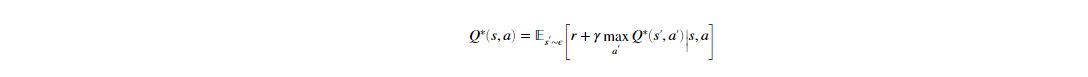Authors: Bhartendu Thakur, Viji Narayan
Description
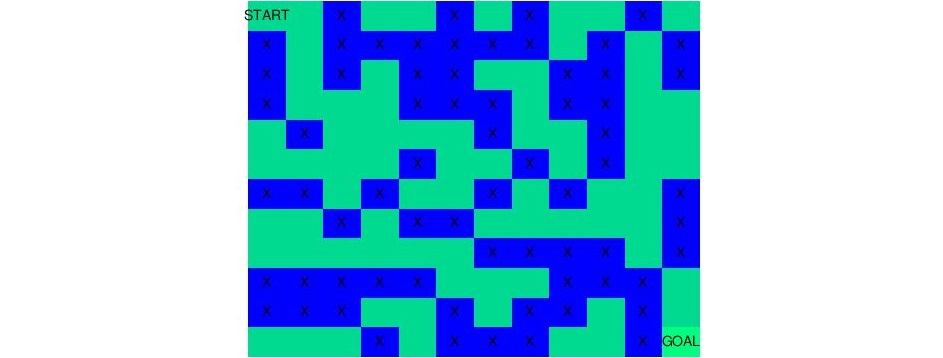
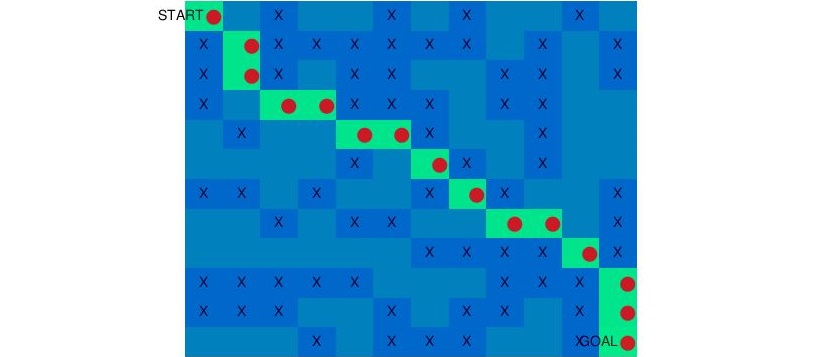
In this example we will sovle maze shown above using Q-Learning (Reinforcement Learning)
Reinforcement Learning
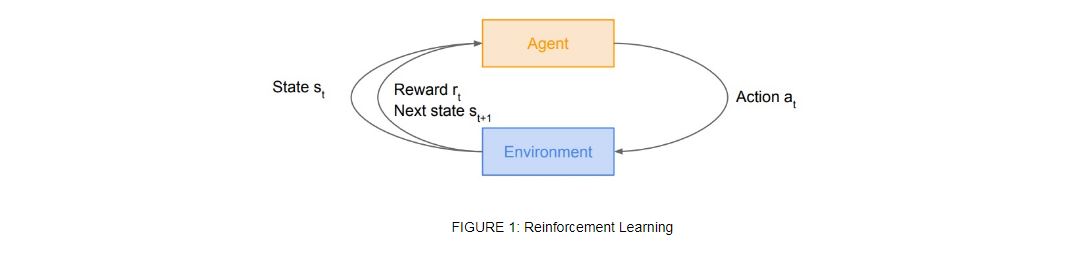
Reinforcement learning (Sutton & Barto, 1998) is a principled mathematical framework for experience-driven, goal-directed learning and decision making. RL starts with interaction between agent and environment, agent take action in environment, which drives it to next state and receives a rewards based on the goodness of that action. As shown in figure 1, at any time-step t, agent being in state take action in environment gets reward and observe next state . Reinforcement learning algorithms, push up the probabilities of taking good actions to achieve desired goals. In this example we'll solve n x n maze using Q-learning technique.
Q-Learning
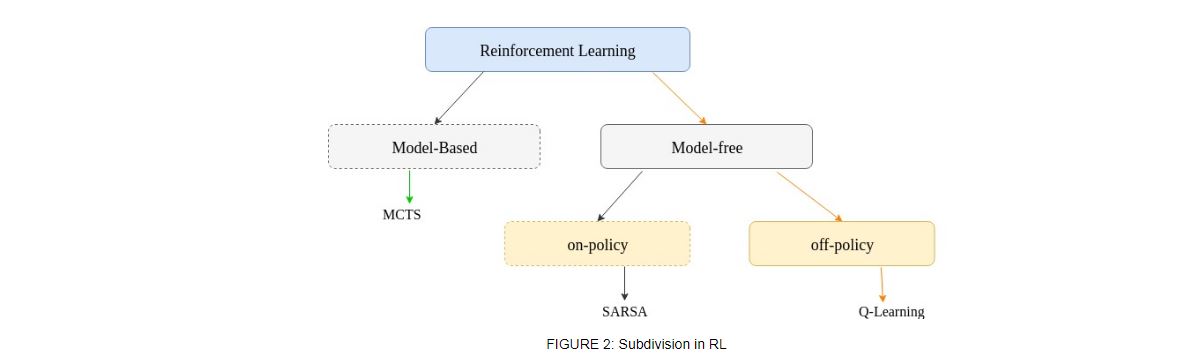
Reinforcement learning can generally be sub-divided into model-free & model-based as shown in figure 2. In model-based RL dynamical model of the environment is used & in model-free RL, a policy or value function is learnt.
Model-free RL is divided into two broad categories, off-policy & on-policy learning. On-policy method such as SARSA, return for state-action pairs assuming the current policy continues to be followed is estimated, where return is termed for total discounted future reward. In off-policy methods policy used to generate training data (Behaviour policy) & policy to be estimated (Target policy) are different.
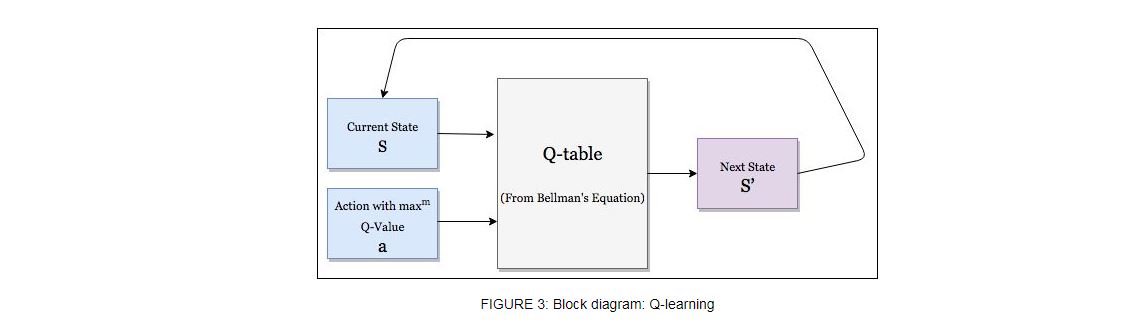
Q-learning as shown in figure 2, a model-free, off-policy learning proposed by (Watkins & Dayan, 1992) is basically process of evaluating the goodness of a state-action pair. Q-value at state s and action a, is defined the expected cumulative reward from taking action a in state s and then following the policy. In other words Q-Learning is off-policy learning as one can choose our action just by looking at , without worrying about what happens next. In each episode, Q-values of current state s are updated using the Q-value of next state s' and the greedy action a' using Bellman Optimality Equation which is given below,
Bellman Equation for Q-value Function serves as a target (greedy) policy along with ϵ greedy policy as behavior policy where random action is chosen with a small probability of ϵ, greedy action with probability of (1 - ϵ). Decaying-ϵ, with time another kind of behavior policy.