Collaborators: Marco Santos & Harris Nathel
- Goal
- Data Gathering
- Data Cleaning
- Data Exploration
- Classification Modeling
- Deep Learning with Keras
- Potential Improvements
- Closing
Given a specific subject and two different cities. Using NLP and classification models; can a tweet be classified as coming from the first or second city by regarding its language towards the specific subject?
- Used the module Twint to webscrape tweets from Twitter
- Specific tweets were scraped based on a user-defined subject
- Tweets were selected by two user-defined cities
- Any subject and two cities can be inputted within the program to test the classifiers
- 10,000 tweets were grabbed from the two different cities totaling 20,000 tweets
For the sake of consistency, the focus for this specific iteration was on the subject of Trump within Seattle and Jacksonville.
- Lowercased all words for every tweet
- URLs and special characters such as emojis and punctuations were removed
- Lemmatization with the nltk library was used for the remaining words
After gathering and cleaning all of the tweets we wanted to look at how what words were more common in each of the cities.
Because our subject was "Trump", we wanted to look at how specific words were in each city and compare the two cities. WordtoVec was used to get similarity scores.
It was interesting to see that words associated with negative things in the news were more common in Seattle (the more liberal city) than in Jacksonville. Words that we thought would be associated pro-trump tweets were more common in Jacksonville.
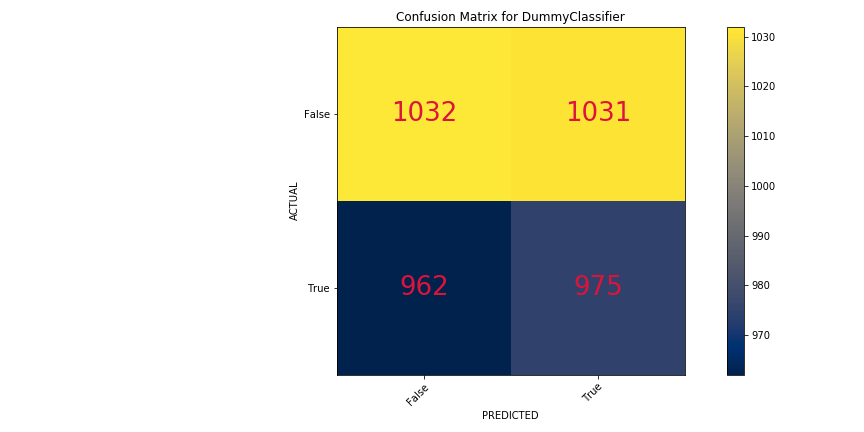
- Dummy Classifier - Baseline Model
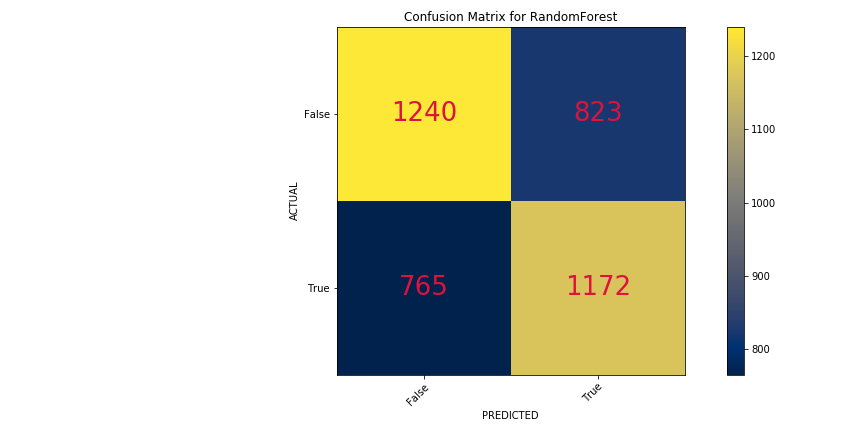
- Random Forest
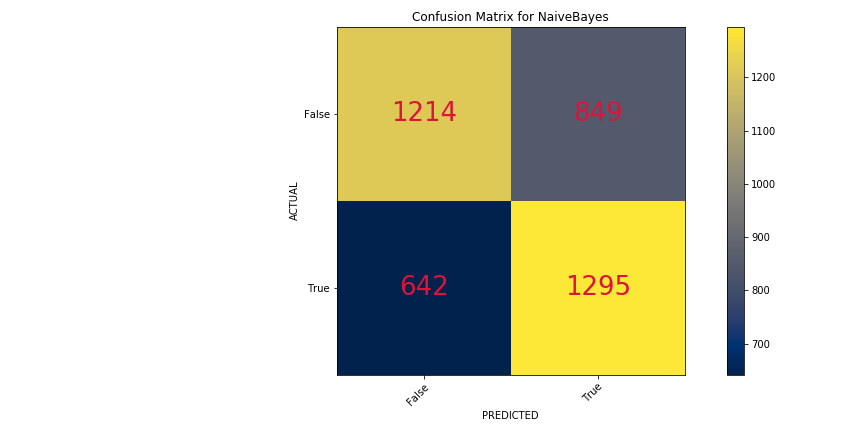
- Naive Bayes
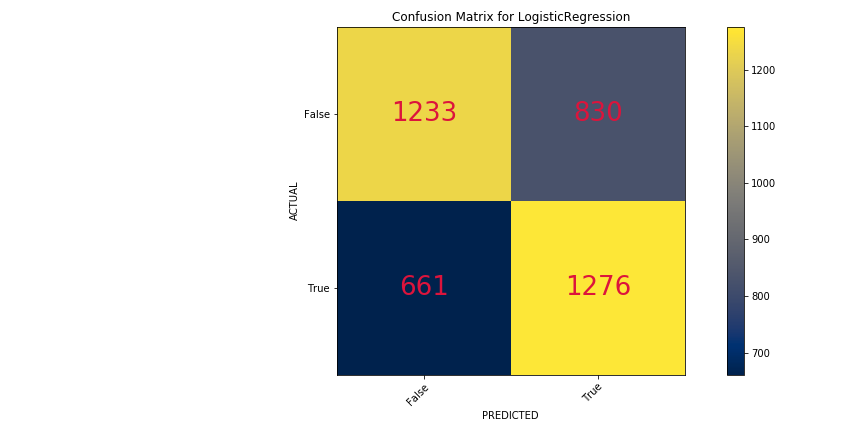
- Logistic Regression
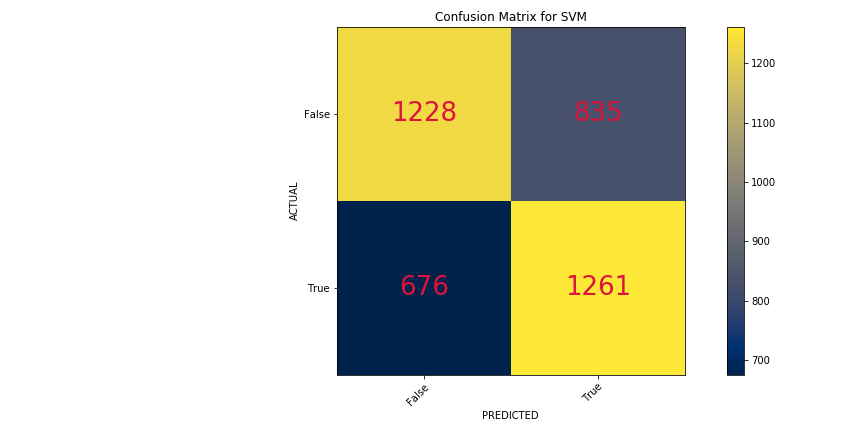
- Support Vector Machine
Both CountVectorizer and tf_idfVectorizer were used in order to compare the performance of the models with each. In the end, the performance for both were similar but tf_idfVectorizer had slightly better overall results. As a result, tf_idfVectorizer was chosen as the default Vectorizer.
Training Score - 50%
Testing Score - 49%
Training Score - 96%
Testing Score - 60%
Training Score - 79%
Testing Score - 62%
Training Score - 82%
Testing Score - 61%
Training Score - 87%
Testing Score - 59%
A Sequential model was used with only 3 layers within the neural network. After training for 300 epochs with a batch size of 256, the results were similar to the other classification models. No significant changes warranted the need for a neural network for the tweets.
- More models could be applied such as XGBoost, KNN, etc. for more comparisons and potential improved results.
- Feature engineering such as ngrams for possibly better results.
- More cleaning with other techniques or different modules such as SpaCy
- More experimentation with the neural network
Due to the nature of the question, it is inherently difficult to classify whether a tweet comes from one location or not. However, these classification models did perform better than randomly guessing (dummy classifier). Most models performed at least 10% better than the Dummy Classifier and the best performing model was Naive Bayes. Even though these models performed this way for this dataset, a new subject and cities could significantly alter the overall results.