Python template for KBC Component creation. Defines the default structure and all Bitbucket pipeline CI scripts for automatic deployment.
Use as a starting point when creating a new component.
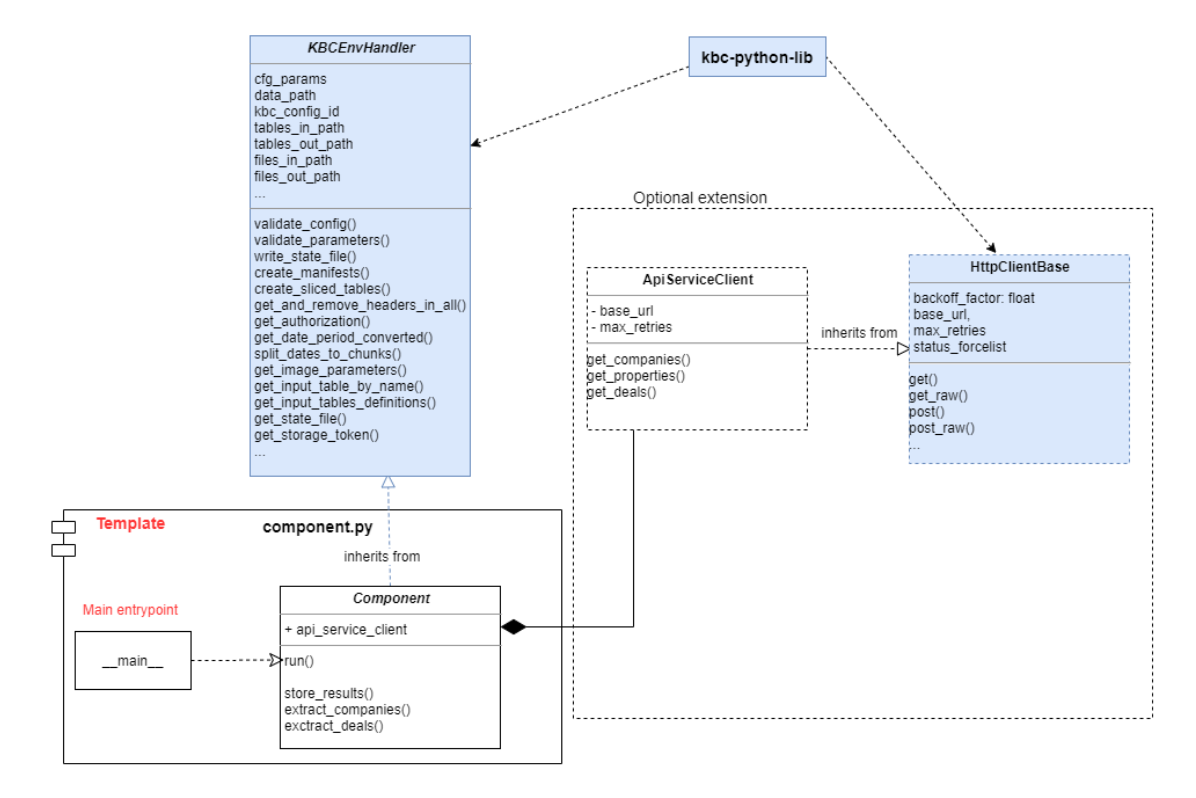
Example uses keboola-python-util-lib library providing useful methods for KBC related tasks and boilerplate methods often needed by components, for more details see documentation
Table of contents:
[TOC]
It is recommended to use the keboola-python-util-lib library, for each component. Major advantage is that it reduces the boilerplate code replication, the developer can focus on core component logic and not on boilerplate tasks. If anything is missing in the library, please fork and create a pull request with additional changes, so we can all benefit from it
Base components on KBCEnvHandler
- No need to write configuration processing and validation code each time
- No need to setup logging environment manually
- No need to write code to store manifests, write statefile, retrieve dates based on relative period, and many more.
- The main focus can be the core component logic, which increases the code readability for new comers.
Base Client on HtttpClientBase
- No need to write HTTP request handling over and over again
- Covers basic authentication, retry strategy, headers, default parameters
Process results using result.py package
- No need to use pandas
- Enables basic json response flattening
- Fixed headers, user values and more useful functionality
This template contains functional example of an extractor component,
it can be run with sample configuration and it produces valid results.
It is advisable to use this structure as a base for new components. Especially the component.py module, which should only
contain the base logic necessary for communication with KBC interface, processing parameters, collecting results
and calling targeted API service methods.
Clone this repository into new folder and remove git history
git clone https://bitbucket.org/kds_consulting_team/kbc-python-template.git my-new-component
cd my-new-component
rm -rf .git
git init
git remote add origin PATH_TO_YOUR_BB_REPO
git add .
git update-index --chmod=+x deploy.sh
git update-index --chmod=+x scripts/update_dev_portal_properties.sh
git commit -m 'initial'
git push -u origin master- Enable pipelines in the repository.
- Set
KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_APPenv variable in Bitbucket (dev portal app id)
In case it is not set on the account level, set also other required dev portal env variables:
KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_PASSWORD- service account passwordKBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_USERNAME- service account usernameKBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_VENDOR- dev portal vendorAPP_IMAGE- arbitrary tag name of the docker image e.g. “keboola-component”KBC_STORAGE_TOKEN- in case you wish to run KBC automated tests
The script execution is defined in three stages:
This script is executed on push to any branch except the master branch. It executes basic build and code quality steps. Following steps are performed: Build docker image Execute flake8 lint tests Execute python unittest (Optional) Push image with tag :test into the AWS repository for manual testing in KBC If any of the above steps results in non 0 status, the build will fail. It is impossible to merge branches that fail to build into the master branch.
This script is executed on any push or change in the master branch. It performs every step as the default stage. Additionally,
the ./scripts/update_dev_portal_properties.sh script is executed.
This script propagates all changes in the Component configuration files (component_config folder) to the Developer portal.
Currently these Dev Portal configuration parameters are supported:
configuration_schema.jsonshort_description.mdlong_description.md
The choice to include this script directly in the master branch was made to simplify ad-hoc changes of the component configuration parameters. For instance if you wish to slightly modify the configuration schema without affecting the code itself, it is possible to simply push the changes directly into the master and these will be automatically propagated to the production without rebuilding the image itself. Solely Developer Portal configuration metadata is deployed at this stage.
Whenever a tagged commit is added, or tag created this script gets executed. This is a deployment phase, so a successful build results in new code being deployed in KBC production.
At this stage all steps present in the default and master stage are executed. Additionally,
deploy.sh script that pushes the newly built image / tag into the ECR repository and KBC production is executed.
The deploy script is executed only after all tests and proper build steps passed.
Moreover, the deploy.sh script will be executed only in the master branch. In other words if you create a tagged commit in another branch, the pipeline gets triggered but deployment script will fail, because it is not triggered within a master branch. This is to prevent accidental deployment from a feature branch.
The template automatically chooses between STDOUT and GELF logger based on the Developer Portal configuration.
To fully leverage the benefits such as outputting the Stack Trace into the log event detail (available by clicking on the log event)
log exceptions using logger.exception(ex).
Recommended GELF logger setup (Developer Portal) to allow debug mode logging:
{
"verbosity": {
"100": "normal",
"200": "normal",
"250": "normal",
"300": "normal",
"400": "verbose",
"500": "camouflage",
"550": "camouflage",
"600": "camouflage"
},
"gelf_server_type": "tcp"
}This example contains runnable container with simple unittest. For local testing it is useful to include data folder in the root
and use docker-compose commands to run the container or execute tests.
If required, change local data folder (the CUSTOM_FOLDER placeholder) path to your custom path:
volumes:
- ./:/code
- ./CUSTOM_FOLDER:/dataClone this repository, init the workspace and run the component with following command:
git clone https://bitbucket.org:kds_consulting_team/kbc-python-template.git my-new-component
cd my-new-component
docker-compose build
docker-compose run --rm dev
Run the test suite and lint check using this command:
docker-compose run --rm test
The preset pipeline scripts contain sections allowing pushing testing image into the ECR repository and automatic testing in a dedicated project. These sections are by default commented out.
Running KBC tests on deploy step, before deployment
Uncomment following section in the deployment step in bitbucket-pipelines.yml file:
# push test image to ECR - uncomment when initialised
# - export REPOSITORY=`docker run --rm -e KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_USERNAME -e KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_PASSWORD -e KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_URL quay.io/keboola/developer-portal-cli-v2:latest ecr:get-repository $KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_VENDOR $KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_APP`
# - docker tag $APP_IMAGE:latest $REPOSITORY:test
# - eval $(docker run --rm -e KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_USERNAME -e KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_PASSWORD -e KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_URL quay.io/keboola/developer-portal-cli-v2:latest ecr:get-login $KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_VENDOR $KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_APP)
# - docker push $REPOSITORY:test
# - docker run --rm -e KBC_STORAGE_TOKEN quay.io/keboola/syrup-cli:latest run-job $KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_APP BASE_KBC_CONFIG test
# - docker run --rm -e KBC_STORAGE_TOKEN quay.io/keboola/syrup-cli:latest run-job $KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_APP KBC_CONFIG_1 test
- ./scripts/update_dev_portal_properties.sh
- ./deploy.shMake sure that you have KBC_STORAGE_TOKEN env. variable set, containing appropriate storage token with access
to your KBC project. Also make sure to create a functional testing configuration and replace the BASE_KBC_CONFIG placeholder with its id.
Pushing testing image for manual KBC tests
In some cases you may wish to execute a testing version of your component manually prior to publishing. For instance to test various
configurations on it. For that it may be convenient to push the test image on every push either to master, or any branch.
To achieve that simply uncomment appropriate sections in bitbucket-pipelines.yml file, either in master branch step or in default step.
# push test image to ecr - uncomment for testing before deployment
# - echo 'Pushing test image to repo. [tag=test]'
# - export REPOSITORY=`docker run --rm -e KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_USERNAME -e KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_PASSWORD -e KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_URL quay.io/keboola/developer-portal-cli-v2:latest ecr:get-repository $KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_VENDOR $KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_APP`
# - docker tag $APP_IMAGE:latest $REPOSITORY:test
# - eval $(docker run --rm -e KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_USERNAME -e KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_PASSWORD -e KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_URL quay.io/keboola/developer-portal-cli-v2:latest ecr:get-login $KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_VENDOR $KBC_DEVELOPERPORTAL_APP)
# - docker push $REPOSITORY:testOnce the build is finished, you may run such configuration in any KBC project as many times as you want by using run-job API call, using the test image tag.
For information about deployment and integration with KBC, please refer to the deployment section of developers documentation