This application component let's you enhance your entities with a generic tagging functionality.
taggableis available in the CUBA marketplace- Select a version of the add-on which is compatible with the platform version used in your project:
| Platform Version | Add-on Version |
|---|---|
| 7.2.x | 0.6.x |
| 7.1.x | 0.5.x |
| 7.0.x | 0.4.x |
| 6.10.x | 0.3.x |
| 6.9.x | 0.1.x - 0.2.x |
Add custom application component to your project:
- Artifact group:
de.diedavids.cuba.taggable - Artifact name:
taggable-global - Version: add-on version
dependencies {
appComponent("de.diedavids.cuba.taggable:taggable-global:*addon-version*")
}To see this application component in action, check out this example: cuba-example-using-taggable.
Information on changes that happen through the different versions of the application component can be found in the CHANGELOG. The Changelog also contains information about breaking changes and tips on how to resolve them.
The following databases are supported by this application component:
- HSQLDB
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
All other DBMS systems are also possible to work with by the fact that CUBA studio generates the corresponding init / update scripts within the application.
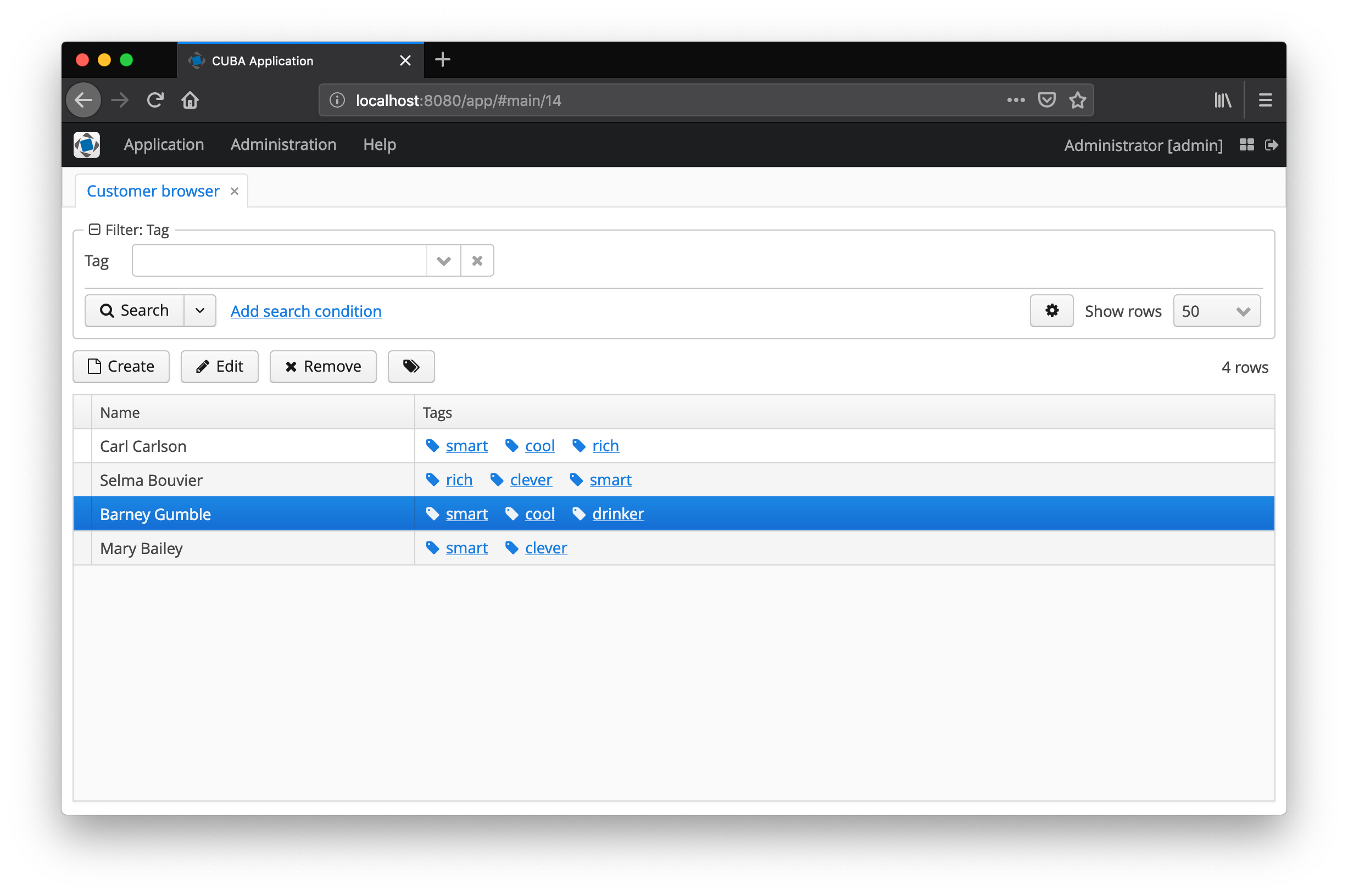
Annotate your browse screens with the @WithTags annotation or by implementing the WithTagsSupport interface.
The resulting UI looks like this:
@WithTags(listComponent = "customersTable", showTagsInList = true, showTagsAsLink = true, tagLinkOpenType = "NEW_TAB")
class CustomerBrowse extends AnnotatableAbstractLookup {
}class CustomerBrowse extends StandardLookup<Customer> implements WithTagsSupport {
@Inject
private GroupTable<Customer> customersTable;
@Inject
private ButtonsPanel buttonsPanel;
@Override
Table getListComponent() {
return customersTable;
}
@Override
ButtonsPanel getButtonsPanel() {
return buttonsPanel;
}
}With that your Customer entity will be taggable and might look like the following:
The following options are available for the Annotation / Interface:
listComponent- the list component the tagging functionality should be placed upon (normally the Table of the browse screenshowTagsInList- this option will create a column in the table and renders all tags for the corresponding rowshowTagsAsLink- renders the tags as links, which open screen that displays all entites that are tagged with this linktagLinkOpenType- configures the open type of the tag link screen (only applicable ifshowTagsAsLink= true)persistentAttribute- if a persistent attribute in a subclass ofTaggingis used for faster data access, it can be defined to be used heretagContext- a string that identifies the context of this tag usage
With the plain use of the @WithTags annotation, it is not directly possible to use the Tag entity within the JPA layer alongside with your entities.
One example of this restriction is the filter component to filter all entries (like Customers) for a given tag. Also programmatic joins from business entities
to Tag is by default not possible. The reason is that in order to do that, the JPA layer needs to know about the relationship between a Tagging (one entity within this application component)
and the entity to filter for (e.g. Customer).
But it is possible to enable this kind of interaction with the Tagging entity by extending it and making the entity aware of the relationships.
In the application you have to create an Entity that extends Tagging and uses CUBAs @Extends functionality to replace the original entity with the new subclass.
@Extends(Tagging.class)
@Entity(name = "myApp$ExtendedTagging")
public class ExtendedTagging extends Tagging {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6795917365659671988L;
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "CUSTOMER_ID")
protected Customer customer;
public void setCustomer(Customer customer) {
this.customer = customer;
}
public Customer getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
}
With that it is possible to create an additional reference from the Customer entity to the Tagging entity like this:
@NamePattern("%s|name")
@Table(name = "MYAPP_CUSTOMER")
@Entity(name = "myApp$Customer")
public class Customer extends StandardEntity {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2263337300282568L;
@Column(name = "NAME")
protected String name;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "customer")
protected List<ExtendedTagging> taggings;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public List<ExtendedTagging> getTaggings() {
return taggings;
}
public void setTaggings(List<ExtendedTagging> taggings) {
this.taggings = taggings;
}
}
The second step is then to define the persistentAttribute in the usage of the @WithTags annotation (CUBA 6) or WithTagsSupport interface (CUBA 7) like this:
@WithTags(
listComponent = "customersTable",
persistentAttribute = "customer"
)
class CustomerBrowse extends AnnotatableAbstractLookup {
}
With that configuration in place, the persistent reference attribute will also be used to store the reference from the Tagging entity
to the customer entity. When the Tagging functionality is used for multiple different entities, each of those entities can get a different persistent
Attribute in the ExtendedTagging.
Now it is possible to use e.g. the filter functionality of CUBA directly, to search e.g. for all Customers that are tagged with a particular tag.
By default the created tags in the application are available for selection in all contexts. So if both a Customer and a Order entity
both use the Tag functionality, a new Tag that is entered in the context of the Customer browse screen, the same Tag will also be available
for selection in the context of the Order browse screen.
This global behavior might not always be desired. Therefore there is an option to set a String identifier called tagContext that will scope
the Tags that are available for selection for only this context.
In the example above, it is possible to scope the available tags for the customer use case to only be available within this screen:
@WithTags(
listComponent = "customersTable",
tagContext = "customer"
)
class CustomerBrowse extends AnnotatableAbstractLookup {
}
The scope might not only be applicable on a per entity basis. But also for different use-cases for one Entity it is possible to define different contexts on a per-screen basis.