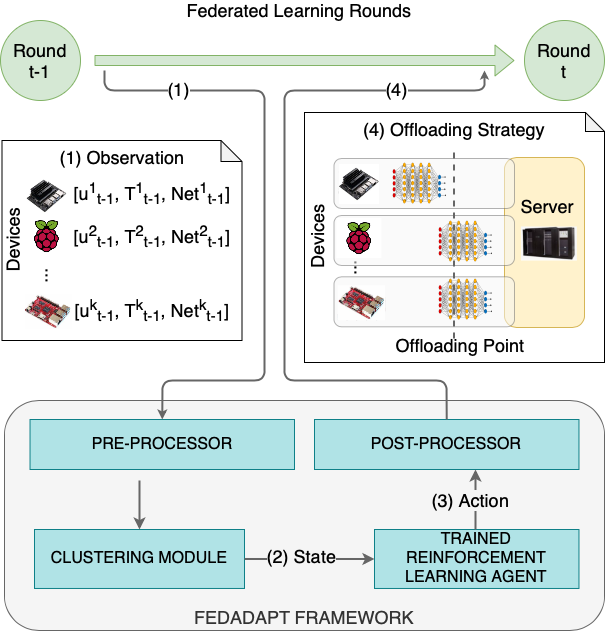
FedAdapt is a holistic framework for an IoT-edge environment that surmounts the challenges of accelerating federated learning on resource constrained devices, reducing the impact of stragglers arising from computational heterogeneity of IoT devices and adapting to varying network bandwidth between devices and an edge server.
FedAdapt was developed at the Edge Computing Hub.
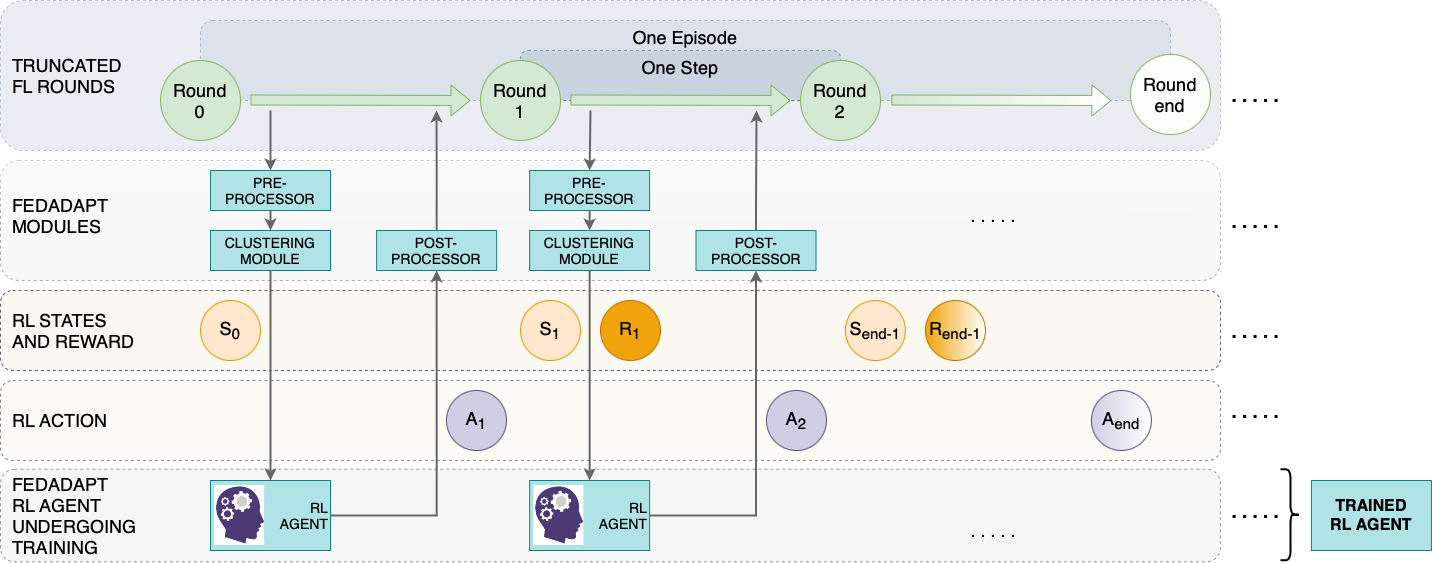
To accelerate the training process of federated learning, FedAdapt is underpinned by an offloading technique in which the layers of a Deep Neural Network (DNN) model can be offloaded from the device to an edge server to alleviate the computational burden of training on the device. To reduce the impact of stragglers, FedAdapt incorporates a reinforcement learning approach to automatically identify the layers that need to be offloaded from the device to the edge. FedAdapt further optimizes the reinforcement learning approach to develop different offloading strategies for each device while accounting for changing network bandwidth. A clustering technique is implemented to rapidly generate the offloading strategy.
More information on the states, observations, rewards, actions, offloading strategy, and the FedAdapt modules are presented in the research article entitled, "FedAdapt: Adaptive Offloading for IoT Devices in Federated Learning".
The repository contains the source code of FedAdapt. The code is organised as:
- Federated learning training code using FedAdapt in
FL_trainingfolder. - Reinforcement learning training code for FedAdapt agent in
RL_trainingfolder.
The results are saved as pickle files in the results folder.
All configuration options are given in config.py , which contains the architecture, model, FL training hyperparameters and RL training hyperparameters.
Currently, CIFAR10 dataset and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) models are supported. The code can be extended to support other datasets and models.
The code is tested on Python 3 with Pytorch version 1.4 and torchvision 0.5. In order to test the code, install Pytorch and torchvision on each IoT device (Raspberry Pi and Jetson). The simplest way is to install from pre-built PyTorch and torchvision pip wheel. Please download respective pip wheel as follows:
- Pyotrch: https://github.com/FedML-AI/FedML-IoT/tree/master/pytorch-pkg-on-rpi
- Jetson: https://forums.developer.nvidia.com/t/pytorch-for-jetson-version-1-8-0-now-available/72048
Then, modify the respective hostname and ip address in config.py. CLIENTS_CONFIG and CLIENTS_LIST in config.py are used for indexing and sorting.
# Network configration
SERVER_ADDR= '192.168.0.10'
SERVER_PORT = 51000
K = 5 # Number of devices
G = 3 # Number of groups
# Unique clients order
HOST2IP = {'pi41':'192.168.0.14' , 'pi42':'192.168.0.15', 'jetson-desktop':'192.168.0.25' , 'pi31':'192.168.0.26', 'pi32':'192.168.0.29'}
CLIENTS_CONFIG= {'192.168.0.14':0, '192.168.0.15':1, '192.168.0.25':2, '192.168.0.26':3, '192.168.0.29':4}
CLIENTS_LIST= ['192.168.0.14', '192.168.0.15', '192.168.0.25', '192.168.0.26', '192.168.0.29']
Finally, download the CIFAR10 datasets manually and put them into the datasets/CIFAR10 folder (python version).
To test the code:
- Run FL training using FedAdapt: please follow instructions in
FL_trainingfolder. - Run RL training for FedAdapt agent: please follow instructions in
RL_trainingfolder.
Please cite the paper as follows: Di Wu, Rehmat Ullah, Paul Harvey, Peter Kilpatrick, Ivor Spence and Blesson Varghese, "FedAdapt: Adaptive Offloading for IoT Devices in Federated Learning," 2021.
@misc{wu2021fedadapt,
title={FedAdapt: Adaptive Offloading for IoT Devices in Federated Learning},
author={Di Wu and Rehmat Ullah and Paul Harvey and Peter Kilpatrick and Ivor Spence and Blesson Varghese},
year={2021},
eprint={2107.04271},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.DC}
}