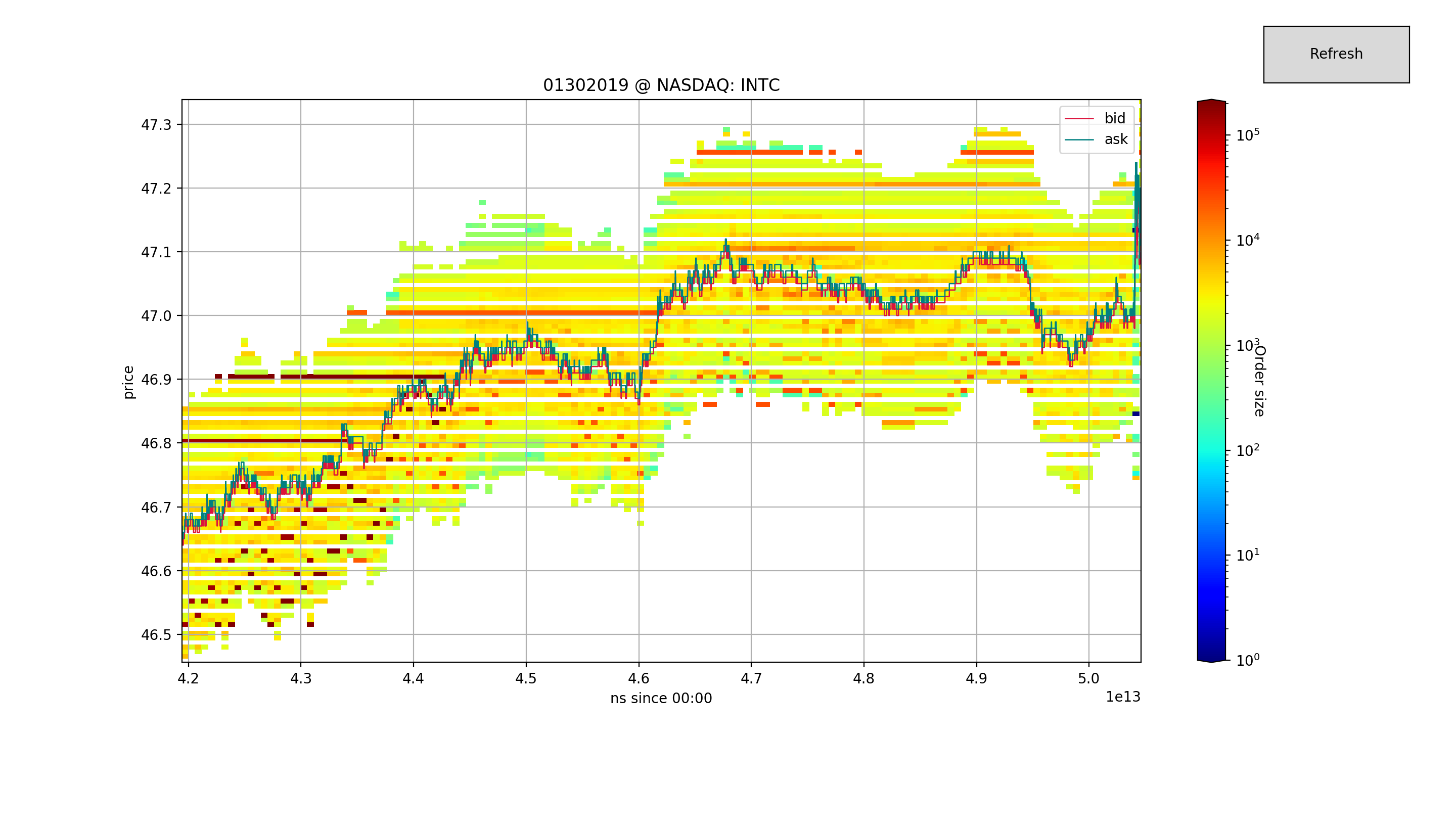
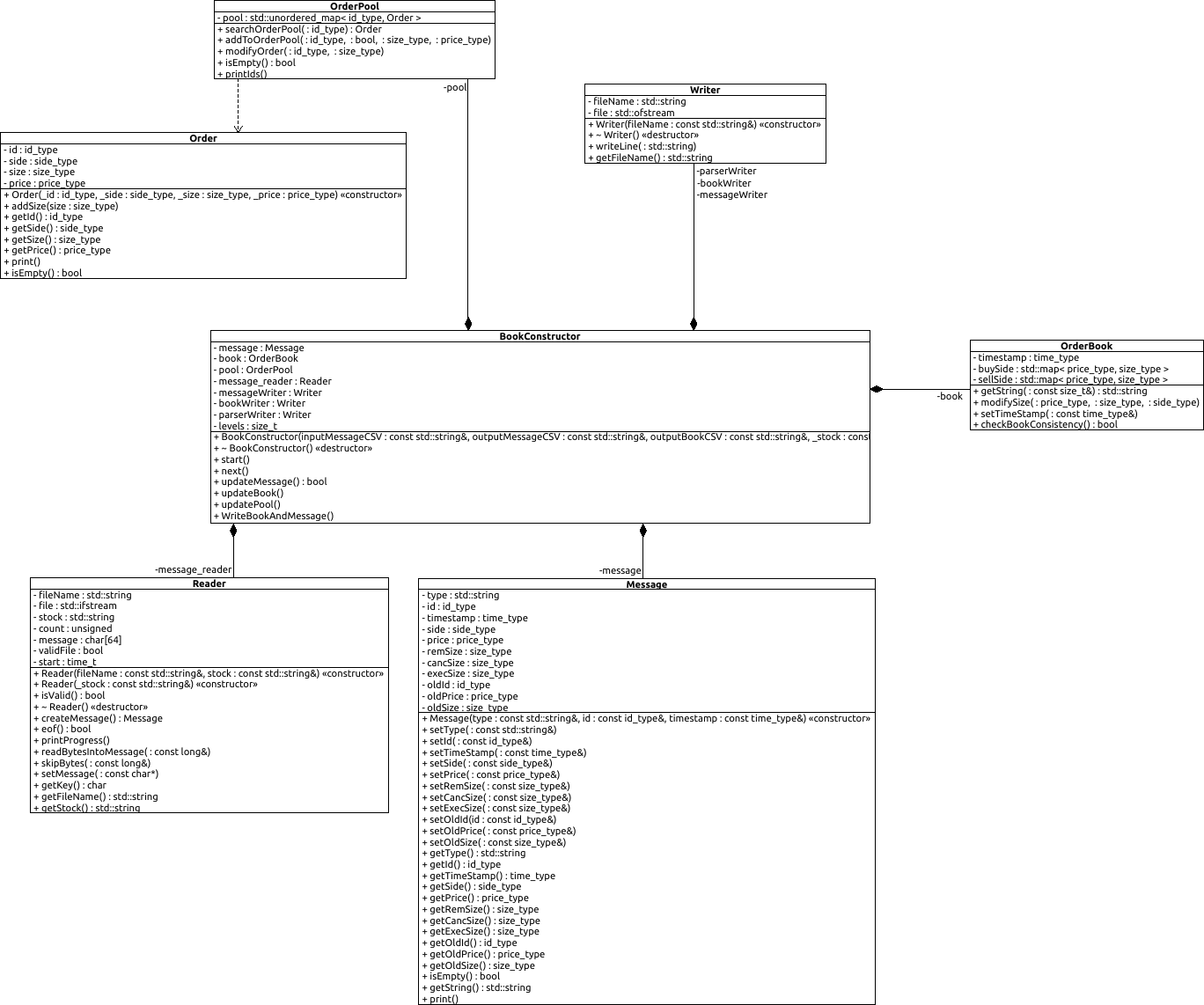
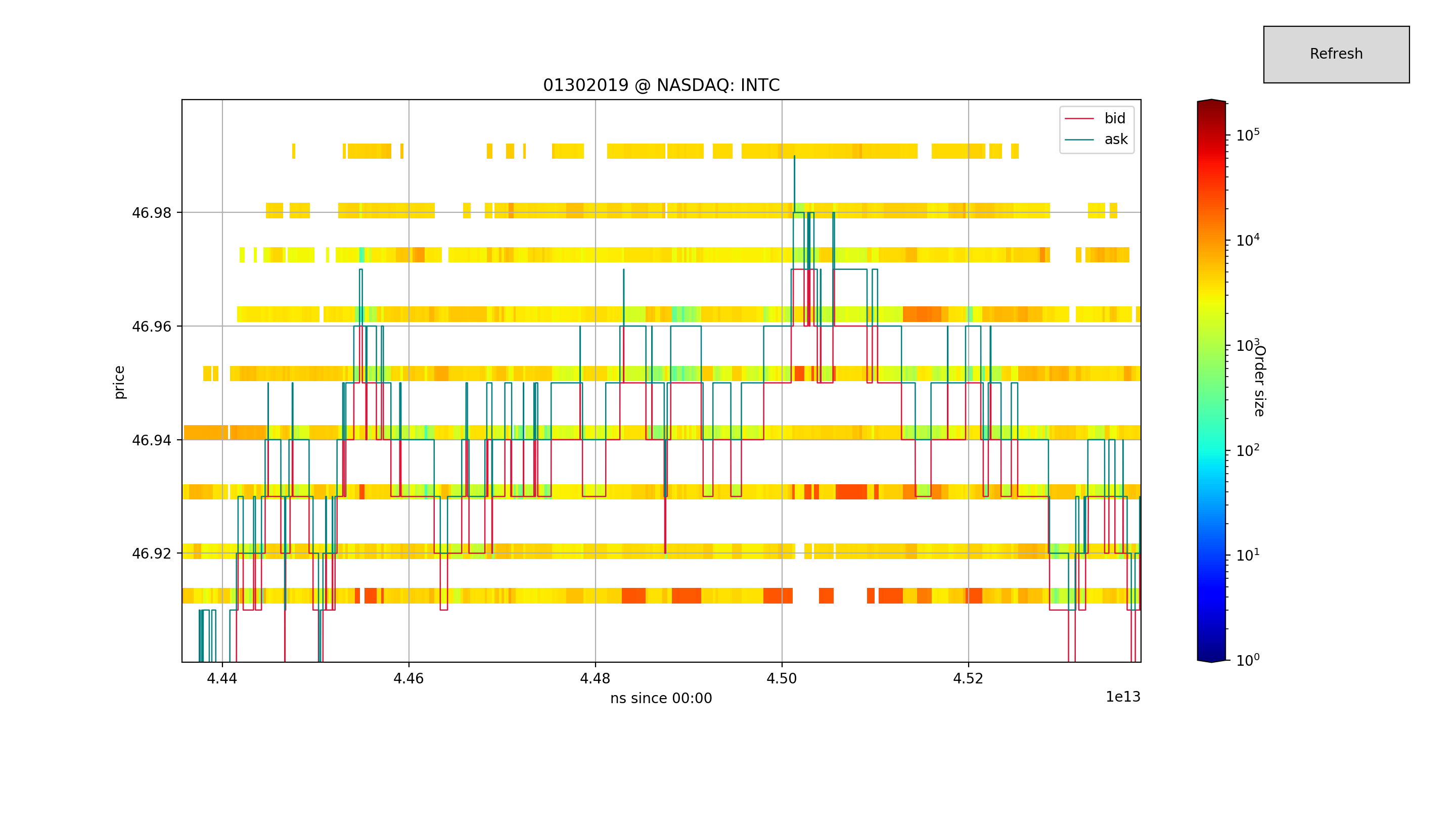
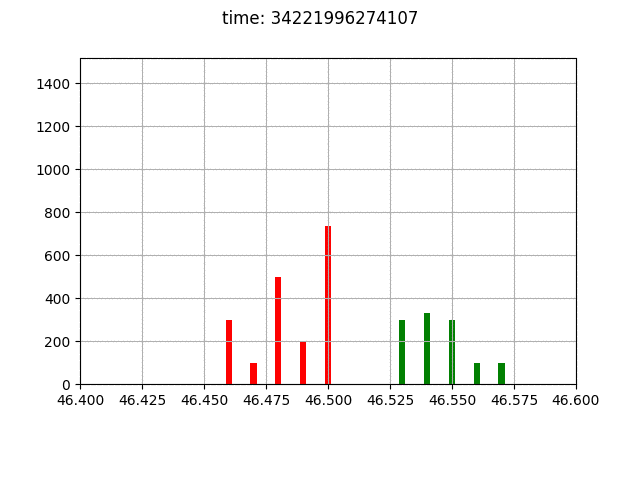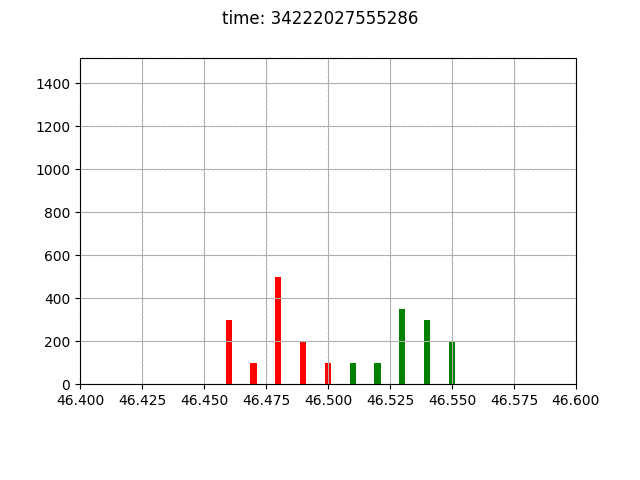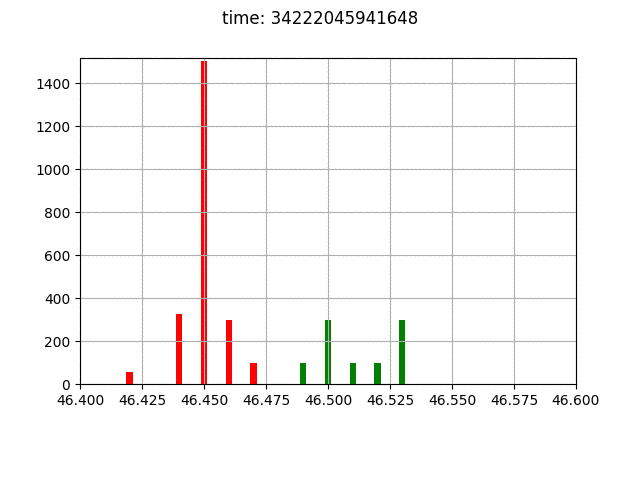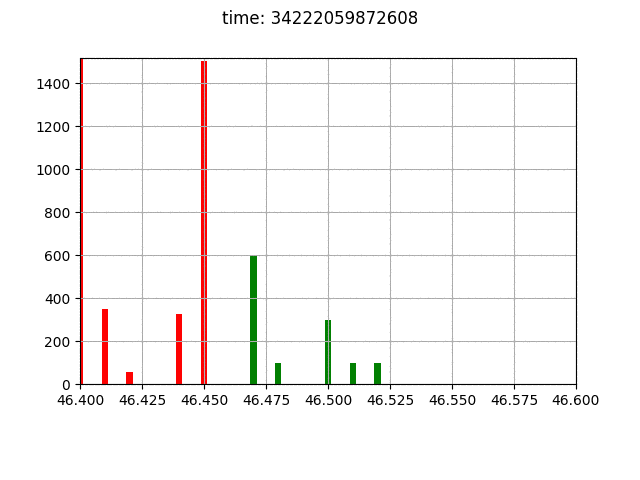
Given the NASDAQ Total View ITCH 50 data feed, reconstruct the full depth order book and related messages.
This is an efficient c++ implementation of reconstructing a Limit Order Book from data feed messages issued by NASDAQ according to the ITCH 50 data protocol specified at https://www.nasdaqtrader.com/content/technicalsupport/specifications/dataproducts/NQTVITCHSpecification.pdf. Some samples data are publicly available through NASDAQ public ftp at ftp://emi.nasdaq.com/ITCH/. The program outputs two csv files containing the messages and the related limit order book for the relative stock.
ITCH
│
└───bin (c++ executable)
│
└───build (dependency and object files)
│
└───doc
│ │
│ └───latex (LaTex-pdf documentation created with Doxygen)
│
└───data
│ │
│ └───binary (ITCH binary gzip compressed files from NASDAQ)
│ │
│ └───book (output of book csv)
│ │
│ └───messages (output of messages csv)
│ │
│ └───pk (pickle object files)
│
└───gtests (.cpp for tests)
│
└───images (images for README.md Markdown)
│
└───include (.hpp for main program)
│
└───examples (python implementation of some application example)
│
└───src (.cpp for main program)
This program aims to facilitate research in High Frequency Trading (HFT) providing the maximum amount of data released by NASDAQ, ready for use.
NASDAQ receives orders by traders and market participants, then its matching engine constructs the order book according to specific rules that may depend on the venue, and eventually sells to clients the data feed.
We were able to reconstruct the book with total depth at about 1Mio-2Mio messages per second, this figure also includes the parsing from the binary data.
To understand the difficulties of such an exercise is important to understand that the messages do not coincide with the orders received by NASDAQ, i.e. we do not need a matching engine to match supply and demand, but we are already given the result of the matching engine. Apart from interpreting the binary data according to the specification of the protocol we also have to retrieve information of past orders that new messages are referring to.
We can see this in the following example of submission and deletion of an order, according to the specifications the Add and Delete order would be:
| Message Type | Locate | Tracking | ns since 00:00 | Order id | Buy/Sell | Size | Stock | Price | MPID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 8007 | 0 | 28802131792425 | 45785 | B | 3000 | USO | 14.7200 | id_1 |
| ... | |||||||||
| D | 8007 | 0 | 28802131843697 | 45785 | id_1 |
As we can see once we observe the deletion order no information about the direction, size, stock and price are reported. Hence at each time we have to keep track of all the active orders in the book, in order to know what to do once we encounter the deletion order.
The output of the program are two .csv file with the following structure:
| time | type | id | side | size | price | cancSize | execSize | oldId | oldSize | oldPrice | MPID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29041353544851 | A | 49816 | 1 | 100 | 223.39 | id_1 | |||||
| 29041495720727 | D | 49816 | 1 | 0 | 223.39 | 100 | id_1 | ||||
| ... | ... |
| time | 1_bid_price | 1_bid_vol | 1_ask_price | 1_ask_vol | ... | n_ask_vol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29041353544851 | 223.39 | 100 | ... | ... | ||
| 29041495720727 | ||||||
| ... |
OS X & Linux:
git clone https://github.com/martinobdl/ITCH
cd ITCH
makeIn order to get some data needed to run the program (800MB)
wget ftp://anonymous:@emi.nasdaq.com/ITCH/Nasdaq\ PSX\ ITCH/20190327.PSX_ITCH_50.gz -P ./data/binary
# this file exists at date 05/02/2019
# otherwise download manually from the ftp and put the
# .gz file in ITCH/data/binaryTo reconstruct the book we can use the bash wrapper BookConstructor.sh which has the following usage:
usage: ./BookConstructor.sh [-lfh] [-n #] data_folder mm/dd/yyyy venue ticker
./BookConstructor.sh [-l] data_folder
./BookConstructor.sh [-h]
-h, --help Display usage instructions
-l, --list Display all the date venues available at data_folder/binary
-f, --force To force program execution if output files already exists
-n, Number of levels to store for the book, default is 5
for example ./BookConstructor.sh data_folder mm/dd/yyyy venue ticker -n N
will produce two output files named:
data_folder/book/mmddyyyy.venue_ITCH50_ticker_book_N.csv
data_folder/messages/mmddyyyy.venue_ITCH50_ticker_message.csv
Given that you have in /../../ITCH/data/binary the file PSX_ITCH/20190327.PSX_ITCH_50.gz
cd /../../ITCH
./BookConstructor.sh ./data 03/27/2019 PSX SPYthis will create two output .csv files, namely:
/../../ITCH/data/book/03272019.PSX_ITCH50_AAPL_book_5.csv
/../../ITCH/data/messages/03272019.PSX_ITCH50_AAPL_message.csvHere we report detailed description of message file output of the program:
At discrete time T1,T2,T3,... an output will be released by NASDAQ, the field names may have different meaning depending on the type of message. Hence here we will give a detailed description of the message csv.
| time | type | id | side | size | price | cancSize | execSize | oldId | oldSize | oldPrice | MPID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ... | A | ... | ... | added size | limit price of the add order | - | - | - | - | - | mpid of the market partecipant who issued the order |
| ... | D | ... | ... | remaining size after the deletion (may be total or partial) | price of the original order | canceled size by the message | - | - | - | - | mpid of the market partecipant who deleted the order |
| ... | E | ... | ... | remaining size after the execution | price of the order being executed | - | size being executed | - | - | - | mpid of the mp whos resting order is being executed |
| ... | P | ... | ... | execution of an hidden order | price of the execution | - | size of the hidden execution | - | - | - | - |
| ... | R | new id | equal to the old order | new size | new limit size | - | - | old order id | size of the order being replaced | price of the order being replaced | same as the old order (if any) |
| ... | C | ... | ... | remaining size after the execution | price at which the order is being executed | - | - | - | - | original price of the order | the mpid of the executed order |
In the gtest folders there are unit tests in order to test the principal components of the software, they are the Google c++ unittesting libraries. To compile and run the tests you would need the gtests and gmock libraries. They can be installed in the following way. Refer to https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/master/googletest/README.md for more details about the installation.
To install gtest-gmock:
# gtests
sudo apt-get install libgtest-dev
sudo apt-get install cmake
cd /usr/src/gtest
sudo cmake CMakeLists.txt
sudo make
sudo cp *.a /usr/lib
#gmock
sudo apt-get install libgmock-dev
cd /usr/src/gmock
sudo mkdir build
sudo cmake ..
sudo make
sudo cp *.a /usr/libTo run the tests:
cd /../../ITCH
make test
./bin/executeTestsIn the python folder there are some examples on how the program might be used to perform research on HFT.
environment.py is the environment definition and Algo.py is the agent abstract class from which we would implement the strategy.
The environment definition provides also some visualization tools.
requirements:
python3
numpy
pandas
matplotlib
tkinter
tqdm
python3 /../../ITCH/python/environment.py mmddyyyy venue stockpython3 /../../ITCH/python/Algo_fixedSpread.pyThe implemented strategy can be found at
[# 2013] Abernethy, J., Kale, S., Adaptive Market Making via Online Learning.
For more details about the API see the documentation in the doc/ folder
If you use this software in your research, please cite the paper using the following BibTeX:
@misc{https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5209267,
doi = {10.5281/ZENODO.5209267},
url = {https://zenodo.org/record/5209267},
author = {Bernasconi-De-Luca, Martino and Fusco, Luigi and Dragić, Ozrenka},
title = {martinobdl/ITCH: ITCH50Converter},
publisher = {Zenodo},
year = {2021},
copyright = {Open Access}
}
- Luigi Fusco https://github.com/luigif9
- Ozrenka Dragić https://github.com/oz-dr
- Martino Bernasconi-de-Luca https://github.com/martinobdl