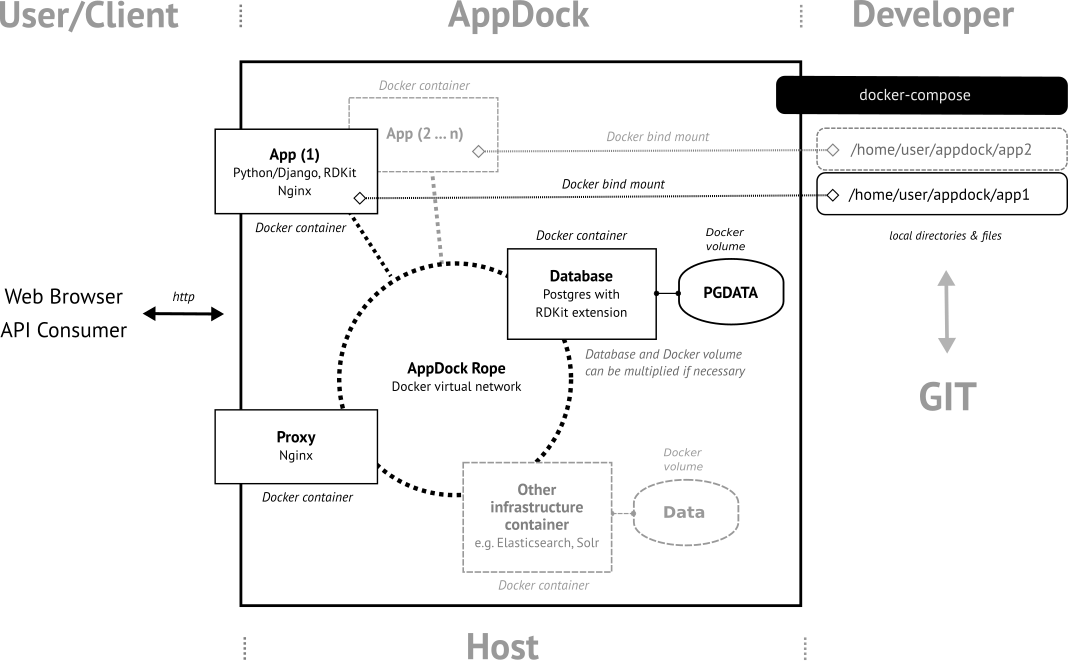
AppDock is a Docker based platform intended for the rapid development of scientific web applications and microservices. It has been develop as component for the InChI-Resolver project (the alpha version of) the resolver is currently in the process of being migrated from a predecessor version of AppDock) At its current (early) development stage, AppDock supports the quick deployment of Python/Django based services and specifically includes RDKit for building chemoinformatics-centric applications. The following schema gives an overview.
If launched, Appdock creates a Docker virtual network ("AppDock Rope") on the Docker host system and starts up several Docker containers which connect to this network. Currently, this includes a Postgres database container with RDKit extension readily available, a Nginx container which is configured as reverse proxy, and a basic application (App) container which provides a Django installation extended by the Django REST framework and RDKit on Python-level. The Django installation is set up to to establishes a connection to the database instance at the Postgres container and to link to the local Nginx web server instance inside the same App container (by uswgi). If the Nginx instance of the Proxy container senses another container with Nginx running inside the AppDock Rope network, it automatically looks up the (sub) domain specification of this additional Nginx instance and makes it available to the outside of AppDock (which either might be localhost or any Web-accessible domain). This mechanism allows to easily bring up additional App containers or update or remove existing ones.
Please have at least Docker CE 17.09 and Docker Compose 1.17 installed on your system.
Clone this repository:
https://github.com/markussitzmann/appdock.git appdock
go into directory
cd appdock/
and edit the file .env to appropriate settings, in particular, variable APPDOCK_HOME to a file directory location where the user
running the build in the next is allowed to create a directory. If the directory specified in APPDOCK_HOME does not exist, it will be
created during the first start up of a Docker container. It will be mounted as volume in all containers.
Start the Docker build of the system by going to the build-directory of the appdock-directory and run docker-compose build (it is
actually important to be in this directory because docker-compose needs the corresponding docker-compose.yml configuration file available in the
directory it is run):
cd build/ docker-compose build
This will build all Docker image files needed for APPDOCK.
go back into the appdock directory:
cd ..
and change into the bin directory and run docker-compose up:
cd bin/ docker-compose up
This will bring up all services defined in the file docker-compose.yml there and keep all database and search index containers running persistently.
APPDOCK will run with the settings provided in appdock/.env. Bringing APPDOCK down is performed by:
docker-compose down
also in the bin directory. Any data stored in any databases or search indices will persist and will be available again after restarting the system
with docker-compose up again.
It is possible to change settings in the appdock/.env file while the system is down, however, PLEASE NOTE, this may have unwanted side effects.
with:
docker-compose run --rm shell
If this is the first start-up of the shell container, the directory specified in APPDOCK_HOME will be created and mounted as a Docker volume.
Inside the shell container, this directory is available under /home/appdock.
with:
docker-compose run --rm shell psql -h db -U appdock appdock
Password is the one specified APPDOCK_DB_PASSWORD in .env.