This repository provides the source code of RedTell.
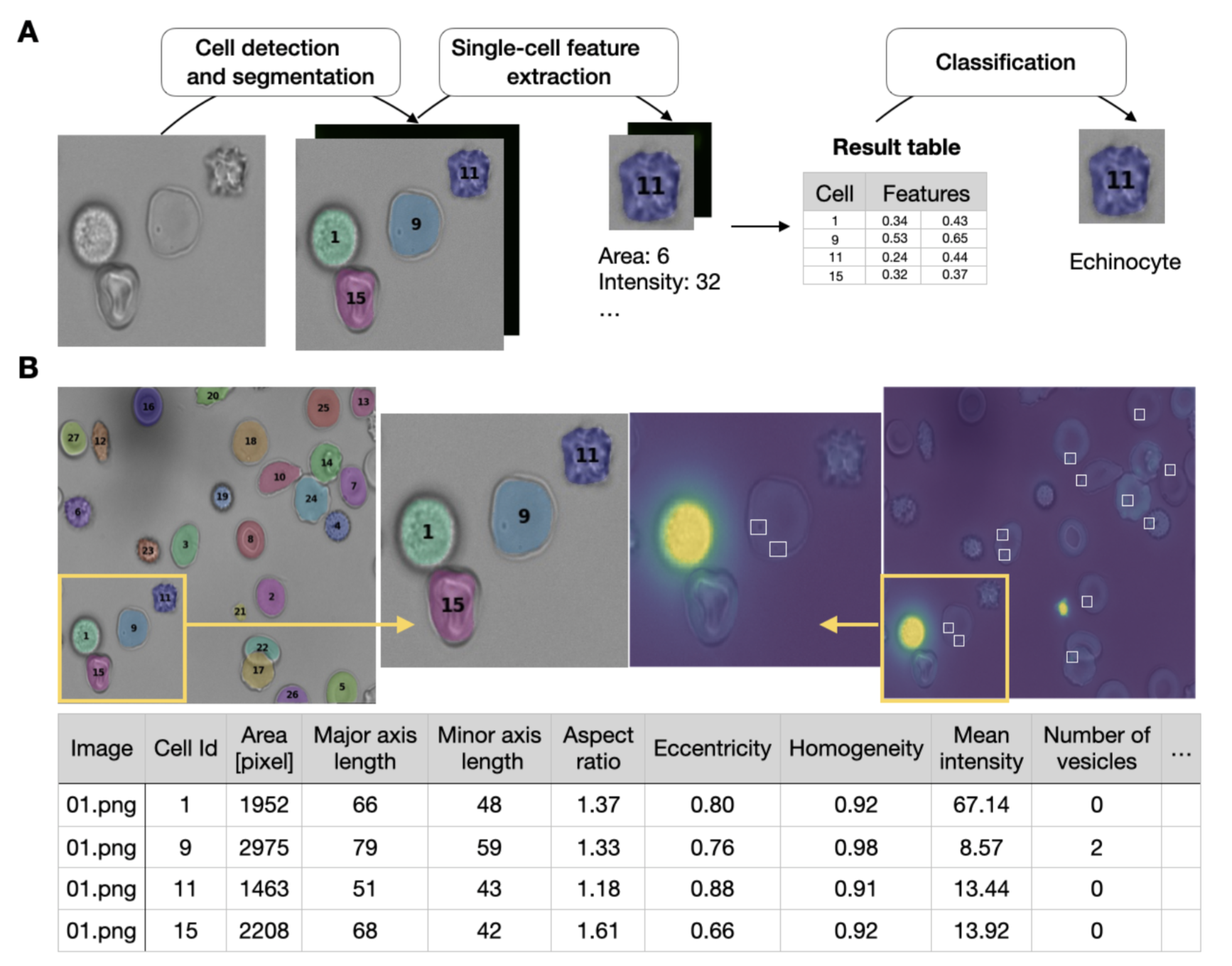
Hematologists analyze microscopic images of red blood cells to study their morphology and functionality, detect disorders and search for drugs. However, accurate analysis of a large number of red blood cells needs automated computational approaches that rely on annotated datasets, expensive computational resources, and computer science expertise. We introduce RedTell, an AI tool for the interpretable analysis of red blood cell morphology comprising four single-cell modules: segmentation, feature extraction, assistance in data annotation, and classification. Cell segmentation is performed by a trained Mask R-CNN working robustly on a wide range of datasets requiring no or minimum fine-tuning. Over 130 features that are regularly used in research are extracted for every detected red blood cell. If required, users can train task-specific, highly accurate decision tree-based classifiers to categorize cells, requiring a minimal number of annotations and providing interpretable feature importance. We demonstrate RedTell's applicability and power in three case studies. In the first case study we analyze the difference of the extracted features between the cells coming from patients suffering from different diseases, in the second study we use RedTell to analyze the control samples and use the extracted features to classify cells into echinocytes, discocytes and stomatocytes and finally in the last use case we distinguish sickle cells in sickle cell disease patients. We believe that RedTell can accelerate and standardize red blood cell research and help gain new insights into mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment of red blood cell associated disorders.
We publish two datasets:
- The SDE-sequnce dataset containing RBC microscopy images of healthy patients from the CoMMiTMenT study. It has annotation for instance segmentation and classification (discocyte-stomatocyte-echinocyte sequence).
- Anemia dataset containing RBC microscopy images of healthy, sickle cell disease and thalassemia patients from CoMMiTMenT & MemSID studies. No ground truth annotations are available for this dataset.
A default RedTell segmentation model can be downloaded from here. It should be put inside the segmentation directory in models folder.
RedTell is a software package implemented in Python and is easily accessible through the command line under any operating system. A user has to navigate to the retell code directory to execute the tool. The data directory must be placed inside the retell directory and contain images subdirectory with images of format .tif, .png and .jpg to be processed.
-
The following command performs segmentation using RedTell native Mask R-CNN model:
$python redtell.py --funct segment --data <data_dir> --model <model_name>The variable --data denotes path to the data directory. It should contain images subdirectory, where images to be segmented are stored. If model name is specified then <model_name>.model from model directory is used for segmentation. Running command without specifying the model (without--model <model_name>) results in using RedTell default segmentation model trained on the SDE-sequnce dataset. It creates in the data folder two new directories: masks with segmentation masks and segmentation_results with segmentation masks overlaid on the original images and containing unique cell identifiers. -
To train a new segmentation model adjusted to a custom dataset, a user has to create Training directory with Images and Ground-Truth subdirectories containing raw images and segmentation masks, respectively. Every segmentation mask must have distinct integer values for regions corresponding to different cells and 0 for the background. It also must have the same name as the corresponding raw image. RedTell requires at least 25 annotated images for training. The training is performed by running
$python redtell.py --funct train_segmentation --data <data_dir> --model <model_name>This command trains new segmentation model and saves it under <model_name>.model into model directory. To apply it on images the previous segmentation command with new model as--model <model_name>parameter has to be executed again. -
In the next step, the features are extracted by the command
$python redtell.py --funct feature_extraction --data <data_dir> --channel <channel>The variable<channels>defines what channels the features are extracted from. It can have multiple values:-channel maskextracts only shape features from segmentation masks in masks directory saved after performing segmentation in<data_dir>,-channel bfextracts intensity-based statistical and texture features from brightfield images saved in images directory in<data_dir>and-channel fluo-4extracts intensity-based statistical, texture features and counts vesicles from fluo-4 fluorescent images saved in fluo-4 directory in<data_dir>. The extracted features are saved in features.csv table in<directory containing data>directory. The table contains image names, cell identifiers and corresponding cell-wise features for every detected cell. In case of fluo-4 channel, it also creates a directory vesicle_results with overlaid brightfield and Ca2+ images and highlighted detected vesicles. To extract features from other fluorescent channels use-channel <fl_channel_name>parameter. For this a directory containing fluorescent images<fl_channel_name>should be created in<directory containing data>directory. It is also possible to extract features from multiple channels. For this, specify what channels to use separated by space, e.g.-channel mask bf fluo-4. -
In case cell classification is intended, first, RedTell provides assistance in data annotation by running
$python redtell.py --funct annotate --data <data_dir> --num_cells <num_cells>The parameter<num_cells>denotes the number of cells the user is willing to annotate. The minimum number is 200 cells. The command creates a directory annotation in<data_dir>with saved single-cell images randomly derived from the original dataset, where every cell image is given a unique identifier in its name. It also provides an annotations.csv table with a cell column containing names of every cell image in<data_dir>directory, a label column user has to fill in and additional columns to map each annotated cell to the corresponding entry in the features.csv table. -
The classification is then done by running
$python redtell.py --funct classify --data <data_dir>It trains a classification model and extends the features.csv table with a label column, where cells used for annotation have expert given labels and all other cells have predicted labels obtained with the best model of RedTell Auto-ML module. It also outputs for this model evaluation.csv, a table of metric values for the cross validation to assess model generalization ability, and feature_importance.csv, a table providing importance of every feature for the classifier. Both tables are stored in<data_dir>directory. The features.csv table can be further used for the downstream analysis to support the research objective.
We provide this notebook on Google Colab to test RedTell online.