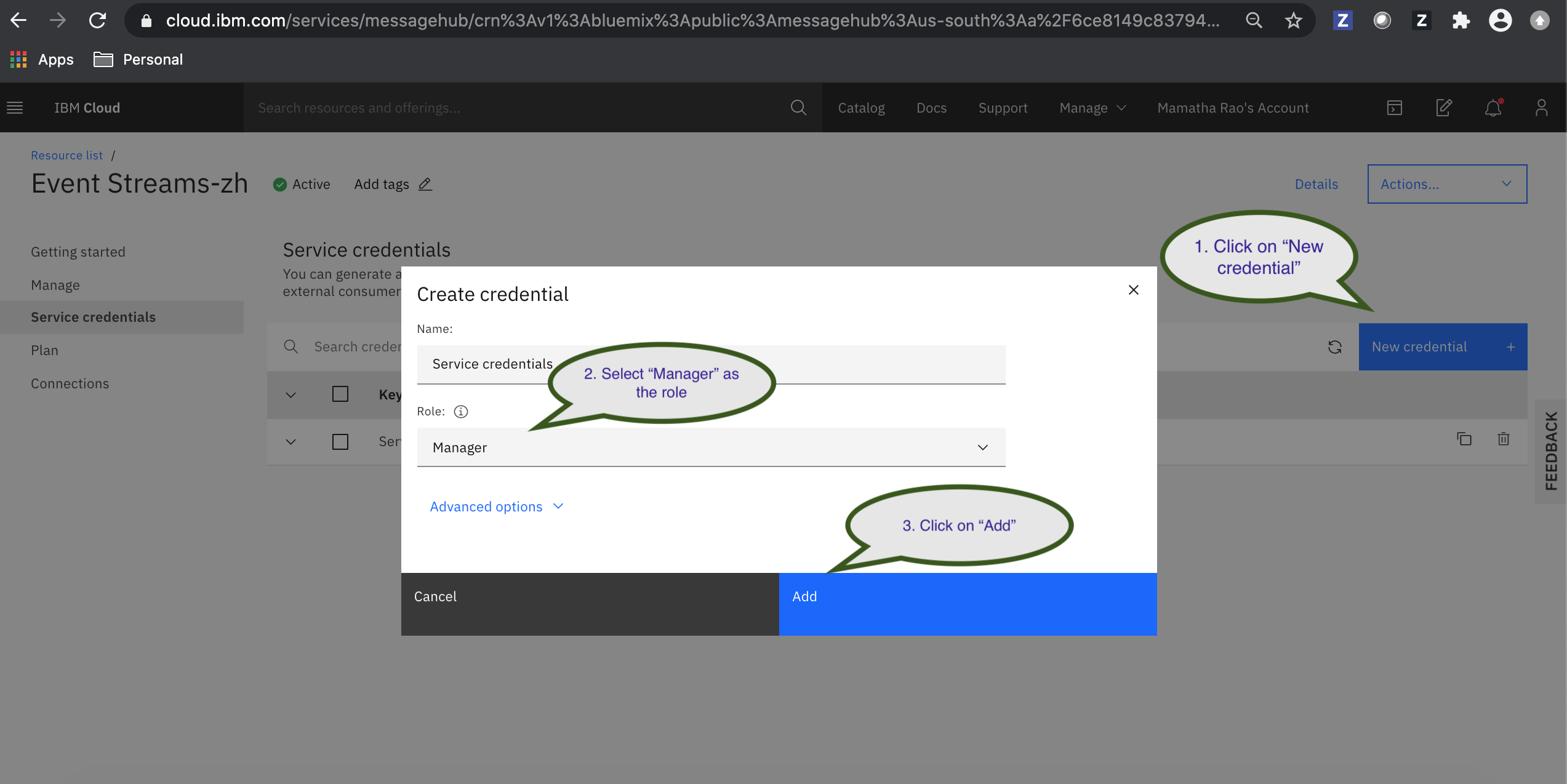
b. Click New credential.
-Give the credential a name so you can identify its purpose later. You can accept the default value.
-Give the credential the Manager role so that it can access the topics, and create them if necessary.
-Click Add. The new credential is listed in the table in Service credentials.
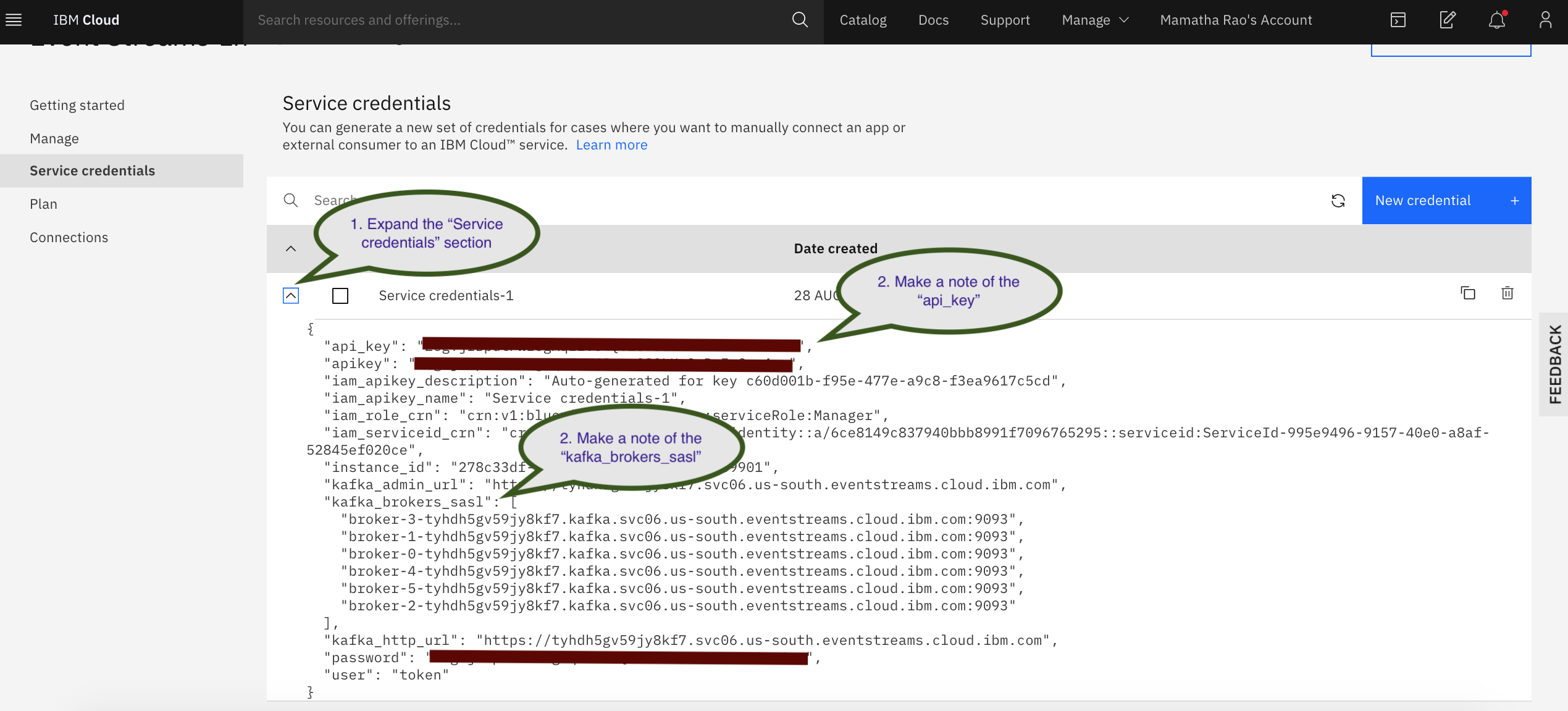
c. Click View credentials to see the api_key and kafka_brokers_sasl values.
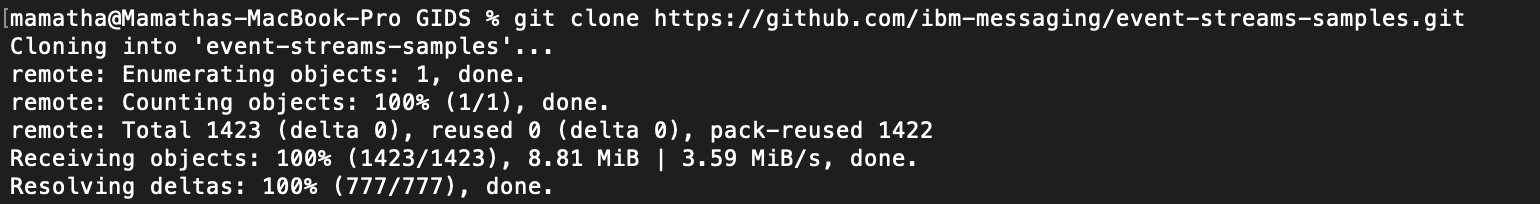
a. The sample application is stored in Github. Clone the event-streams-samples repository by running the clone command from the command line.
`git clone https://github.com/ibm-messaging/event-streams-samples.git`
b. When the repository is cloned, from the command line change into the kafka-java-console-sample directory.
`cd event-streams-samples/kafka-java-console-sample`
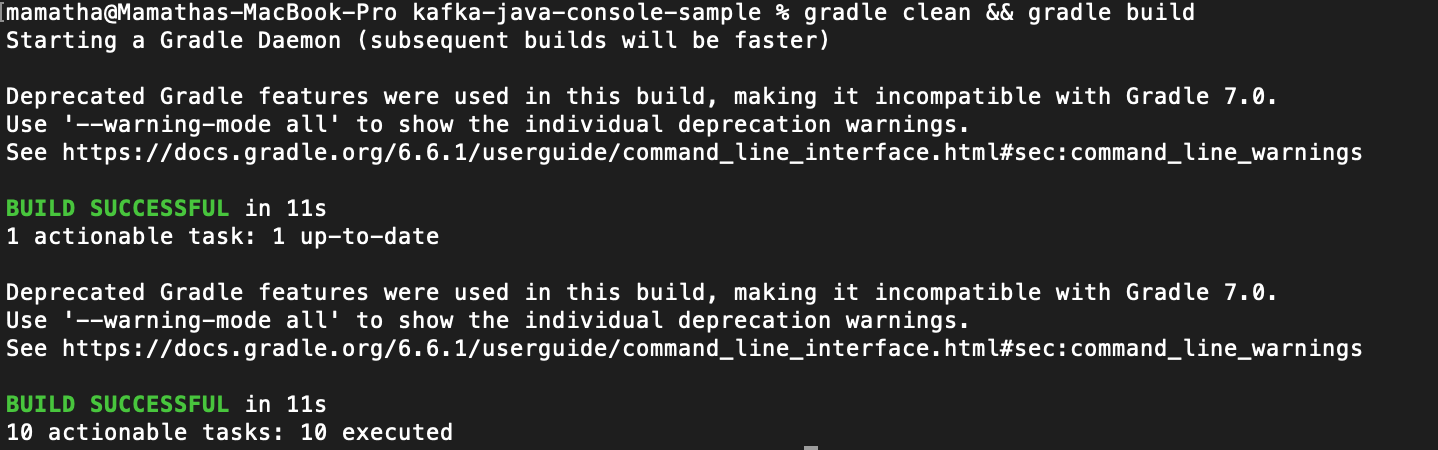
c. Build the contents of the kafka-java-console-sample directory.
`gradle clean && gradle build`
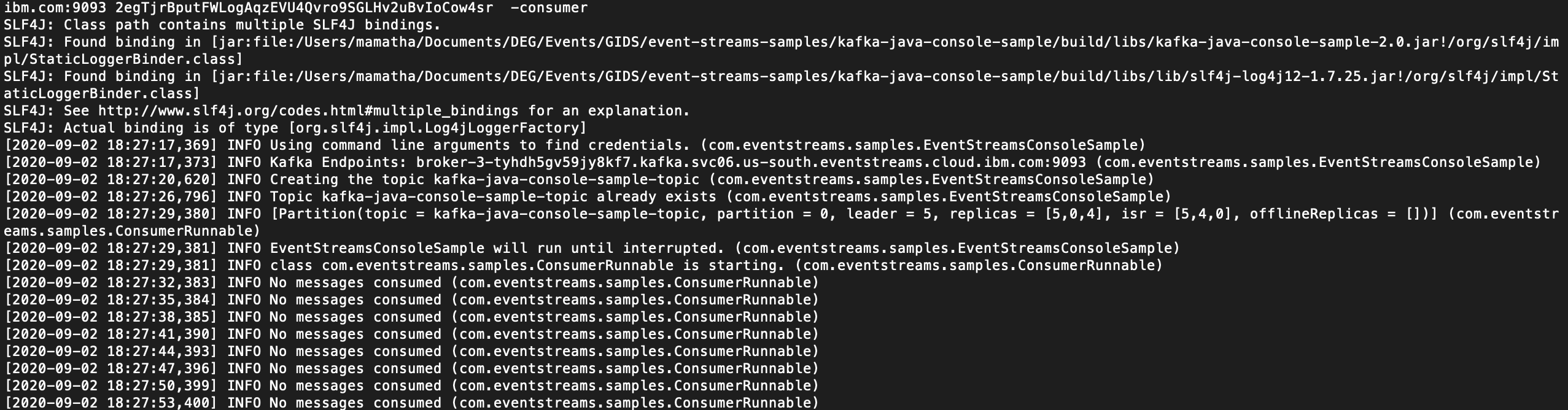
a. Start the sample consuming application from the command line: replacing the kafka_brokers_sasl and api_key values.
`java -jar ./build/libs/kafka-java-console-sample-2.0.jar <kafka_brokers_sasl> <api_key> -consumer`
The java -jar ./build/libs/kafka-java-console-sample-2.0.jar part of the command identifies the locations of the .JAR file to run within the cloned repository. You do not need to change this.
Use the kafka_brokers_sasl from the Service credentials created in Step 3. You could use one or more of the kafka_brokers_sasl listed in the Service credentials that you created.
The kafka_brokers_sasl must be formatted as "host:port,host2:port2". Format the contents of kafka_brokers_sasl in a text editor before entering it in the command line.
Then, use the api_key from the Service credentials created in Step 3. -consumer specifies that the consumer should start.
b. An INFO No messages consumed is displayed when the consuming application is running, but there is no data being consumed.
a. Open a new command line window and change into the kafka-java-console-sample directory.
`cd event-streams-samples/kafka-java-console-sample`
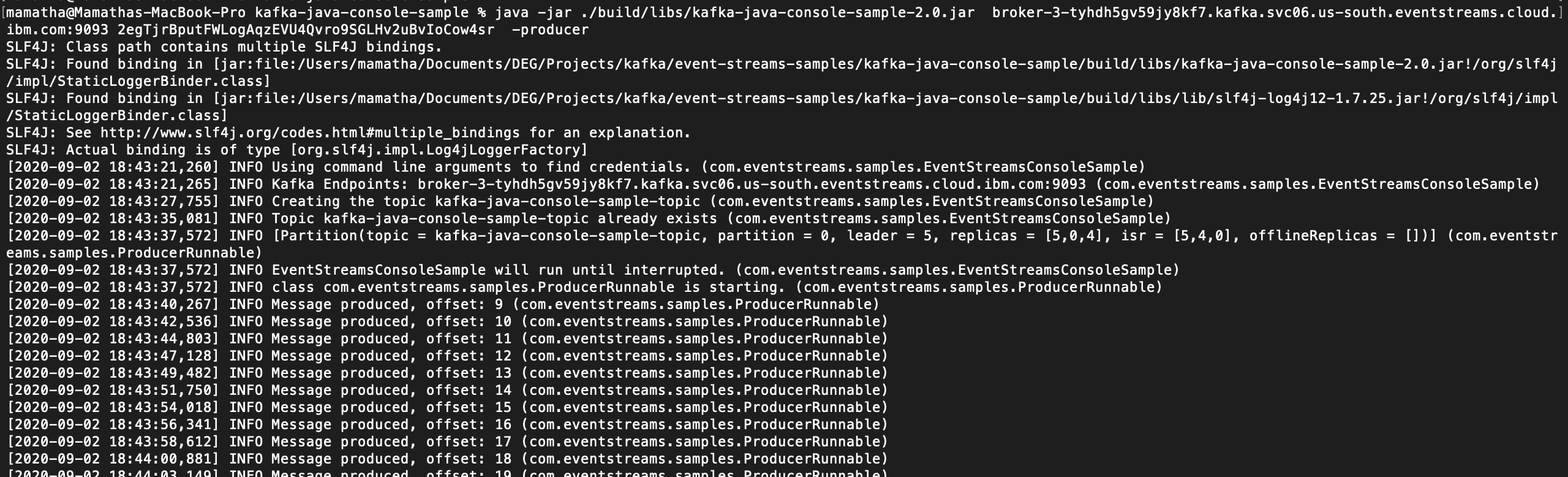
b. start the sample producing application from the command line:
`java -jar ./build/libs/kafka-java-console-sample-2.0.jar <kafka_brokers_sasl> <api_key> -producer`
The java -jar ./build/libs/kafka-java-console-sample-2.0.jar part of the command identifies the locations of the .JAR file to run within the cloned repository. You do not need to change this.
Use the kafka_brokers_sasl from the Service credentials created in Step 3.
The kafka_brokers_sasl must be formatted as "host:port,host2:port2". Format the contents of kafka_brokers_sasl in a text editor before entering it in the command line.
Use the api_key from the Service credentials created in Step 3. -producer specifies that the producer should start.
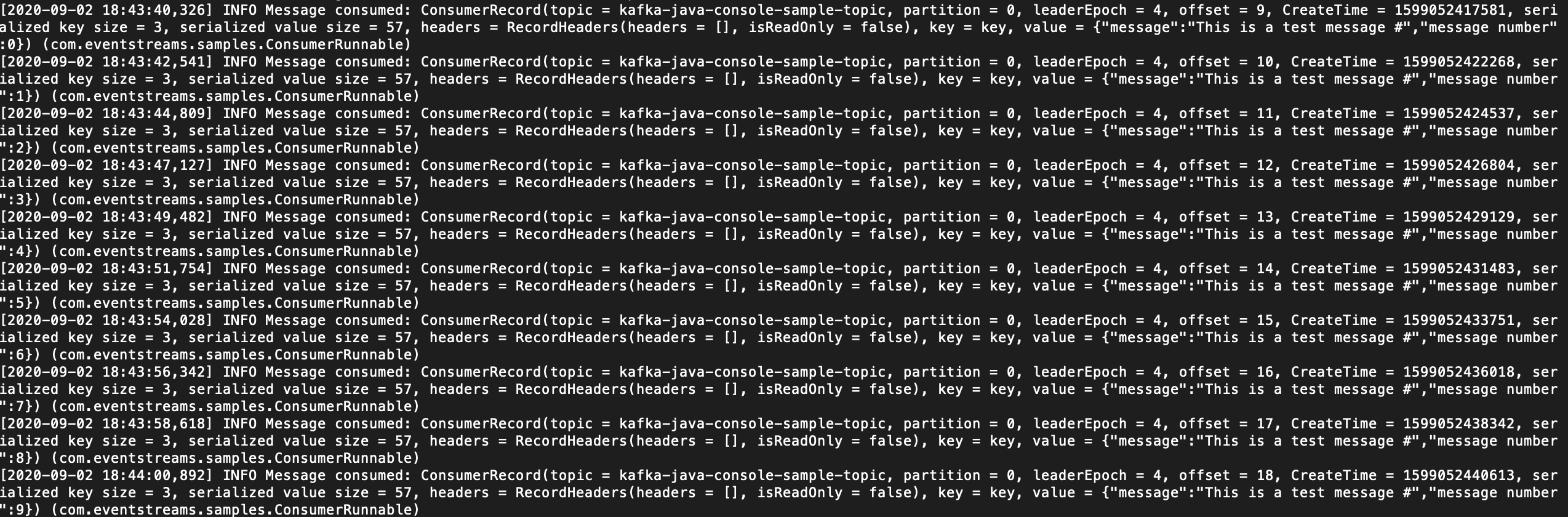
When the producer starts, messages are produced to the topic. Messages are then consumed from the topic by the consuming application. You can verify the successful flow of messages when you see:
INFO Message consumed on the consumer application.
The sample runs indefinitely until you stop it. To stop the process, run an exit command Ctrl+C