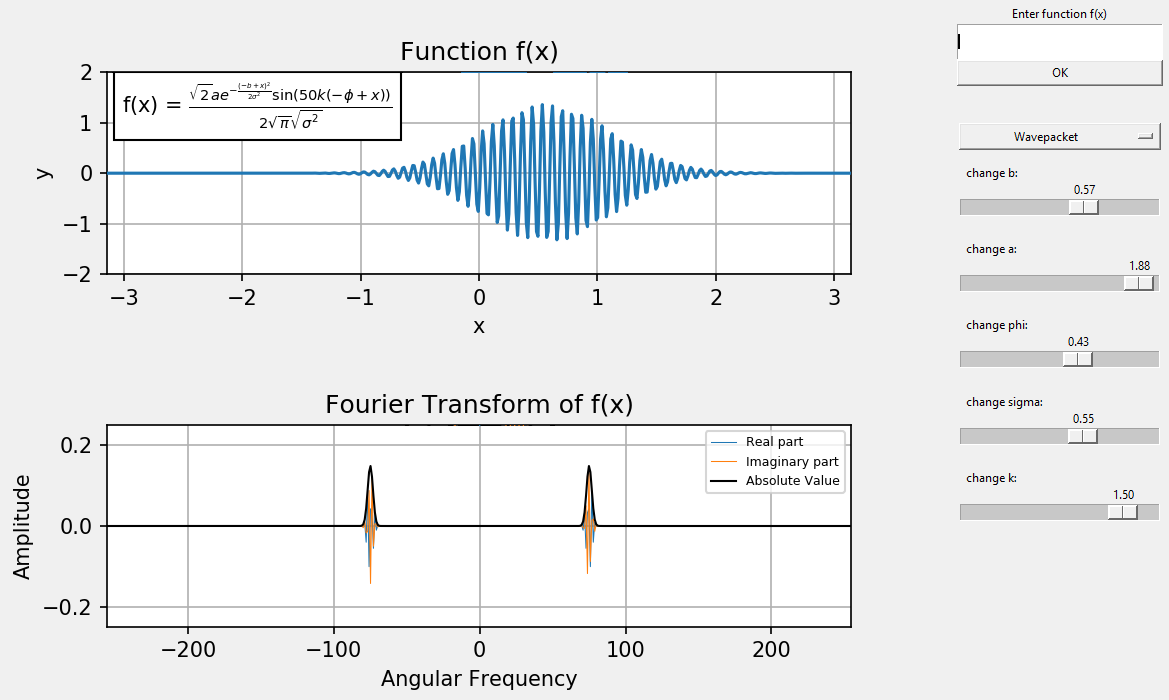
To run this program, first ensure that python3 with the modules tkinter, numpy, sympy, and matplotlib
are installed on your computer. The first of these comes with Python. The other three can be installed with
pip3 by typing pip3 install numpy sympy matplotlib in the command line. Now clone or download this
repository and run the file main.py. You should obtain a GUI with two graphs and GUI controls on the right side.
The top graph displays the function in position space, while the bottom graph displays its Fourier transform.
To enter a new function, type a new function into the Enter function f(x) entry box, or pick a new function
in the Preset function f(x) dropdown menu. The function entered can contain any variable, where those
variables that are not x can be controlled with the sliders.
Special thanks to the creators and maintainers of Sympy. Their fantastic module makes it possible to parse and manipulate functions in a symbolic fashion. Also thanks to those who contributed to Numpy, Matplotlib, and Tkinter.
Newman, M. (2013). Fourier Transforms. In Computational Physics, chapter 7. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform.