- Overview
- Prerequisites
- Step One: Run k8s-docker.sh
- Step Two: Get kubectl
- Step Three: Enable addons
- Test it out
- Run an application
- Expose it as a service:
The following instructions show you how to set up a simple, single node kubernetes cluster using Docker. This differs from the official kubernetes docker instructions in that it supports the kube-ui and skydns addons.
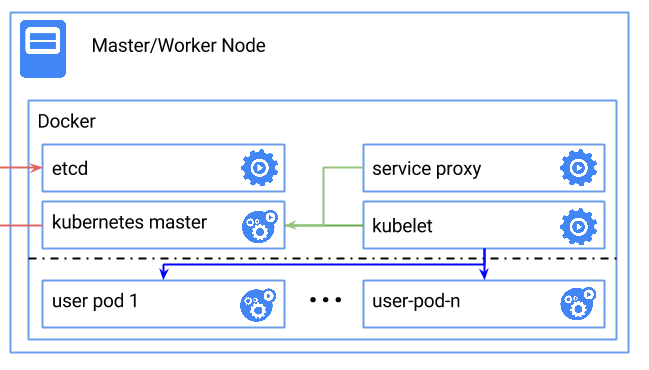
Here's a diagram of what the final result will look like:
- You need to have docker (and docker-compose) installed on one machine (either natively on linux, or via boot2docker).
- Modify
.envrcto suit your needs
source .envrc- You may want to change the variables in the top of the file first. Most users will not need to do this.
- This may take some time to complete.
docker-compose up -dNote: On OS/X you will need to set up port forwarding via ssh:
boot2docker ssh -L8080:localhost:8080At this point you should have a running kubernetes cluster. You can test this by downloading the kubectl binary (OS X) (linux)
- This enables kube-dashboard and skydns
- You may need to modify skydns-rc.yaml so that it has a correct master ip address on the line that looks like:
- -kube-master-url=http://172.17.42.1:8080
kubectl create --namespace=kube-system -f dashboard-controller.yaml
kubectl create --namespace=kube-system -f dashboard-service.yaml
kubectl create --namespace=kube-system -f skydns-rc.yaml
kubectl create --namespace=kube-system -f skydns-svc.yamlYou can test out dns by doing the following:
kubectl create -f busybox.yaml
kubectl exec busybox -- nslookup kubernetesWhich should print:
Server: 10.0.0.10
Address 1: 10.0.0.10
Name: kubernetes
Address 1: 10.0.0.1
You can get to kube-dashboard at http://localhost:8080/ui.
List the nodes in your cluster by running::
kubectl get nodesThis should print:
NAME LABELS STATUS
127.0.0.1 kubernetes.io/hostname=127.0.0.1 Ready
If you are running different kubernetes clusters, you may need to specify -s http://localhost:8080 to select the local cluster.
kubectl -s http://localhost:8080 run-container nginx --image=nginx --port=80now run docker ps you should see nginx running. You may need to wait a few minutes for the image to get pulled.
kubectl expose rc nginx --port=80This should print:
NAME LABELS SELECTOR IP PORT(S)
nginx <none> run=nginx <ip-addr> 80/TCP
Hit the webserver:
curl <insert-ip-from-above-here>Note that you will need run this curl command on your boot2docker VM if you are running on OS X.