In this project we visualize the change in a deep neural network as it is fine-tuned towards a new task is assessed using feature visualization. For a detailed description of this project, see this blog post.
There are two main parts to this repo:
- feature_vis: a python package which is a partial pytorch implementation of the tensorflow feature visualization library lucid.
- transfer: a collection of python scripts which perform the fine-tuning task, generate the feature visualizations using
feature_vis, and compare the change in the resulting visualizations.
To install this package locally, first install all of the requirements using the following command:
conda install pytorch=1.6.0 torchvision=0.7.0 kornia=0.5.8 tqdm=4.65.0 -c pytorch -c conda-forgeand then simply run the following from the root level of this project:
pip install .
⚠️ This project will need to be updated to use the newertorch.fftAPI introduced in PyTorch 1.7+. For now the version is pinned to 1.6.0.
Once installed, you can generate a feature visualization using the following code:
from feature_vis.render import FeatureVisualizer
import torch
from torchvision.models import resnet50
# load a pre-trained model
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = resnet50(pretrained=True)
model.eval()
model.to(device)
# set up the visualizer
visualize = FeatureVisualizer(model, device=device)
# create the feature visualization as a PIL image
img = visualize(act_idx=309)The snippet above produces the feature visualization for the activation of the 309th index in resnet50's output vector. This corresponds to the "bee" class in ImageNet and the resulting feature visualization can be seen below. The user can configure the learning rate, number of iterations, image shape, and more.
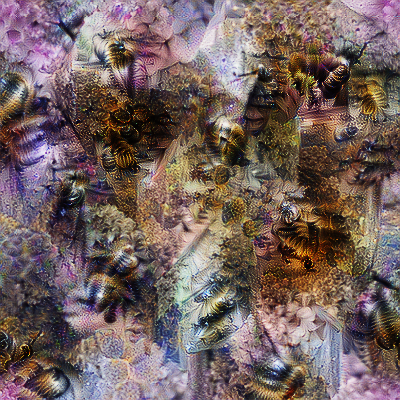

The easiest way to specify the target activation is to alter the model such that it outputs the target layer and then specify the index within the resulting activation vector or volume. Note, if the layer outputs a volume then the target activation is the average of the i-th feature map in the volume. Pytorch hooks can also be used isolate the target activation. See the docstrings in the code and the tutorial notebook for more details.
Note, this is only a partial implementation of feature visualization as described in this distill article. Only the parts necessary for this project were converted to pytorch from lucid library.
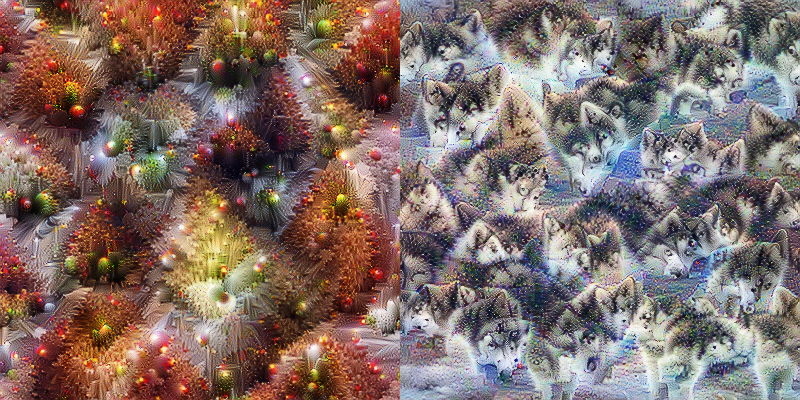
The transfer directory contains scripts for recreating this project. Here is a description for each script, in the order that they should be executed:
This script fine-tunes a ResNet-50 network pre-trained on ImageNet to the Stanford Dog Dataset. The state of the model is saved at each epoch. Note, this project uses the version of this dataset hosted by Kaggle, not the source linked above.
This script repeats the steps of "finetune_dog_classifier" but the target dataset is instead the Stanford Car Dataset.
This script creates and saves the feature visualizations for the base network, the fine-tuned dog network, and the fine-tuned car network.
This script identifies the channels in each of the fine-tuned networks which resulted in faulty, gray feature visualizations. A CSV file is created containing the information.
This script calculates the embedding cosine similarity between the respective channels of the base network + the dog network and the base network + the car network.
This file provides pytorch Dataset classes which help index and load the datasets used in this project.
This file defines the cosine similarity metric (and the gram matrix distance) between two feature visualizations.
This file provides several utility functions to help train a pytorch neural network.