Fast low memory consuming mathematical evaluation without endless string parsing! Parses string formula once and uses its object sequence in each evaluation. Moreover provides user defined functions and variables.



Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection


- Features
- Performance
- Quick start
- Extra types
- Variables
- Operators
- Boolean operators
- Functions
- Options
- Documentation
- Thanks for contribution

- TODO
- Fast math evaluation
- Zero-allocation code (object pooling)
- User defined functions
- User defined variables with any chars
- Mixed result type
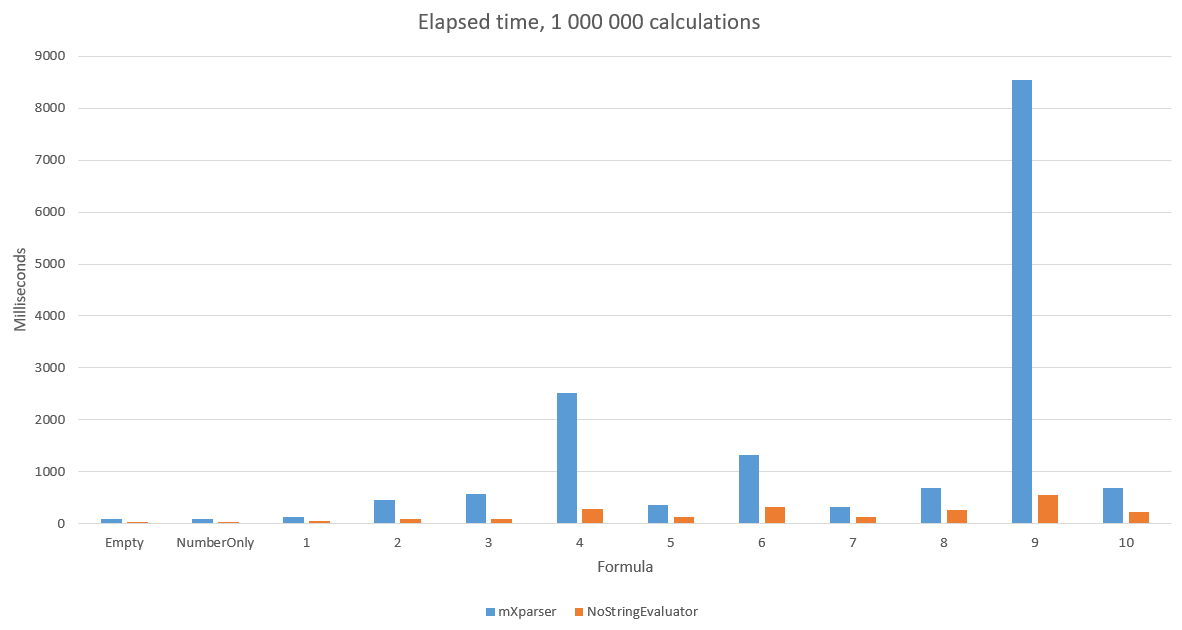
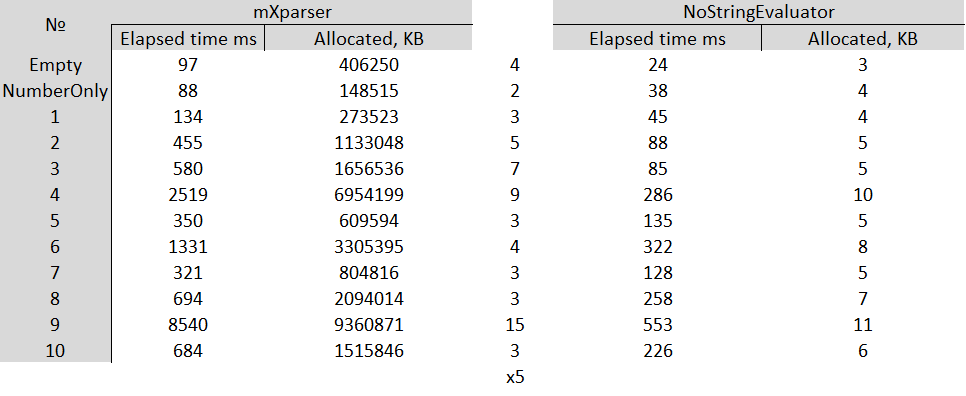
Compared with a good solution mXparser
- In general, x5 faster!
| № | Formula |
|---|---|
| Empty | |
| NumberOnly | 3 |
| 1 | 3 * 9 |
| 2 | 3 * 9 / 456 * 32 + 12 / 17 - 3 |
| 3 | 3 * (9 / 456 * (32 + 12)) / 17 - 3 |
| 4 | (2 + 6 - (13 * 24 + 5 / (123 - 364 + 23))) - (2 + 6 - (13 * 24 + 5 / (123 - 364 + 23))) + (2 + 6 - (13 * 24 + 5 / (123 - 364 + 23))) * 345 * ((897 - 323)/ 23) |
| 5 | Arg1 * Arg2 + Arg3 - Arg4 |
| 6 | Arg1 * (Arg2 + Arg3) - Arg4 / (Arg5 - Arg6) + 45 * Arg7 + ((Arg8 * 56 + (12 + Arg9))) - Arg10 |
| 7 | add(1; 2; 3) |
| 8 | add(add(5; 1) - add(5; 2; 3)) |
| 9 | if(Arg1 > 0; add(56 + 9 / 12 * 123.596; or(78; 9; 5; 2; 4; 5; 8; 7); 45;5); 9) * 24 + 52 -33 |
| 10 | kov(1; 2; 3) - kovt(8; 9) |
As you can see this solution is faster in all cases, furthermore there isn't any garbage collection.
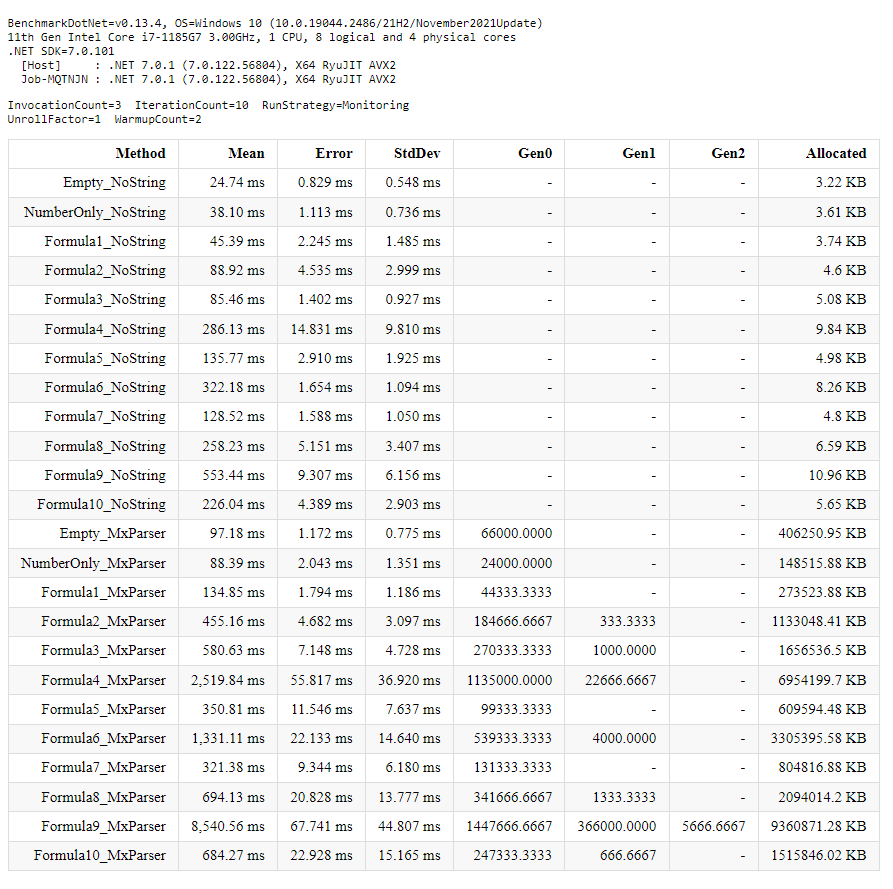
Benchmark code - ConsoleApp/Benchmark/BenchmarkNumberService.cs
Benchmark excel - BenchResults/Benchmark.xlsx
There are two ways to use evaluator:
- Static initialization
public void SomeMethod()
{
var facade = NoStringEvaluator.CreateFacade();
var evaluator = facade.Evaluator;
}- DI from the package
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
// ......
services.AddNoStringEvaluator();
}Add INoStringEvaluator to your controller, service, etc...
And just send string or FormulaNodes to evaluation:
public class MyService
{
private INoStringEvaluator _noStringEvaluator;
public MyService(INoStringEvaluator noStringEvaluator)
{
_noStringEvaluator = noStringEvaluator;
}
public double CalcNumber(string formula)
{
return _noStringEvaluator.CalcNumber(formula);
}
public string CalcWord(string formula)
{
return _noStringEvaluator.CalcWord(formula);
}
public EvaluatorValue Calc(string formula)
{
return _noStringEvaluator.Calc(formula);
}
}If you have variables, you can send IDictionary or your IVariablesContainer implementation:
public class MyService
{
private INoStringEvaluator _noStringEvaluator;
public MyService(INoStringEvaluator noStringEvaluator)
{
_noStringEvaluator = noStringEvaluator;
}
public double Calc(string formula, IDictionary<string, EvaluatorValue> variables)
{
return _noStringEvaluator.CalcNumber(formula, variables);
}
}If you need your function, just implement the interface IFunction If you want to returnt extra type, use factory.
As an argument's separator can be:
- ;
- ,
For instance, usage function "YouAre('Vitaly'; 26)":
public class MyFunction : IFunction
{
public string Name { get; } = "YouAre";
public bool CanHandleNullArguments { get; }
public InternalEvaluatorValue Execute(List<InternalEvaluatorValue> args, ValueFactory factory)
{
var name = args[0].Word;
var age = args[1];
var ageAfterDecade = age + 10;
var result = $"Hello, {name}. After 10 years you will be {ageAfterDecade} y.o.";
return factory.Word.Create(result);
}
}And don't forget to initialize your functions via options or directly in IFunctionReader
public void SomeMethod()
{
// NoStringEvaluator.CreateFacade(opt => opt.WithFunctionsFrom(<type from source assembly>));
// NoStringEvaluator.CreateFacade(opt => opt.WithFunctionsFrom(<source assembly>));
// NoStringEvaluator.CreateFacade(opt => opt.WithFunctions(new MyFunction()));
// same with DI
// services.AddNoStringEvaluator(opt => opt.WithFunctions(new MyFunction()));
}Apart from double calculations you can work with types:
- Boolean
- DateTime
- String
- List of string
- List of double
- Null
- Object
Object is a special type to allow using, for example, services inside function.
public void Should_Evaluate_Service()
{
// arrange
var service = _serviceFactory(null);
var args = new Dictionary<string, EvaluatorValue>
{
["myService"] = new EvaluatorValue(new MyService()),
["myNum"] = 10
};
var expected = 50.5;
// act
var actual = service.CalcNumber("TestService(myService; myNum)", args);
// assert
actual.Should().BeApproximatelyNumber(expected);
}
private class ServiceFunction : IFunction
{
public string Name { get; } = "TestService";
public bool CanHandleNullArguments { get; }
public InternalEvaluatorValue Execute(List<InternalEvaluatorValue> args, ValueFactory factory)
{
return args[0].GetObject<MyService>().GetTemperature() + args[1];
}
}
private class MyService
{
public double GetTemperature()
{
return 40.5;
}
}You can describe a list inside the formula
| Example | Result |
|---|---|
| IsMember({'printer', 'computer', 'monitor'}; 'computer') | 1 |
| Unique({'NEW','OLD','NEW','HEAVEN','OLD'}) | {'NEW','OLD','HEAVEN'} |
| Add({1, 2, 3, 10, 3}) | 19 |
You can use two types of variables:
- Simple variable
- Bordered variable
Simple variable means that it named without unique symbols and starts with a letter. Only one extra symbol is possible, it's "_"
Some examples:
- "25 + myArgument - 1"
- "25 + myArg1 - 2"
- "arg5684argArg_arg"
- "25 + myArgument_newAge - 3"
Bordered variable means that it has a tricky name with any symbols, except for square brackets.
Some examples:
- "25 + [myVariable and some words] - 1"
- "25 + [Provider("my provider").Month(1).Price] - 2"
- "[myVariable ♥]"
- "[simpleVariable]"
Needless to say, you can write simple variable with brackets as well.
There are some known variables, you shouldn't send them to Calc method.
| Key word | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| pi | Pi, Archimedes' constant or Ludolph's number | 3.14159265358979323846 |
| tau | A circle constant equal to 2π | 6.283185307179586476925 |
| e | Napier's constant, or Euler's number, base of Natural logarithm | 2.7182818284590452354 |
| true | Boolean True | True |
| false | Boolean False | False |
| ASC | Boolean True | True |
| DESC | Boolean False | False |
These variables are register independent, you can write Pi, [PI], pI, True, etc...
| Key word | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | a + b |
| - | Subtraction | a - b |
| * | Multiplication | a * b |
| / | Division | a / b |
| ^ | Exponentiation | a^b |
| Key word | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| < | Lower than | a < b |
| <= | Lower or equal | a <= b |
| > | Greater than | a > b |
| >= | Greater or equal | a >= b |
| == | Equality | a == b |
| = | Equality | a = b |
| != | Inequation | a != b |
| <> | Inequation | a <> b |
| && | Logical conjunction (AND) | a && b |
| || | Logical disjunction (OR) | a || b |
| ! | Negation | !IsNull(a) |
| Key word | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| add | Summation operator | add(a1; a2; ...; an) can include List |
| multi | Multiplication | multi(a1; a2; ...; an) can include List |
| mean | Mean / average value | mean(a1; a2; ...; an) can include List |
| min | Minimum function | min(a; b) can include List |
| max | Maximum function | max(a; b) can include List |
| Rpund | Rounds the designated number to the specified decimals | Round(a; decimals) |
| ln | Natural logarithm function (base e) | ln(x) |
| log | Logarithm function (base b) | log(a; b) |
| log2 | Binary logarithm function (base 2) | log2(x) |
| log10 | Common logarithm function (base 10) | log10(x) |
| sqrt | Squre root function | sqrt(x) |
| abs | Absolut value function | abs(x) |
| sgn | Signum function | sgn(x) |
| sign | Signum function | sign(x) |
| floor | Floor function | floor(x) |
| ceil | Ceiling function | ceil(x) |
| mod | Modulo function | mod(a; b) |
| fact | Factorial function | fact(x) |
| fib | Fibonacci number | fib(x) |
| gcd | Greatest common divisor | gcd(a1; a2; ...; an) |
| lcm | Least common multiple | lcm(a1; a2; ...; an) |
| Key word | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| sin | Trigonometric sine function | sin(x) |
| cos | Trigonometric cosine function | cos(x) |
| tg | Trigonometric tangent function | tg(x) |
| tan | Trigonometric tangent function | tan(x) |
| ctg | Trigonometric cotangent function | ctg(x) |
| cot | Trigonometric cotangent function | cot(x) |
| ctan | Trigonometric cotangent function | ctan(x) |
| sec | Trigonometric secant function | sec(x) |
| csc | Trigonometric cosecant function | csc(x) |
| cosec | Trigonometric cosecant function | cosec(x) |
| asin | Inverse trigonometric sine function | asin(x) |
| arsin | Inverse trigonometric sine function | arsin(x) |
| arcsin | Inverse trigonometric sine function | arcsin(x) |
| acos | Inverse trigonometric cosine function | acos(x) |
| arcos | Inverse trigonometric cosine function | arcos(x) |
| arccos | Inverse trigonometric cosine function | arccos(x) |
| atg | Inverse trigonometric tangent function | atg(x) |
| atan | Inverse trigonometric tangent function | atan(x) |
| arctg | Inverse trigonometric tangent function | arctg(x) |
| arctan | Inverse trigonometric tangent function | arctan(x) |
| actg | Inverse trigonometric cotangent function | actg(x) |
| acot | Inverse trigonometric cotangent function | acot(x) |
| actan | Inverse trigonometric cotangent function | actan(x) |
| arcctg | Inverse trigonometric cotangent function | arcctg(x) |
| arccot | Inverse trigonometric cotangent function | arccot(x) |
| arcctan | Inverse trigonometric cotangent function | arcctan(x) |
| sinh | Hyperbolic sine function | sinh(x) |
| cosh | Hyperbolic cosine function | cosh(x) |
| tgh | Hyperbolic tangent function | tgh(x) |
| tanh | Hyperbolic tangent function | tanh(x) |
| coth | Hyperbolic cotangent function | coth(x) |
| ctgh | Hyperbolic cotangent function | ctgh(x) |
| ctanh | Hyperbolic cotangent function | ctanh(x) |
| sech | Hyperbolic secant function | sech(x) |
| csch | Hyperbolic cosecant function | csch(x) |
| cosech | Hyperbolic cosecant function | cosech(x) |
| arcsec | Inverse trigonometric secant | arcsec(x) |
| asinh | Inverse hyperbolic sine function | asinh(x) |
| arsinh | Inverse hyperbolic sine function | arsinh(x) |
| arcsinh | Inverse hyperbolic sine function | arcsinh(x) |
| acosh | Inverse hyperbolic cosine function | acosh(x) |
| arcosh | Inverse hyperbolic cosine function | arcosh(x) |
| arccosh | Inverse hyperbolic cosine function | arccosh(x) |
| atgh | Inverse hyperbolic tangent function | atgh(x) |
| atanh | Inverse hyperbolic tangent function | atanh(x) |
| arctgh | Inverse hyperbolic tangent function | arctgh(x) |
| arctanh | Inverse hyperbolic tangent function | arctanh(x) |
| acoth | Inverse hyperbolic cotangent function | acoth(x) |
| actgh | Inverse hyperbolic cotangent function | actgh(x) |
| actanh | Inverse hyperbolic cotangent function | actanh(x) |
| arccoth | Inverse hyperbolic cotangent function | arccoth(x) |
| arcctgh | Inverse hyperbolic cotangent function | arcctgh(x) |
| arcctanh | Inverse hyperbolic cotangent function | arcctanh(x) |
| asech | Inverse hyperbolic secant function | asech(x) |
| arsech | Inverse hyperbolic secant function | arsech(x) |
| arcsech | Inverse hyperbolic secant function | arcsech(x) |
| acsch | Inverse hyperbolic cosecant function | acsch(x) |
| arcsch | Inverse hyperbolic cosecant function | arcsch(x) |
| arccsch | Inverse hyperbolic cosecant function | arccsch(x) |
| acosech | Inverse hyperbolic cosecant function | acosech(x) |
| arcosech | Inverse hyperbolic cosecant function | arcosech(x) |
| rad | Degrees to radians function | rad(x) |
| deg | Radians to degrees function | deg(x) |
| exp | Exponential function | exp(x) |
| Key word | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| if | If function | if(cond; expr-if-true; expr-if-false) |
| iff | If function | iff( cond-1; expr-1; ... ; cond-n; expr-n ) |
| and | Logical conjunction (AND) | and(a1; a2; ...; an) |
| or | Logical disjunction (OR) | or(a1; a2; ...; an) |
| not | Negation function | not(x) |
| IsNaN | Returns true if value is a Not-a-Number (NaN) | isNaN(x) |
| IsError | Returns true if this is a double.NaN | IsError(ToNumber('Text')) |
| IsMember | Checks if second argument is a member of list from first | IsMember({'printer', 'computer', 'monitor'}; 'computer') |
| IsNumber | Returns true if this is a number | IsNumber(256) |
I've implemented some of excel functions. If you wanna see more, just send me a message.
| Key word | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Count | Returns a number of elements | Count(a; b; ...) can include List |
| Len | Returns the number of characters in a text string | Len("my word") |
| Sort | Sorts a List. sortType: true - asc, false - desc | Sort(myList; sortType) |
| ToNumber | Returns number from word | ToNumber('03') |
| Key word | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| DateDif | Calculates the number of days, months, or years between two dates. Can be: Y, M, D | DateDif(date1; date2; 'Y') |
| TimeDif | Calculates the number of hours, minutes, or seconds between two dates. Can be: H, M, S | DateDif(time1; time2; 'H') |
| Now | Returns Datetime.Now | Now() |
| Today | Returns the current date | Today() |
| Day | Returns a day from dateTime | Day(Now()) Day(Now(); 'DD') |
| Month | Returns a month from dateTime | Month(Now()) Month(Now(); 'MM') |
| Year | Returns a year from dateTime | Year(Now()) Year(Now(); 'YY') |
| ToDateTime | Returns datetime value from string | ToDateTime('8/15/2002') |
| WeekDay | Takes a date and returns a number between 1-7 representing the day of week | WeekDay(Today()) |
| DateFormat | Format dateTime to string | DateFormat(Now(); 'HH:mm:ss') |
| AddHours | Adds a number of hours to a datetime | AddHours(date; 17) |
| AddMinutes | Adds a number of minutes to a datetime | AddMinutes(date; 17) |
| AddSeconds | Adds a number of seconds to a datetime | AddSeconds(date; 17) |
| Key word | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Concat | Concates values | Concat(56; ' myWord') Concat(myList; myArg; 45; myList2) |
| Explode | Returns a text list composed of the elements of a text string. Separator by default is white space " " | Explode(myWord) Explode(myWord; separator) |
| Implode | Concatenates all members of a text list and returns a text string. separator by default is empty "" | Implode(myList) Implode(myList; separator) Implode(myList; 5; 'my wordd'; separator) last value is separator |
| Left | Searches a string from left to right and returns the leftmost characters of the string | Left(myWord) Left(myWord; numberOfChars) Left(myWord; wordNeededChars) |
| Middle | Returns any substring from the middle of a string | Middle(myWord; indexStart; numberChars) Middle(myWord; indexStart; wordEnd) Middle(myWord; wordStart; numberChars) Middle(myWord; wordStart; wordEnd) |
| Right | Searches a string from right to left and returns the rightmost characters of the string | Right(myWord) Right(myWord; numberOfChars) Right(myWord; wordNeededChars) |
| Lower | Converts text to lowercase | Lower(myWord) Lower(myWordList) |
| Upper | Converts text to uppercase | Upper(myWord) Upper(myWordList) |
| Proper | Capitalizes the first letter in each word of a text | Proper(myWord) |
| Replace | Replaces characters within text | Replace(myWord; oldPart; newPart) Replace(myList; oldPart; newPart) |
| Text | Returns text from first argument | Text(26) |
| Unique | If second parameter is true then returns only unique If second parameter is false then returns list without doubles | Unique(myList) Unique(myList; true) |
| IsText | Returns true if this is a word | IsText('my word') |
| Key word | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| IfNull | Returns second argument if the first is null | IfNull(x,3) |
| NullIf | Returns null if the first argument is equal to the second | NullIf(x,3) |
| IsNull | Returns null if the first argument null | IsNull(x) |
When you use AddNoStringEvaluator or CreateFacade you can configure evaluator.
To illustrate, I change floating point from default dot to comma:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
// ......
services.AddNoStringEvaluator(opt => opt.SetFloatingPointSymbol(FloatingPointSymbol.Comma));
}| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| FormulaNodes Parse(string formula) | Return parsed formula nodes |
| FormulaNodes Parse(ReadOnlySpan formula) | Return parsed formula nodes |
| List ParseWithoutRpn(ReadOnlySpan formula) | Return parsed formula nodes without RPN |
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| void AddFunction(IFunction func, bool replace = false) | Add function |
| void RemoveFunction(string functionName) | Remove function |
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| FormulaNodes GetFormulaNodes(string formula) | Return cached formula nodes |
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| CheckFormulaResult CheckSyntax(string formula) | Check syntax |
| CheckFormulaResult CheckSyntax(ReadOnlySpan formula) | Check syntax |
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| IVariable AddOrUpdate(string name, double value) | Add or update variable |
| EvaluatorValue GetValue(string name) | Return variable's value |
| bool TryGetValue(string name, out EvaluatorValue value) | Return variable's value if possible |
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| string Name { get; } | Name of function |
| bool CanHandleNullArguments { get; } | If false and any argument is null - function wont be executed and null will be returned |
| InternalEvaluatorValue Execute(List args, ValueFactory factory) | Evaluate value |
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| SetWordQuotationSingleQuote() | Set word quotation mark - ' |
| SetWordQuotationDoubleQuote() | Set word quotation mark - " |
| SetWordQuotationMark(string mark) | Set word quotation mark |
| SetFloatingTolerance(double floatingTolerance) | Set floating tolerance |
| SetFloatingPointSymbol(FloatingPointSymbol floatingPointSymbol) | Set floating point symbol |
| SetThrowIfVariableNotFound(bool isThrow) | Set throw if variable not found |
| WithFunctionsFrom(Type typeFromSourceAssembly) | Add assembly to register functions |
| WithFunctionsFrom(Assembly sourceAssembly) | Add assembly to register functions |
| WithoutDefaultFunctions(bool withoutDefaultFunctions = true) | Remove root assembly from functions registration |
| WithFunctions(params IFunction[] functions) | Add functions |
| Method |
|---|
| double CalcNumber(string formula, IVariablesContainer variables) |
| double CalcNumber(FormulaNodes formulaNodes, IVariablesContainer variables) |
| double CalcNumber(string formula, IDictionary<string, EvaluatorValue> variables) |
| double CalcNumber(FormulaNodes formulaNodes, IDictionary<string, EvaluatorValue> variables) |
| double CalcNumber(string formula) |
| double CalcNumber(FormulaNodes formulaNodes) |
| string CalcWord(... |
| DateTime CalcDateTime(... |
| List CalcWordList(... |
| List CalcNumberList(... |
| bool CalcBoolean(... |
| EvaluatorValue Calc(... |
Referenced methods are same as in INoStringEvaluator
| Method |
|---|
| double? CalcNumber(string formula, IVariablesContainer variables) |
| DateTime? CalcDateTime(string formula, IVariablesContainer variables) |
| bool? CalcBoolean(string formula, IVariablesContainer variables) |
Static initialization if you don't have DI
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| static Facade CreateFacade(Action<NoStringEvaluatorOptions> options = null) | Create evaluator facade |
Static initialization if you don't have DI
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| static Facade CreateFacade(Action<NoStringEvaluatorOptions> options = null) | Create evaluator facade |
- Add more functions
- Any idea?