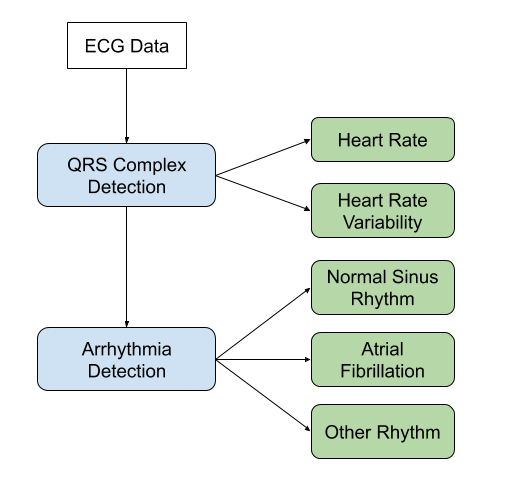
An algorithm that automatically detects atrial fibrillation and other arrhythmias from the ECG signal.
The data we will use comes from the Computing in Cardiology (CinC) Challenge 2017 dataset hosted on Physionet.
The dataset contains thousands of short ECG snippets (30s - 60s) from the AliveCor mobile ECG monitor. The original challenge was to build a 4-class classifier for sinus rhythm, atrial fibrillation, alternative rhythm, and noisy record. We will throw out the noisy records and build a two-class classifier distinguishing between sinus rhythm and another rhythm (atrial fibrillation included).
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a condition where the heartbeat becomes erratic and the upper chambers of the heart quiver and shake. If there’s a lurking blood clot, this shaking can break it loose and send it up through the blood vessels to the brain, where it can cause a stroke. People with AFib have a 5 times greater likelihood of having a stroke, and doctors typically put patients with the condition on blood-thinning medications that prevent clots. Article
- Arrhythmia: An irregular heart rhythm.
- Sinus Rhythm: The normal, regular heart rhythm, paced by the sinus node.
- Atrial fibrillation: An irregular rhythm caused by multiple, haphazard depolarizations across the atria.
The heart is made up of four chambers, two atria and two ventricles. The atria pump blood into the ventricles and then the ventricles pump blood throughout the body. Each heart cell is polarized, meaning there is a different electrical charge inside and outside of the cell. At rest, the inside of the cell is negatively charged compared to the outside. When the cell depolarizes, positive charges outside of the cell flow inside and makes the interior of the cell positively charged relative to the outside. This depolarization causes the cell to contract. The movement of charges across a heart cell’s membrane is the source of the electrical activity that gets measured by an ECG.
- Pan-Tompkins Algorithm
- Extending Pan-Tompkins
- Computing in Cardiology Challenge 2017
- Data Exploration
- Feature Extraction
- Modelling
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a condition where the heartbeat becomes erratic and the upper chambers of the heart quiver and shake. If there’s a lurking blood clot, this shaking can break it loose and send it up through the blood vessels to the brain, where it can cause a stroke. People with AFib have a 5 times greater likelihood of having a stroke, and doctors typically put patients with the condition on blood-thinning medications that prevent clots
In a normal heart rhythm, the sinus node generates the impulse that causes the atria to contract. This impulse is propagated to the AV node and then throughout ventricles, causing the ventricles to contract. This process results in a very regular rhythm called sinus rhythm.