Piers York
This package acts as an interface to Our World in Data datasets, allowing for an easy way to search through data used in over 3,000 charts and load them into the R environment.
Warning: Package has recently been updated to remove
owid_get_datasets() and change how the syntax works. It’s now simpler
to use but not backwards compatible.
devtools::install_github("piersyork/owidR")The main function in owidR is owid(), which takes a chart id and
returns a tibble (dataframe) of the corresponding OWID dataset. To
search for chart ids you can use owid_search() to list all the chart
ids that match a keyword or regular expression.
Lets use the core functions to get data on how human rights have changed over time. First by searching for charts on human rights.
library(owidR)
owid_search("human rights")
## titles
## [1,] "Human Rights Score vs. Political regime type"
## [2,] "Political regime type vs. Human Rights Score"
## [3,] "Countries with National Human Rights Institutions in compliance with the Paris Principles"
## [4,] "Human Rights Score vs. GDP per capita"
## [5,] "Human Rights Scores"
## [6,] "Human Rights Violations"
## [7,] "Proportion of countries that applied for accreditation as independent National Human Rights Institutions in compliance with Paris Principles"
## chart_id
## [1,] "human-rights-score-vs-political-regime-type"
## [2,] "political-regime-type-vs-human-rights-score"
## [3,] "countries-in-compliance-with-paris-principles"
## [4,] "human-rights-score-vs-gdp-per-capita"
## [5,] "human-rights-scores"
## [6,] "human-rights-violations"
## [7,] "countries-that-applied-for-accreditation-in-paris-principles"Let’s use the human rights scores dataset.
rights <- owid("human-rights-scores")
rights
## # A tibble: 11,717 × 4
## entity code year `Human Rights Score (Schnakenberg & Fariss, 2014; Fa…
## * <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl>
## 1 Afghanistan AFG 1946 0.690
## 2 Afghanistan AFG 1947 0.740
## 3 Afghanistan AFG 1948 0.787
## 4 Afghanistan AFG 1949 0.817
## 5 Afghanistan AFG 1950 0.851
## 6 Afghanistan AFG 1951 0.909
## 7 Afghanistan AFG 1952 0.938
## 8 Afghanistan AFG 1953 0.988
## 9 Afghanistan AFG 1954 1.01
## 10 Afghanistan AFG 1955 1.01
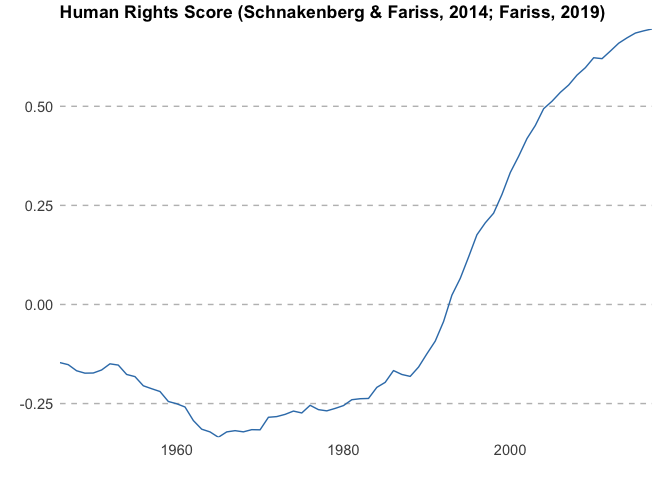
## # … with 11,707 more rowsowid_plot() makes it easy to visualise an owid dataset, plotting the
first value column of an owid dataset. By default the mean score across
all countries is plotted.
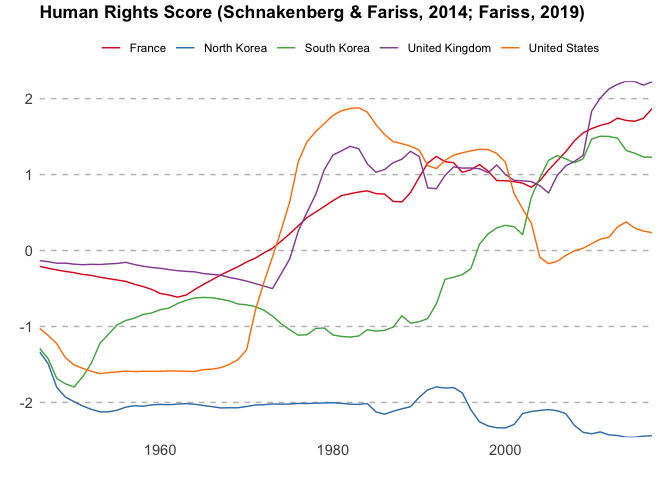
owid_plot(rights)Use summarise = FALSE to show individual countries instead of the mean
score. Unless a vector of entities is specified using the filter
argument 9 random entities will be plotted. If the data is not a
time-series then a bar chart of the entities values will be plotted.
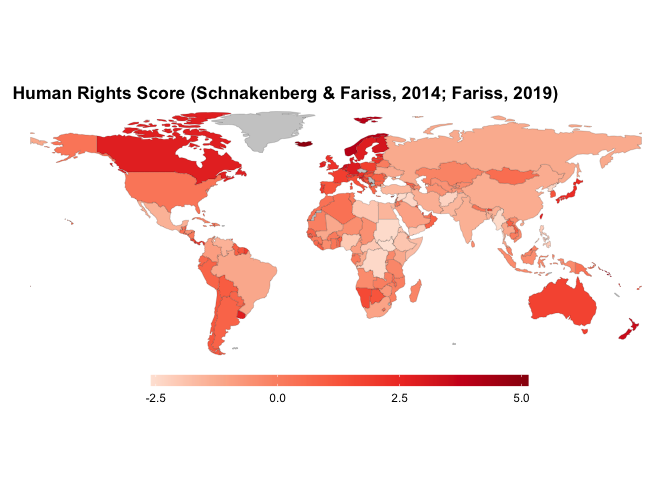
owid_plot(rights, summarise = FALSE, filter = c("North Korea", "South Korea", "France", "United Kingdom", "United States"))owid_map() makes it easy to create a choropleth world map of datasets
that contain country level data. The Entities of the owid data must be
country names. Currently the function plots data for the most recent
year.
owid_map(rights)owid_grapher() creates graphs in the style of Our World in Data. The
output of owid_grapher() can be piped into grapher_line() to add a
line graph, into grapher_map() to add a world map, and into
grapher_labels() to add labels to the graph. The graph is shown in the
RStudio viewer, or when called in an RMarkdown html document is
displayed within the document. Currently this isn’t implemented as an
htmlwidget and requires an internet connection to function.
rights %>%
owid_grapher(x = year, y = `Human Rights Score (Schnakenberg & Fariss, 2014; Fariss, 2019)`,
entity = entity) %>%
grapher_line(selected = c("North Korea", "South Korea", "France", "United Kingdom", "United States")) %>%
grapher_map(palette = "RdYlGn", bins = c(-2, 0, 2, 4)) %>%
grapher_labels(title = "Human Rights Scores",
subtitle = "Values range from around -3.8 to around 5.4 (the higher the better)",
source = "Our World in Data; Schnakenberg and Fariss (2014); Fariss (2019)")