Natural Language Understanding Application 
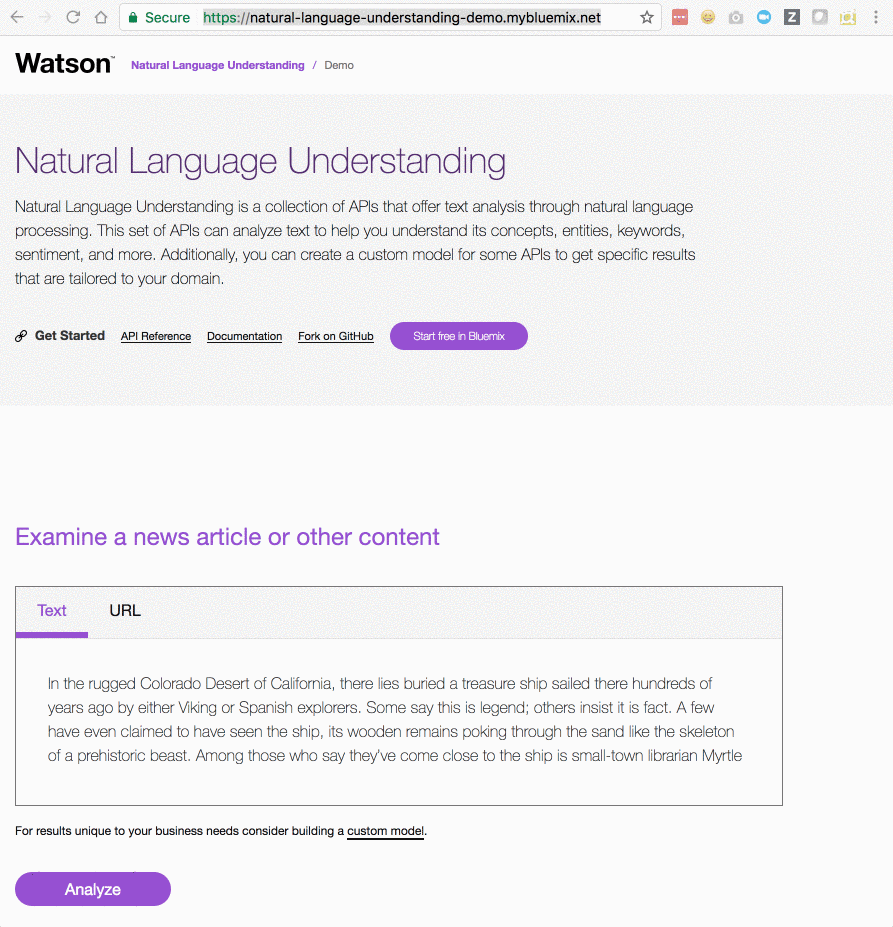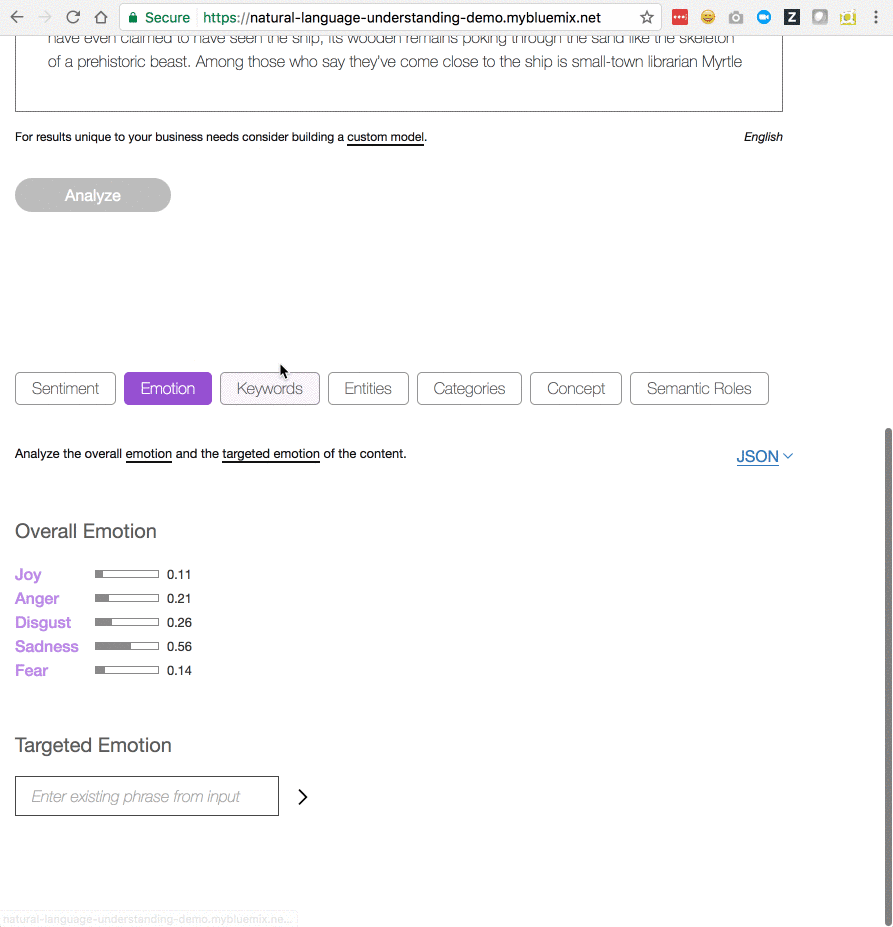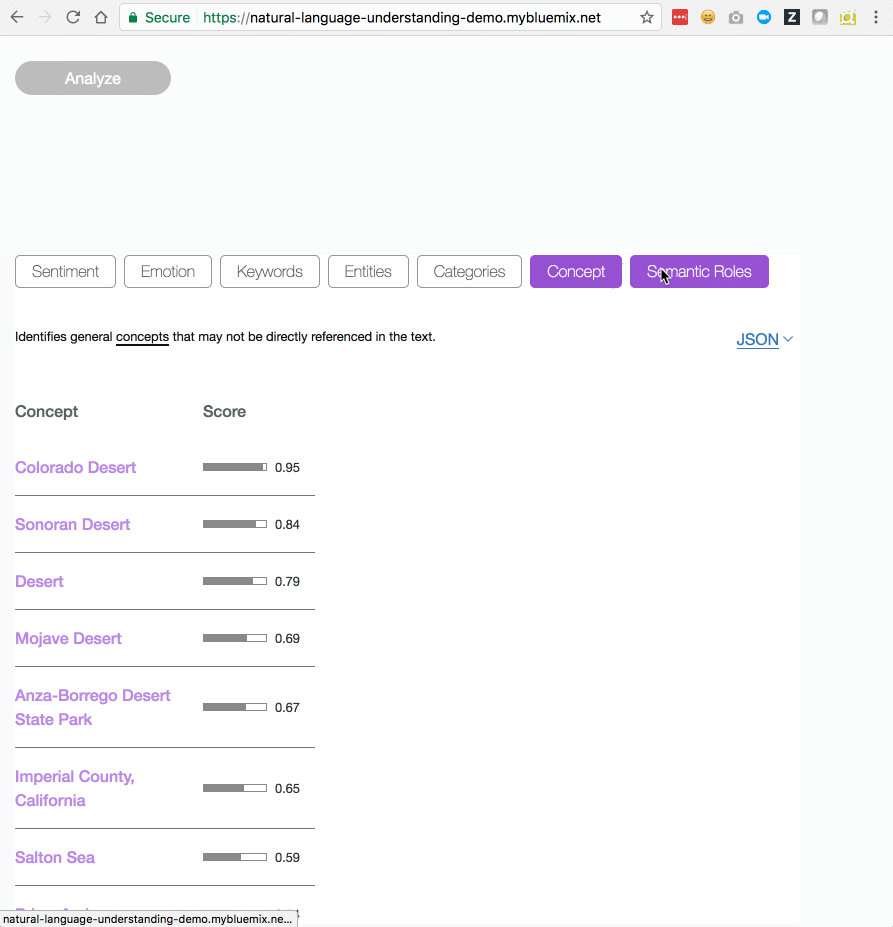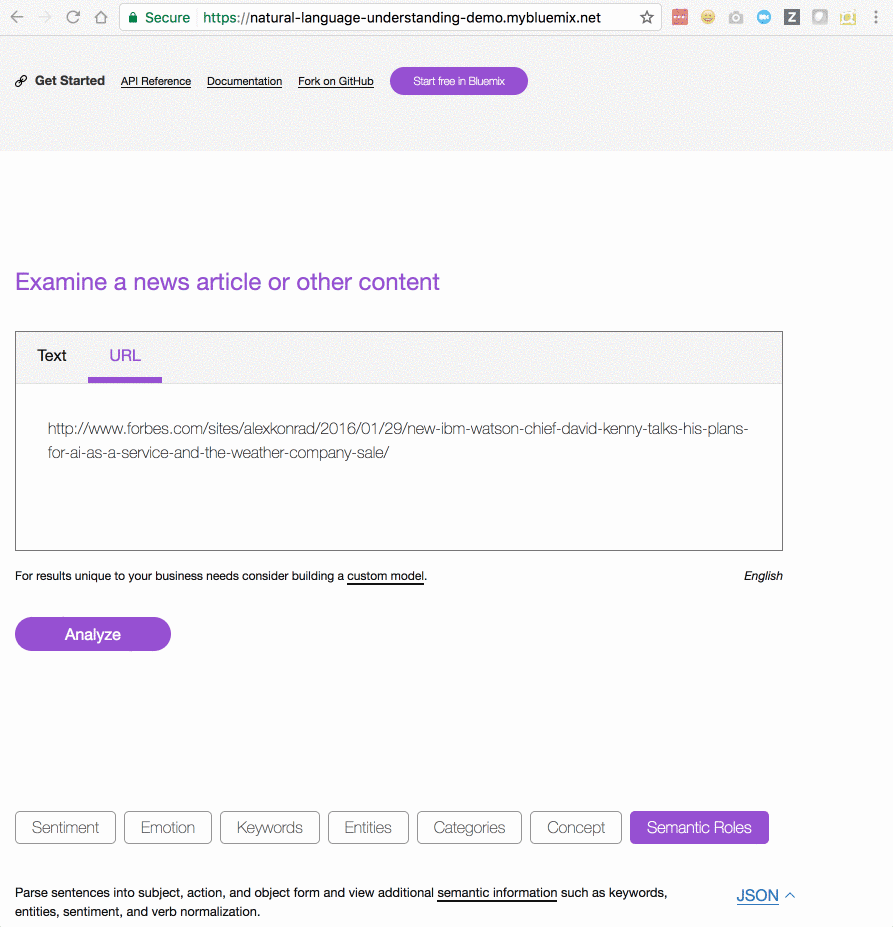
Natural Language Understanding is a collection of APIs that offer text analysis through natural language processing. This set of APIs can analyze text to help you understand its concepts, entities, keywords, sentiment, and more. Additionally, you can create a custom model for some APIs to get specific results that are tailored to your domain.
Getting started
-
You need a Bluemix account. If you don't have one, sign up.
-
Download and install the Cloud-foundry CLI tool if you haven't already.
-
Edit the
manifest.ymlfile and change<application-name>to something unique. The name you use determines the URL of your application. For example,<application-name>.mybluemix.net.
applications:
- services:
- my-service-instance
name: <application-name>
command: npm start
path: .
memory: 512M- Connect to Bluemix with the command line tool.
cf api https://api.ng.bluemix.net
cf login- Create and retrieve service keys to access the Natural Language Understanding service:
cf create-service natural-language-understanding free my-nlu-service
cf create-service-key my-nlu-service myKey
cf service-key my-nlu-service myKey
- Create a
.envfile in the root directory by copying the sample.env.examplefile using the following command:
cp .env.example .env
You will update the .env with the information you retrieved in steps 5.
The .env file will look something like the following:
NATURAL_LANGUAGE_UNDERSTANDING_USERNAME=<username>
NATURAL_LANGUAGE_UNDERSTANDING_PASSWORD=<password>
- Install the dependencies you application need:
npm install
- Start the application locally:
npm start
-
Point your browser to http://localhost:3000.
-
Optional: Push the application to Bluemix:
cf push
After completing the steps above, you are ready to test your application. Start a browser and enter the URL of your application.
<your application name>.mybluemix.net
For more details about developing applications that use Watson Developer Cloud services in Bluemix, see Getting started with Watson Developer Cloud and Bluemix.
Troubleshooting
-
The main source of troubleshooting and recovery information is the Bluemix log. To view the log, run the following command:
cf logs <application-name> --recent
-
For more details about the service, see the documentation for the Natural Language Understanding service.
Directory structure
.
├── app.js // express routes
├── config // express configuration
│ ├── express.js
│ └── security.js
├── manifest.yml
├── package.json
├── public // static resources
├── server.js // entry point
├── test // tests
└── views // react components
Running in Docker
You'll need to update the docker.env file to contain the username, password, and (optionally) the URL
for the NLU service.
$ docker build .
$ docker run -P --env-file docker.env <IMAGEID>License
This sample code is licensed under Apache 2.0.
Contributing
See CONTRIBUTING.
Open Source @ IBM
Find more open source projects on the IBM Github Page
Privacy Notice
Sample web applications that include this package may be configured to track deployments to IBM Bluemix and other Cloud Foundry platforms. The following information is sent to a Deployment Tracker service on each deployment:
- Node.js package version
- Node.js repository URL
- Application Name (
application_name) - Space ID (
space_id) - Application Version (
application_version) - Application URIs (
application_uris) - Labels of bound services
- Number of instances for each bound service and associated plan information
This data is collected from the package.json file in the sample application and the VCAP_APPLICATION and VCAP_SERVICES environment variables in IBM Bluemix and other Cloud Foundry platforms. This data is used by IBM to track metrics around deployments of sample applications to IBM Bluemix to measure the usefulness of our examples, so that we can continuously improve the content we offer to you. Only deployments of sample applications that include code to ping the Deployment Tracker service will be tracked.