Personalized notes for the AZ-900: Microsoft Azure Fundamentals Certification
- Virtual Machines
- Scaling
- PaaS in Azure
- Regions in Azure
- Availability Zones
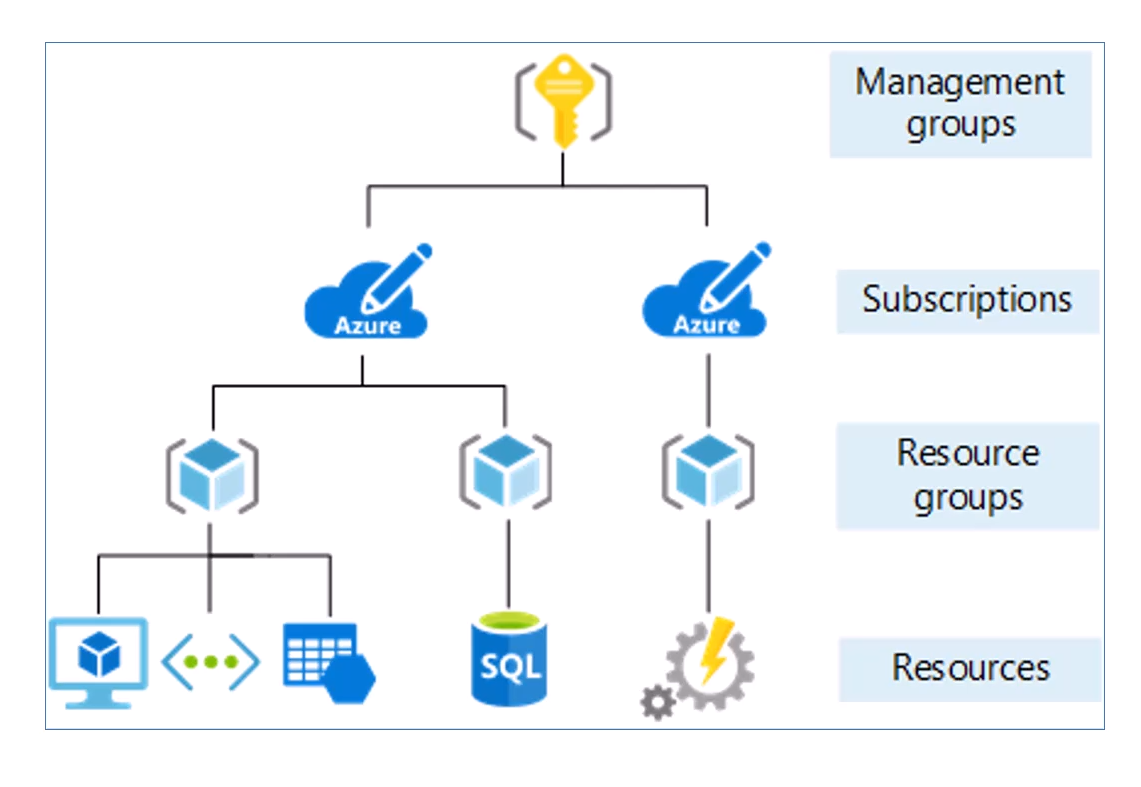
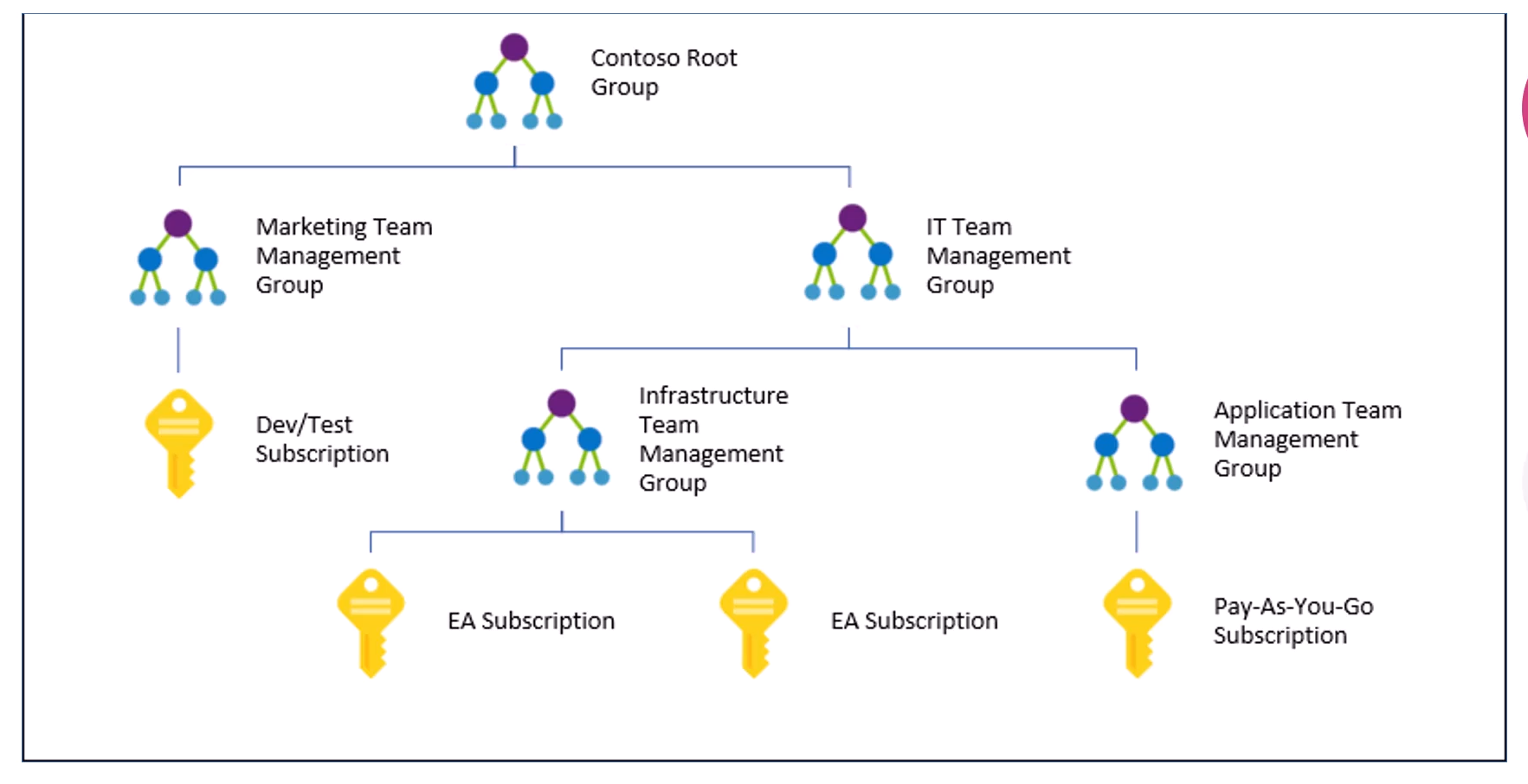
- Resource, Resource Groups and Scubscriptions
- VM Scale Sets
- Networking Services
- Storage Services
- Azure Active Directory
- Pricing Calculator
- Security & Governance
- Azure Arc
- Azure Resource Manager
- Other Services
- Notes from Mock Test
- In Azure, you are charged for the VM per second
- In Windows, you have an Administrator username and password where as in Linux, you have SSH keys to access the instance
- You need to pay for the Windows License by default, but can use yours if you already have one
- You can "resize" VMs to a bigger/smaller instance in Azure
- Auto Shutdown option available
- There is a limit to vertical scaling in Azure
- 96 vCPUs and 384 GB Memory is the upper limit for General Purpose Instances
- Vertical Scaling does not improve availability (since you're upgrading a one single instance)
- There is no limit to horizontal scaling
- PaaS mainly consists of two components: Packaged Code & Configurations
- Azure App Services is a PaaS
- Includes autoscaling features, CI/CD, containers, staging and dev environments, etc ...
- The Azure App Service Environment (ASE) is a Premium feature offering of the Azure App Service. It gives a single-tenant instance of the Azure App Service that runs right in your own Azure virtual network (VNet), providing network isolation and improved scaling capabilities.
- Usually, there is only one region per country, but in Azure, some countries have multiple regions
- As of now, Azure has over 60+ regions. Some regions of the world require special contracts with the local provider such as Germany and China.
- You must select a region while creating most resources
- In Azure, you have something called a region pair, where two regions are paired. And these paired regions have highest speed connections and special treatment during Azure updates. They are usually used for Disaster Recovery (DR)
- Sovereign Regions are special clouds not available to the public but associated with the Government. You need special permissions/approval to connect to those cloud regions
- Not every region in Azure support AZs
- There are 3 types of services in Azure:
- Zonal: You deploy services to a specific AZ and duplicate it to other AZs for backup and availability
- Zone-Redundant: Azure automatically deploys across multiple AZs in the region
- Always Available: Services deployed globally across multiple regions
LRS => Locally Redundant Storage
ZRS => Zone Redundant Storage
GRS => Geo Redundant Storage
RA-GRS => Read-Access Geo Redundant Storage
- Geo-redundant storage (GRS) copies your data synchronously three times within a single physical location in the primary region using LRS. It then copies your data asynchronously to a single physical location in the secondary region. Within the secondary region, your data is copied synchronously three times using LRS
- Resources can be grouped with Resource Groups. RGs are associated with a region but it can contain resources from different regions.
- Each Resource must belong to only one resource group
- Permissions can be assigned at the resource group level
- Subscription is a billing unit in Azure
- There is a payment method associated with each subscription
- Subscription Plans include Free Plan, Pay-As-You-Go, Enterprise Agreement ....
- Subscriptions are usually used to seperate out diff depts in a business, Ex: Finance, IT, Sales.... OR seperate by Geography NA, Europe, Asia
- There is not a limit to the number of subscriptions a single user can be included on
- Multiple Virtual Machines running the same code
- Can handle upto 100 VMs in a single scale set. Can configure it upto a 1000 VMs
- VM Scale set is free but you do pay for the underlying instances
- VMSS provides autoscale features and has a built in load balancer. You still need to have a way to deploy your code to the new servers, as you do with regular VMs
- Azure Availability Sets allow you to tell Azure which virtual machines are identical, so that Azure will keep them apart physically inside the datacenter. This helps when there are either expected or unexpected downtime, by increasing the chances that one issue does not affect all VMs in a single Availability Set.
- Azure Virtual Desktop is a desktop version of Windows that runs in the cloud. You can log into it from anywhere
- ExpressRoute - A high speed private connection to Azure
- Peering Virtual Networks allows instances in one VM to communicate with instances in other VM. This can be global as well
- Virtual networks can be connected by either peering, or with installing network gateway devices on each.
- A VPN Gateway needs to be configured on the company's network to establish a site-to-site VPN connection to connect to Azure
- You have an option of creating a public/private endpoint on a resource that is created.
- A private endpoint is a network interface that uses a private IP address from your virtual network. This network interface connects you privately and securely to a service that's powered by Azure Private Link. By enabling a private endpoint, you're bringing the service into your virtual network.
- In Azure, you create a Storage account and in that account you have 4 different types of storages:
- Containers or Blobs (Similar to object storage in S3)
- File Shares
- Queues
- Tables
- You have
StandardandPremiumperformance types in Azure Storage. Premium Performance = Low Latency - General purpose v2 is the standard storage account type for blobs, file shares, queues, and tables. Recommended for most scenarios using Azure Storage.
- A single Azure subscription can have up to 250 storage accounts per region, and each storage account can store up to 5 Petabytes.
- Azure Files offers two industry-standard file system protocols for mounting Azure file shares: the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol and the Network File System (NFS) protocol
- In Azure storage you pay per GB whereas in Disk Storage, you pay for the full capacity (ex: 8GB Hard Disk)
Azure Storage => Unmanaged
Disk Storage => Managed
- Azure Storage Explorer is a software that can be run on your local machine to upload files to storage. It is getting depreciated soon and is replaced with Storage browser instead which performs similar functionality as well
- AZcopy is a CLI tool that allows you to copy files across blob containers (Storage) in Azure. You can also use it to download files locally or even transfer to a storage bucket on another cloud
- Azure File Sync enables to sync on premises file server in the cloud
- Azure Migrate is a service that allows you to easily migrate to the cloud. It scans for VMs, databases, services in your environments (on-premises) and plans for your migration
- DataBox is a physical device that you can request for to transfer data to Azure offline
- Azure Active Directory (AAD) is an Identity as a Service provided by Azure. It is not the same as the traditional Active Directory that runs on Windows
- Developers can use AAD to implement authentication for their end users
- There is an option called Conditional access in AAD which allows to set up MFA and other restrictions on detecting unusual login
- Azure Active Directory provides the following licenses: Free, Office 365, Premium
- AD Connect is used to synchronize your corporate AD with Azure AD.
- Azure AD can control the access of both the apps and the app resources as well.
- With Azure AD B2B collaboration, you can invite anyone to collaborate with your organization using their own work, school, or social account. ie- as a guest user
- Azure Tenant is a dedicated and trusted instance of Azure AD that's automatically created when your organization signs up for a Microsoft cloud service subscription.
- Azure AD Domain Services (Azure AD DS) provides managed domain services such as domain join, group policy, lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP), and Kerberos/NTLM authentication. You use these domain services without the need to deploy, manage, and patch domain controllers (DCs) in the cloud.
- private preview: Few customers are invited to experience the new features
- public preview:
- Customers with AAD License are allowed to experience the new features:
- Microsoft provides support
- SLAs do not apply
- In this phase, customers can opt-in to the preview experience.
- Generally available (GA):
- the feature is open for any licensed customer to use
- the new feature impacts existing functionality unlike public preview phase
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/support/legal/preview-supplemental-terms/
- Privileged Identity Management (PIM) is a service in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) that enables you to manage, control, and monitor access to important resources in your organization
- PIM provides time-based and approval-based role activation to mitigate the risks of excessive, unnecessary, or misused access permissions on resources that you care about
- Some key features of PIM:
- Enforce multi-factor authentication to activate any role
- Get notifications when privileged roles are activated
- Just In Time (JIT) Model: You request for permissions only when you need it
- Just-Enough-Access (JEA): Least previlege principle
- The three principles of zero trust are: verify explicitly, use least privilege access, and assume breach
- Roles in Azure are similar to GCP. They are permissions binded to users
Policies are attached to resources whereas roles are attached to users
- Azure has a Total Cost Of Ownership (TCO) calculator that include the price of electiricty, cooling, maintenance and so on ...
- This can be used to compare your on-premises(TCO) cost with the cloud
Tools used for security and Governance:
- You can enforce a policy on resources created.
- For Example: You can have all VMs have a backup on a regular basis
- Azure Policy helps to enforce organizational standards and to assess compliance at-scale.
- You can create Blueprints and attach it to a subscription. The blueprint is created when the subscription is active. The blueprint maybe like have 5 VM instances with one Load balancer
- Azure DDos Protection Basic is free, while you can upgrade to Standard for a fee.
- The modern way to store cryptographic keys, signed certificates and secrets in Azure
- Read only locks and cannot delete locks on resources can be used
- Centralized repository for all the compliance artefacts by Azure
- It also contains security audits conducted by third parties
- Azure Security Center - unified security management and threat protection; a security dashboard inside Azure Portal
- Microsoft Defender is a paid service provided by Azure for security protection of cloud services
- Azure Firewall has a threat-intelligence option that will automatically block traffic to/from bad actors on the Internet. It can blacklist IPs
- A common cyber security approach used by organizations to protect their digital assets is to leverage a defense-in-depth strategy. The SANS Institute defines defense-in-depth as 'protecting a computer network with a series of defensive mechanisms such that if one mechanism fails, another will already be in place to thwart an attack.'
- Azure Arc is a service that allows you to manage resources running on on-premises and multi-cloud. It is basically a unified view of all the resources that you are using
-
Azure Resource Manager is what you interact with behind the hood when creating resources in the Console or CLI, powershell or anything ...
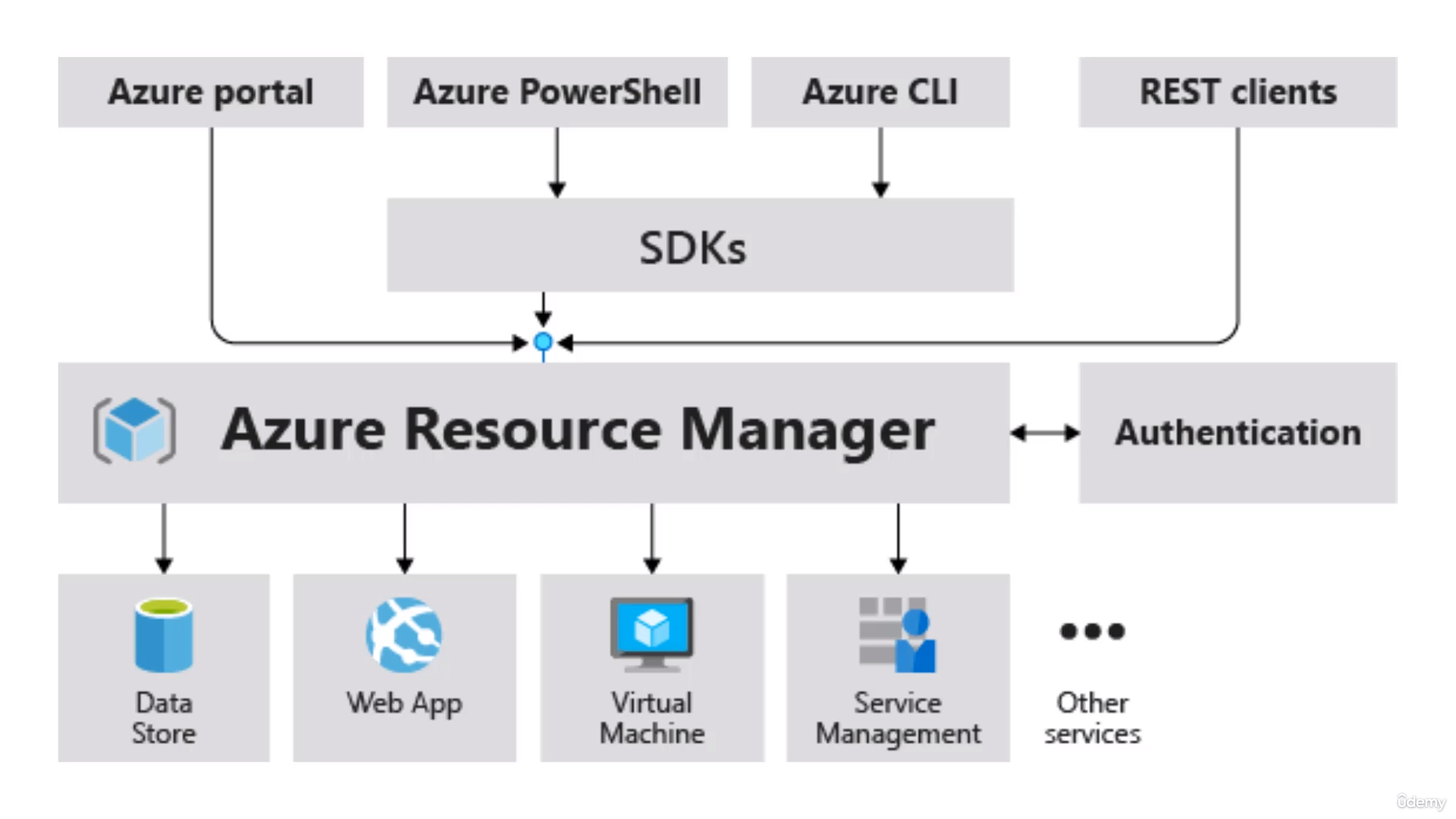
-
You can create ARM templates and deploy those ARM templates to create Resources (more like Infrastrcture as a Code)
-
ARM templates are created in JSON
- Analyzes all your resources and provides recommendations that you can do to save costs, minimize vulnerabilities and so on ...
- Used to alert overall health and wellbeing of Azure Datacenters, Regions if you're resources are present in any one of those regions
- Allows you to monitor all Azure Resources in one place
- Diagnostic settings in many Azure resources allows you to collect, export, query and view logs in Azure Monitor
- Workbooks in Azure Monitor allows you to create and manage a visual reports of your own metrics
- AM allows you to respond to issues by firing alerts that can send notifications or by calling automated solutions. Ex: Fire an alert everytime a new VM is created
- All it takes is an API call to embed the ability to see, hear, speak, search, understand, and accelerate advanced decision-making into your apps.
- Features: Translation, Image Recognition, Text Recognition, Speech-To-Text, Text-to-Speech, openAI and more ...
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/cognitive-services/#overview
- A virtual machine needs a network card, storage and a virtual network. It does not need a public IP address. In fact, most Azure VMs are private and are not accessible from the Internet.
- Azure Powershell scripts and CLI scripts are not compatible with each other. PowerShell has it's own language, different than CLI
- Azure is a public cloud, but has some private cloud offerings such as the GovCloud
- Firewall is part of the perimeter security
- You get 200 USD worth of free credits to spend in Azure for the first time you create an account. Using up the free credits causes all your resources to be stopped until you decide to get a paid account.
- In Azure, we apply NSG(Network Security Groups) at subnet or individual NIC level(VM) whereas in AWS these can only be applied at individual VM level. NACL is applied at subnet level in AWS.
- If Azure does not meet its SLA, A discount will be applied to the customer's azure bill (as service credit)
- Infrastructure as a service is the easiest to migrate into, from an existing hosted app on-premises
- 99.99% is 4 minutes per month of downtime
- Azure DNS private zones provide a simple, reliable, secure DNS service to manage and resolve names in a virtual network without the need to create and manage a custom DNS solution. Use your own domain names and get name resolution for virtual machines within and between virtual networks.
- Additionally, configure zone names with a split-horizon view to allow a private and a public DNS zone to share the same name.
- Application gateway can make load balancing decisions based on the URL path, while a load balancer can't
- Application Gateways also comes with an optional Web Application Firewall (or WAF) as a security benefit
- The Trust Center is a publicly accessible web portal that acts as a single point of focus for an organization that needs resources and in-depth information regarding the Microsoft principles of security, privacy, and compliance.
- Business Continuity means the same as Disaster Recovery
- Each resource in Azure has a Resource Health blade
- A Log Analytics workspace is a unique environment for log data from Azure Monitor and other Azure services
- Cosmos DB is low latency, and even offers sub 5-ms response times at some levels.
- If you don't want to spend over a certain amount in Azure, implement a spending limit in the account center