Explain in short about all 7 layers of OSI
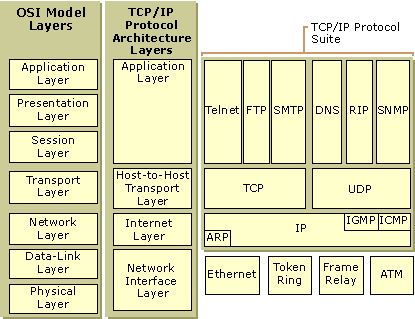
- Application layer = user interface and application
- Presentation layer = Data conversion and transformation
- session layer = keep data of diff. application seperately
- transport layer = end to end connectivity using port numbers.
- network layer = logical addressing like IP address.
- Data link layer = Physical addressing like MAC address.
- Physical layer = Physical transmission of data using 0's and 1's.
Answer :
- CLASS A = 1 to 126
- CLASS B = 128 to 191
- CLASS C = 192 to 223
- CLASS D = 224 to 239 (Multicasting)
- CLASS E = 240 to 255 (Research)
Answer : Pvt. IP are IPs which are not used in Internet or which are not routable in Internet. They are also called as non-routable IP's.
- Class A = 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
- Class B = 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
- Class C = 192.168.0.0. to 192.168.255.255
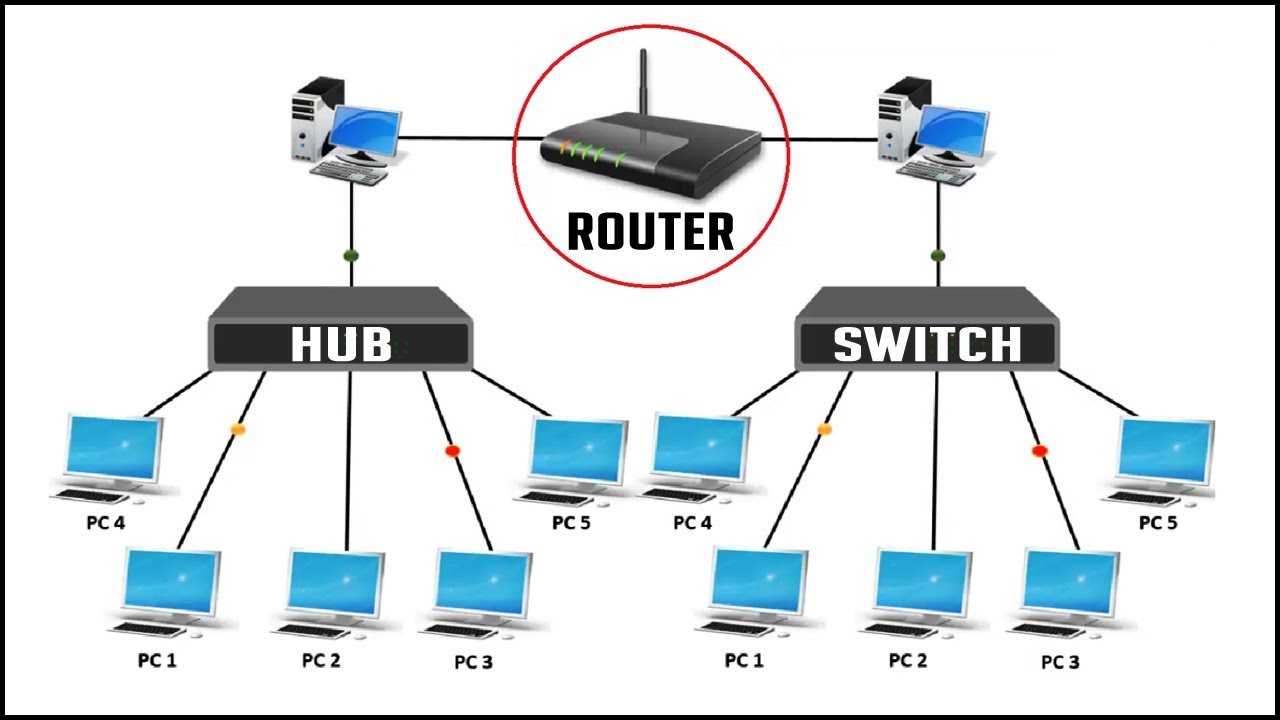
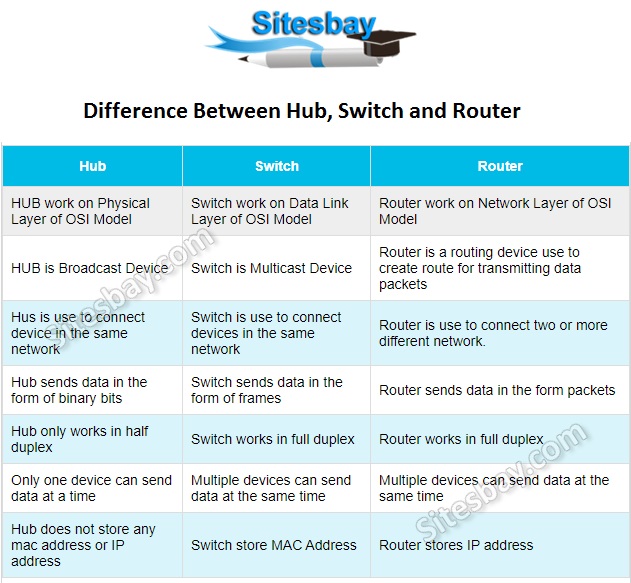
Answer : Router is a device or PC which is used to connect two or more IP networks.
Answer : Default gateway is the address of router.
Answer : Subnet mask is used to differentiate Network ID and Host ID from a given IP address. The default subnet mask are as under
- Class A = 255.0.0.0
- Class B = 255.255.0.0
- Class C = 255.255.255.0
Answer : The loopback address is 127.0.0.1. This address is used to check local TCP/IP suite or local machine.
Answer : Ping uses ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol)
Answer : Tracert is a to find path information between source and desitnation. It show no. of hops between source and desitination. Tracert also uses ICMP protocol.
Answer :
| TCP/IP | NetBEUI |
|---|---|
| industry standard | Microsoft propertiery |
| IP address | NO addressing |
| supports routing | Non routable |
| Large network | small network |
| more confiugration | no configuration |
Answer : Packet Internet Network Gopher
Answer : It is used to resolve FQDN to IP address.
Answer :
- Forward Lookup - it is used to resolve FQDN to IP
- Reverse lookup - it is used to resolve IP to FQDN
Primary Zone Secondary Zone AD integrated Zone Stub Zone
Answer : it is a tool used troubleshoot DNS related issues.
Answer: DHCP is used to automatically provide IP address to client computers.
- Discover = client sends request for IP.
- Offer = DHCP server send and Offer with IP address.
- Request = if clients accepts the IP it sends a request to DHCP.
- Ack = DHCP server sends ack for the same.
Answer : to reserve a specific IP for a specific machine or host.
Answer : DHCP uses UDP port number 67 and 68.
There are total 65536 ports available. Below are the list of some well-known ports.
- LDAP : 389
- Kerberos : 88
- DNS : 53
- SMTP : 25
- POP3 : 110
- Telnet : 23
- NNTP : 119
- IMAP : 143
- RPC : 135
- HTTP : 80
- HTTPS / SSL : 443
- FTP : 21
- SNMP : 161 and 162
Answer : SNMP stands for Simple Network Management Protocol). This protocol is used to monitor and manage network devices like Switches, Routers, Servers, etc. SNMP uses port UDP port number 161 and 162.
Answer : Component Object Model (COM) is Microsoft's object-oriented programming model that defines how objects interact within a single application or between applications.
Answer : It is a software used to provide security to your network by not allowing unauthorized access to your Internal network from External users. Eg : PIX firewall, Checkpoint firewall, etc.
Answer : SNTP (Simple network time protocol)
There are 7 OSI layers: 1) Physical Layer, 2) Data Link Layer, 3) Network Layer, 4) Transport Layer, 5) Session Layer, 6) Presentation Layer, and 7) Application Layer.
Data encapsulation is the process of breaking down information into smaller, manageable chunks before it is transmitted across the network. In this process that the source and destination addresses are attached to the headers, along with parity checks.

NAT is Network Address Translation. This is a protocol that provides a way for multiple computers on a common network to share a single connection to the Internet.
SLIP, or Serial Line Interface Protocol, is an old protocol developed during the early UNIX days. This is one of the protocols that are used for remote access.
Tracert is a Windows utility program that can use to trace the route taken by data from the router to the destination network. It also shows the number of hops taken during the entire transmission route.
DHCP is short for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. Its main task is to assign an IP address to devices across the network automatically. It first checks for the next available address not yet taken by any device, then assigns this to a network device.

TCP/IP is short for Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol. This is a set of protocol layers that is designed to make data exchange possible on different types of computer networks, also known as a heterogeneous network.
Routers have a built-in console that lets you configure different settings, like security and data logging. You can assign restrictions to computers, such as what resources it is allowed access or what particular time of the day, they can browse the Internet. You can even put restrictions on what websites are not viewable across the entire network.