This project aims to analyze stock data from 2017 and 2018 to calculate the yearly return and total daily volume for green energy companies. In addition, the created subroutine allows for the analysis of new data for the future. I made a subroutine to conduct the analysis and then refactored it for optimization for larger datasets.
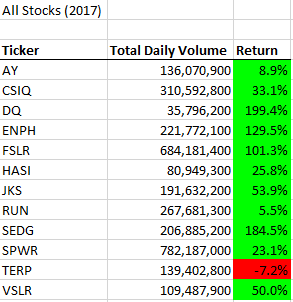
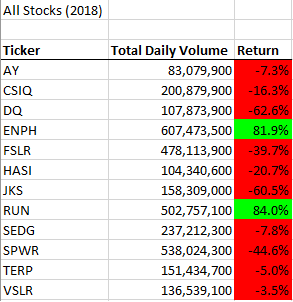
Running the VBA script produces the following tables:
By looking at the tables, we can see that the year 2017 had a higher rate of return compared to 2018. The companies $ENPH and $RUN are worthwhile to research as they both survived the bear market of 2018. However, within our dataset, we do not have enough information to deduce why these two companies had a higher rate of return. For instance, we do not have access to the shares outstanding to determine the market capitalization. It is a possibility that the companies that had positive returns in 2018 were undervalued in 2017, and the market corrected their share price. However, this is purely speculation, and there is no robust evidence to support this statement.
- The script asks the user to input the year they would like to analyze to allow future data analysis and not hardcode the data:
yearValue = InputBox("What year would you like to run the analysis on?")- The script then formats the output worksheet by making a title cell named
All Stocks (YEAR)and three colors with the following headers:
- Ticker
- Total Daily Volume
- Return
' Format the output sheet on All Stocks Analysis worksheet
Worksheets("All Stocks Analysis").Activate
Range("A1").Value = "All Stocks (" + yearValue + ")"
' Create a header row
Range("A3").Value = "Ticker"
Range("B3").Value = "Total Daily Volume"
Range("C3").Value = "Return"- An Array is initialized to assign each ticker to an element in the array:
Dim tickers(11) As String
tickers(0) = "AY"
tickers(1) = "CSIQ"
tickers(2) = "DQ"
tickers(3) = "ENPH"
tickers(4) = "FSLR"
tickers(5) = "HASI"
tickers(6) = "JKS"
tickers(7) = "RUN"
tickers(8) = "SEDG"
tickers(9) = "SPWR"
tickers(10) = "TERP"
tickers(11) = "VSLR"- Two variables are created in Double data format are made to hold the starting and ending stock price. Then, the script switches to the user-specified worksheet to read the yearly stock data and assign the number of rows to the
RowCountvariable.
' 3a) Initialize variables for starting price and ending price
Dim startingPrice As Double, endingPrice As Double
' 3b) Activate data worksheet
Worksheets(yearValue).Activate
' 3c) Get the number of rows to loop over
RowCount = Cells(Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row- The script utilizes a nested loop to iterate through the array of each ticker. The
totalVolume = 0is set to 0 for each ticker. The inner loop goes through the rows to calculate each ticker's total volume, starting price, and ending price.
' 4) Loop through tickers
For i = 0 To 11
ticker = tickers(i)
totalVolume = 0
' 5) loop through rows in the data
Worksheets(yearValue).Activate
For j = 2 To RowCount
' 5a) Find total volume for current ticker
If Cells(j, 1).Value = ticker Then
totalVolume = totalVolume + Cells(j, 8).Value
End If
' 5b) Find starting price for current ticker
If Cells(j - 1, 1).Value <> ticker And Cells(j, 1).Value = ticker Then
startingPrice = Cells(j, 6).Value
End If
' 5c) Find ending price for current ticker
If Cells(j + 1, 1).Value <> ticker And Cells(j, 1).Value = ticker Then
endingPrice = Cells(j, 6).Value
End If
Next j
'6) Output data for current ticker
Worksheets("All Stocks Analysis").Activate
Cells(4 + i, 1).Value = ticker
Cells(4 + i, 2).Value = totalVolume
Cells(4 + i, 3).Value = endingPrice / startingPrice - 1
Next i- Finally, the script makes the table easier to read by adding formatting. The header row has a bold font with a line border on the bottom to visually indicate the column names. The column width is automatically changed to auto-fit the data using the
AutoFitproperty. Color formatting is applied using a for loop to iterate through each cell to determine whether the yearly return is positive or negative. If positive, the interior color will turn green, and if negative, the interior color will be red.
' Formatting
Worksheets("All Stocks Analysis").Activate
Range("A3:C3").Font.Bold = True ' Header
Range("A3:C3").Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = xlContinuous
Range("B4:B15").NumberFormat = "#,##" ' Total Daily Volume
Range("C4:C15").NumberFormat = "0.0%" ' Return %
Columns("B").AutoFit
' Conditional color coding on return %
Dim dataRowStart, dataRowEnd As Integer
dataRowStart = 4
dataRowEnd = 15
For i = dataRowStart To dataRowEnd
If Cells(i, 3) > 0 Then
' Color the cell green if postive return
Cells(i, 3).Interior.Color = vbGreen
ElseIf Cells(i, 3) < 0 Then
' Color the cell red the cell red if negative return
Cells(i, 3).Interior.Color = vbRed
Else
' Clear the cell color in unhandled cases
Cells(i, 3).Interior.Color = xlNone
End If
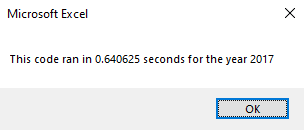
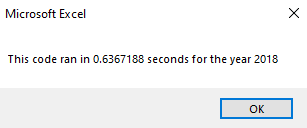
Next iThe time to complete the execution of the VBA code is tested with the following:
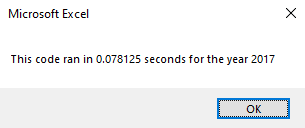
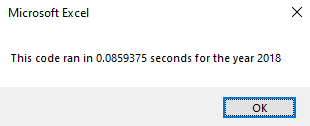
Dim startTime As Single, endTime As Single
startTime = Timer
' Script code runs here...
endTime = Timer
MsgBox "This code ran in " & (endTime - startTime) & " seconds for the year " & (yearValue)There are two variables, startTime and endTime. When the code begins, the startTime and when ending the, endTime is set equal to the Timer function. Subtracting the startTime from the endTime indicates how long the code took to execute.
Refactoring produces the same output as the original code but is now designed differently.
The benefits of refactoring code include:
- Code can take fewer steps
- Optimize to use less memory
- Allow for easier future changes by improving the logic or readability
The disadvantages of refactoring code include:
- Time consumption is the main disadvantage is that the time spent on refactoring is uncertain
- Potential of introducing bugs that were not present beforehand
The main advantage of refactoring the stock analysis code is how long the script took to execute the calculations. There was a speedup time of over 700% in the refactored code compared to the original. The few seconds of reduction may seem insignificant, but the speedup time will be a significant factor when analyzing larger datasets. There were no apparent disadvantages of refactoring the code besides the time spent in this case.