Pulumi's Infrastructure as Code SDK is the easiest way to create and deploy cloud software that use containers, serverless functions, hosted services, and infrastructure, on any cloud.
Simply write code in your favorite language and Pulumi automatically provisions and manages your AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and/or Kubernetes resources, using an infrastructure-as-code approach. Skip the YAML, and use standard language features like loops, functions, classes, and package management that you already know and love.
For example, create three web servers:
let aws = require("@pulumi/aws");
let sg = new aws.ec2.SecurityGroup("web-sg", {
ingress: [{ protocol: "tcp", fromPort: 80, toPort: 80, cidrBlocks: ["0.0.0.0/0"]}],
});
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new aws.ec2.Instance(`web-${i}`, {
ami: "ami-7172b611",
instanceType: "t2.micro",
securityGroups: [ sg.name ],
userData: `#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello, World!" > index.html
nohup python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 &`,
});
}Or a simple serverless timer that archives Hacker News every day at 8:30AM:
const aws = require("@pulumi/aws");
const snapshots = new aws.dynamodb.Table("snapshots", {
attributes: [{ name: "id", type: "S", }],
hashKey: "id", billingMode: "PAY_PER_REQUEST",
});
aws.cloudwatch.onSchedule("daily-yc-snapshot", "cron(30 8 * * ? *)", () => {
require("https").get("https://news.ycombinator.com", res => {
let content = "";
res.setEncoding("utf8");
res.on("data", chunk => content += chunk);
res.on("end", () => new aws.sdk.DynamoDB.DocumentClient().put({
TableName: snapshots.name.get(),
Item: { date: Date.now(), content },
}).promise());
}).end();
});Many examples are available spanning containers, serverless, and infrastructure in pulumi/examples.
Pulumi is open source under the Apache 2.0 license, supports many languages and clouds, and is easy to extend. This
repo contains the pulumi CLI, language SDKs, and core Pulumi engine, and individual libraries are in their own repos.
-
Get Started with Pulumi: Deploy a simple application in AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, or Kubernetes using Pulumi.
-
Learn: Follow Pulumi learning pathways to learn best practices and architectural patterns through authentic examples.
-
Examples: Browse several examples across many languages, clouds, and scenarios including containers, serverless, and infrastructure.
-
Docs: Learn about Pulumi concepts, follow user-guides, and consult the reference documentation.
-
Registry: Find the Pulumi Package with the resources you need. Install the package directly into your project, browse the API documentation, and start building.
-
Pulumi Roadmap: Review the planned work for the upcoming quarter and a selected backlog of issues that are on our mind but not yet scheduled.
-
Community Slack: Join us in Pulumi Community Slack. All conversations and questions are welcome.
-
GitHub Discussions: Ask questions or share what you're building with Pulumi.
See the Get Started guide to quickly get started with Pulumi on your platform and cloud of choice.
Otherwise, the following steps demonstrate how to deploy your first Pulumi program, using AWS Serverless Lambdas, in minutes:
-
Install:
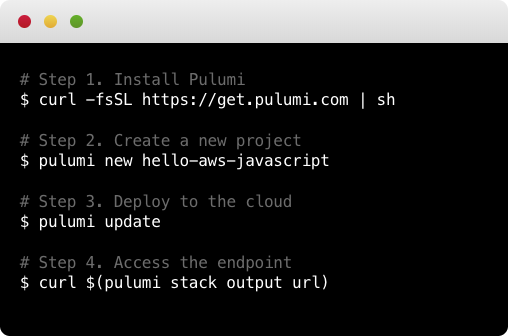
To install the latest Pulumi release, run the following (see full installation instructions for additional installation options):
$ curl -fsSL https://get.pulumi.com/ | sh -
Create a Project:
After installing, you can get started with the
pulumi newcommand:$ mkdir pulumi-demo && cd pulumi-demo $ pulumi new hello-aws-javascript
The
newcommand offers templates for all languages and clouds. Run it without an argument and it'll prompt you with available projects. This command created an AWS Serverless Lambda project written in JavaScript. -
Deploy to the Cloud:
Run
pulumi upto get your code to the cloud:$ pulumi up
This makes all cloud resources needed to run your code. Simply make edits to your project, and subsequent
pulumi ups will compute the minimal diff to deploy your changes. -
Use Your Program:
Now that your code is deployed, you can interact with it. In the above example, we can curl the endpoint:
$ curl $(pulumi stack output url) -
Access the Logs:
If you're using containers or functions, Pulumi's unified logging command will show all of your logs:
$ pulumi logs -f
-
Destroy your Resources:
After you're done, you can remove all resources created by your program:
$ pulumi destroy -y
To learn more, head over to pulumi.com for much more information, including tutorials, examples, and details of the core Pulumi CLI and programming model concepts.
| Architecture | Build Status |
|---|---|
| Linux/macOS x64 | |
| Windows x64 |
The Pulumi CLI v1 and v2 are no longer supported. If you are not yet running v3, please consider migrating to v3 to continue getting the latest and greatest Pulumi has to offer! 💪
-
To migrate from v2 to v3, please see our v3 Migration Guide.
-
To migrate to v2 from v1, please see our v2 Migration Guide.
| Language | Status | Runtime | |
|---|---|---|---|
| JavaScript | Stable | Node.js 14+ | |
| TypeScript | Stable | Node.js 14+ | |
| Python | Stable | Python 3.6+ | |
| Go | Stable | Go 1.14+ | |
| .NET (C#/F#/VB.NET) | Stable | .NET Core 3.1+ | |
| Java | Public Preview | JDK 11+ | |
| YAML | Public Preview | n/a |
Visit the Registry for the full list of supported cloud and infrastructure providers.
Visit CONTRIBUTING.md for information on building Pulumi from source or contributing improvements.