DemoKin uses matrix demographic methods to compute expected (average)
kin counts from demographic rates under a range of scenarios and
assumptions. The package is an R-language implementation of Caswell
(2019), Caswell (2020), and Caswell and Song (2021). It draws on
previous theoretical development by Goodman, Keyfitz and Pullum (1974).
You can install the development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
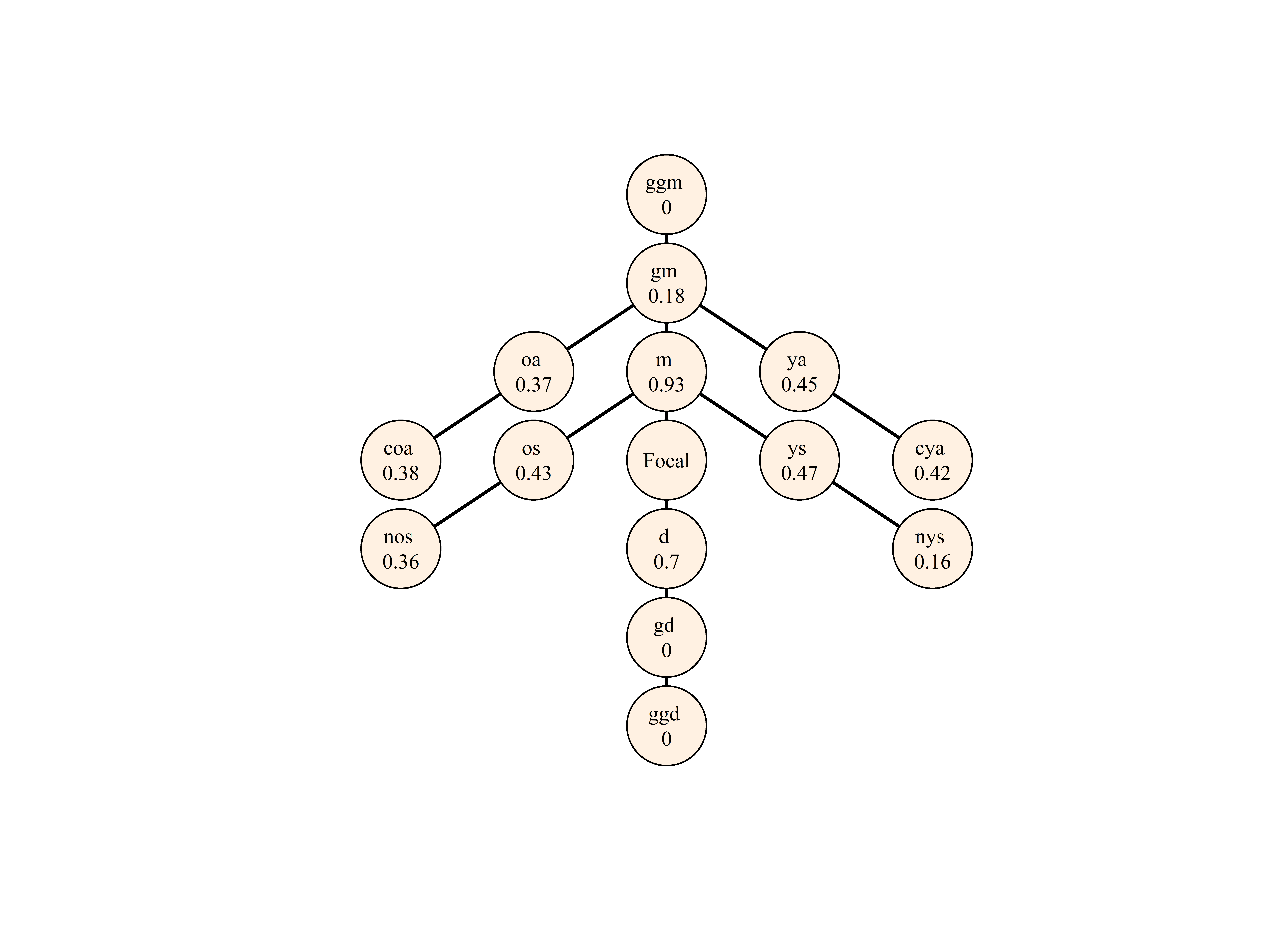
devtools::install_github("IvanWilli/DemoKin")Consider an average Swedish woman called ‘Focal’. For this exercise, we assume a female closed population in which everyone experiences the Swedish 2015 mortality and fertility rates at each age throughout their life (the ‘time-invariant’ assumption in Caswell [2019]).
We then ask:
How many living relatives does Focal have at each age?
Let’s explore this using the Swedish data already included with
DemoKin.
library(DemoKin)
swe_surv_2015 <- swe_px[,"2015"]
swe_asfr_2015 <- swe_asfr[,"2015"]
swe_2015 <- kin(U = swe_surv_2015, f = swe_asfr_2015, time_invariant = TRUE)px is the survival probability by age from a life table and f are
the age specific fertility raties by age (see ?kin for details).
Now, we can visualize the implied kin counts (i.e., the average number
of living kin) of Focal at age 35 using a network or ‘Keyfitz’ kinship
diagram with the function plot_diagram:
# We need to reformat the data a little bit
kin_total <- swe_2015$kin_summary
# Keep only data for Focal's age 35
kin_total <- kin_total[kin_total$age_focal == 35 , c("kin", "count_living")]
names(kin_total) <- c("kin", "count")
plot_diagram(kin_total, rounding = 2)Relatives are identified by a unique code:
| DemoKin | Label |
|---|---|
| coa | Cousins from older aunt |
| cya | Cousins from younger aunt |
| d | Daughter |
| gd | Grand-daughter |
| ggd | Great-grand-daughter |
| ggm | Great-grandmother |
| gm | Grandmother |
| m | Mother |
| nos | Nieces from older sister |
| nys | Nieces from younger sister |
| oa | Aunt older than mother |
| ya | Aunt younger than mother |
| os | Older sister |
| ys | Younger sister |
For more details, including an extension to time varying-populations
rates, deceased kin, and multi-state models, see
vignette("Reference", package = "DemoKin"). If the vignette does not
load, you may need to install the package as
devtools::install_github("IvanWilli/DemoKin", build_vignettes = T).
Williams, Iván; Alburez-Gutierrez, Diego; Song, Xi; and Hal Caswell. (2021) DemoKin: An R package to implement demographic matrix kinship models. URL: https://github.com/IvanWilli/DemoKin.
We thank Silvia Leek from the Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research for designing the DemoKin logo. The logo includes elements that have been taken or adapted from this file, originally by Ansunando, CC BY-SA 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons. Sha Jiang provided useful comments for improving the package.
DemoKin is under constant development. If you’re interested in
contributing, please get in touch, create an issue, or submit a pull
request. We look forward to hearing from you!
Caswell, H. 2019. The formal demography of kinship: A matrix formulation. Demographic Research 41:679–712. doi:10.4054/DemRes.2019.41.24.
Caswell, H. 2020. The formal demography of kinship II: Multistate models, parity, and sibship. Demographic Research 42: 1097-1144. doi:10.4054/DemRes.2020.42.38.
Caswell, Hal and Xi Song. 2021. “The Formal Demography of Kinship. III. Kinship Dynamics with Time-Varying Demographic Rates.” Demographic Research 45: 517–46. doi:10.4054/DemRes.2021.45.16.
Goodman, L.A., Keyfitz, N., and Pullum, T.W. (1974). Family formation and the frequency of various kinship relationships. Theoretical Population Biology 5(1):1–27. doi:10.1016/0040-5809(74)90049-5.