Mangiola et al., (2020). tidyHeatmap: an R package for modular heatmap production based on tidy principles. Journal of Open Source Software, 5(52), 2472, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.02472
Please have a look also to
- tidygate for adding custom gate information to your tibble
- tidySingleCellExperiment for tidy manipulation of Seurat objects
- tidyseurat for tidy manipulation of Seurat objects
- tidybulk for tidy high-level data analysis and manipulation
- tidySummarizedExperiment for heatmaps produced with tidy principles
website: stemangiola.github.io/tidyHeatmap
tidyHeatmap is a package that introduces tidy principles to the
creation of information-rich heatmaps. This package uses
ComplexHeatmap
as graphical engine.
Advantages:
- Modular annotation with just specifying column names
- Custom grouping of rows is easy to specify providing a grouped tbl.
For example
df |> group_by(...) - Labels size adjusted by row and column total number
- Default use of Brewer and Viridis palettes
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
heatmap |
Plots base heatmap |
group_by |
dplyr function - groups heatpmap rows/columns |
annotation_tile |
Adds tile annotation to the heatmap |
annotation_point |
Adds point annotation to the heatmap |
annotation_bar |
Adds bar annotation to the heatmap |
annotation_line |
Adds line annotation to the heatmap |
layer_point |
Adds layer of symbols on top of the heatmap |
layer_square |
Adds layer of symbols on top of the heatmap |
layer_diamond |
Adds layer of symbols on top of the heatmap |
layer_arrow_up |
Adds layer of symbols on top of the heatmap |
layer_arrow_down |
Add layer of symbols on top of the heatmap |
layer_star |
Add layer of symbols on top of the heatmap |
layer_asterisk |
Add layer of symbols on top of the heatmap |
split_rows |
Splits the rows based on the dendogram |
split_columns |
Splits the columns based on the dendogram |
save_pdf |
Saves the PDF of the heatmap |
+ |
Integrate heatmaps side-by-side |
as_ComplexHeatmap |
Convert the tidyHeatmap output to ComplexHeatmap for non-standard “drawing” |
wrap_heatmap |
Allows the integration with the patchwork package |
To install the most up-to-date version
devtools::install_github("stemangiola/tidyHeatmap")To install the most stable version (however please keep in mind that this package is under a maturing lifecycle stage)
install.packages("tidyHeatmap")If you want to contribute to the software, report issues or problems with the software or seek support please open an issue here
The heatmaps visualise a multi-element, multi-feature dataset, annotated with independent variables. Each observation is a element-feature pair (e.g., person-physical characteristics).
| element | feature | value | independent_variables |
|---|---|---|---|
chr or fctr |
chr or fctr |
numeric |
… |
Let’s transform the mtcars dataset into a tidy “element-feature-independent variables” data frame. Where the independent variables in this case are ‘hp’ and ‘vs’.
mtcars_tidy <-
mtcars |>
as_tibble(rownames="Car name") |>
# Scale
mutate_at(vars(-`Car name`, -hp, -vs), scale) |>
# tidyfy
pivot_longer(cols = -c(`Car name`, hp, vs), names_to = "Property", values_to = "Value")
mtcars_tidy## # A tibble: 288 × 5
## `Car name` hp vs Property Value[,1]
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 Mazda RX4 110 0 mpg 0.151
## 2 Mazda RX4 110 0 cyl -0.105
## 3 Mazda RX4 110 0 disp -0.571
## 4 Mazda RX4 110 0 drat 0.568
## 5 Mazda RX4 110 0 wt -0.610
## 6 Mazda RX4 110 0 qsec -0.777
## 7 Mazda RX4 110 0 am 1.19
## 8 Mazda RX4 110 0 gear 0.424
## 9 Mazda RX4 110 0 carb 0.735
## 10 Mazda RX4 Wag 110 0 mpg 0.151
## # … with 278 more rows
For plotting, you simply pipe the input data frame into heatmap, specifying:
- The rows, cols relative column names (mandatory)
- The value column name (mandatory)
- The annotations column name(s)
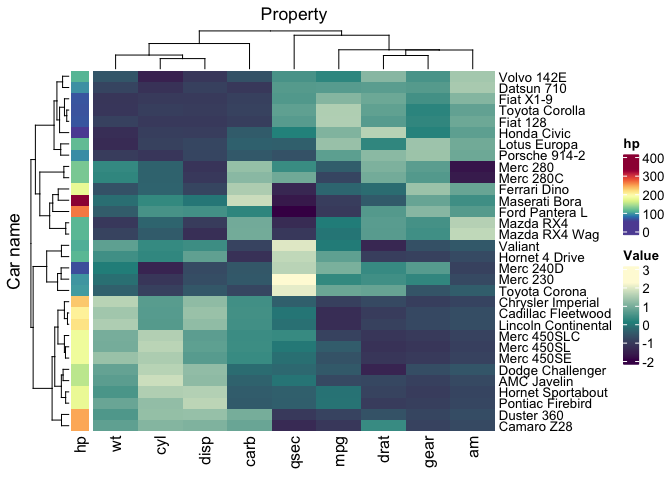
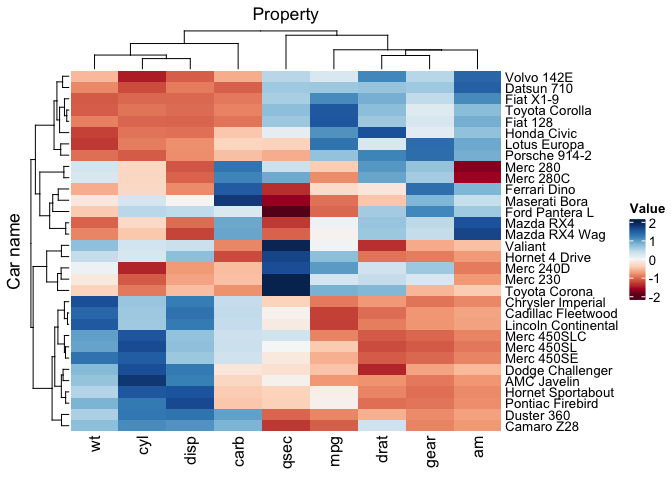
mtcars
mtcars_heatmap <-
mtcars_tidy |>
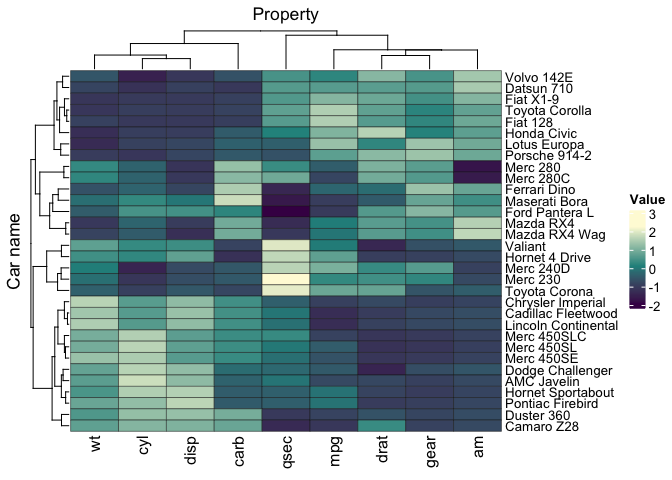
heatmap(`Car name`, Property, Value, scale = "row" ) |>
annotation_tile(hp)
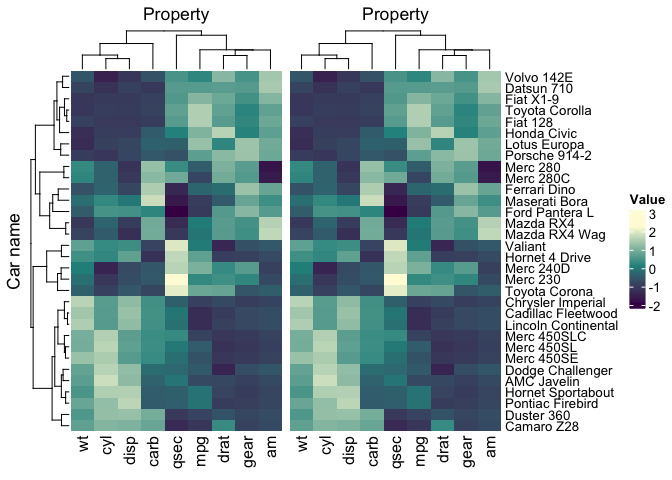
mtcars_heatmapmtcars_heatmap |> save_pdf("mtcars_heatmap.pdf")We can easily group the data (one group per dimension maximum, at the moment only the vertical dimension is supported) with dplyr, and the heatmap will be grouped accordingly
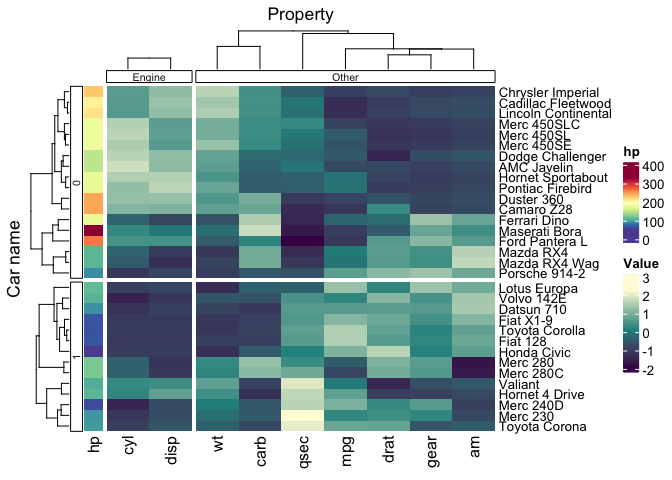
# Make up more groupings
mtcars_tidy_groupings =
mtcars_tidy |>
mutate(property_group = if_else(Property %in% c("cyl", "disp"), "Engine", "Other"))
mtcars_tidy_groupings |>
group_by(vs, property_group) |>
heatmap(`Car name`, Property, Value, scale = "row" ) |>
annotation_tile(hp)We can provide colour palettes to groupings
mtcars_tidy_groupings |>
group_by(vs, property_group) |>
heatmap(
`Car name`, Property, Value ,
scale = "row",
palette_grouping = list(
# For first grouping (vs)
c("#66C2A5", "#FC8D62"),
# For second grouping (property_group)
c("#b58b4c", "#74a6aa")
)
) |>
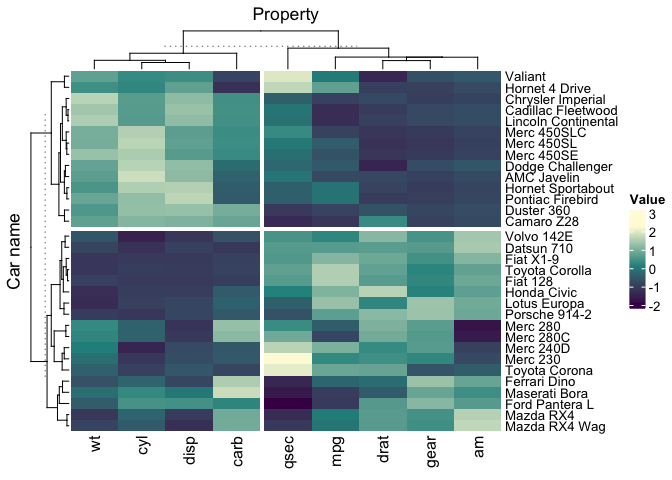
annotation_tile(hp)We can split based on the cladogram
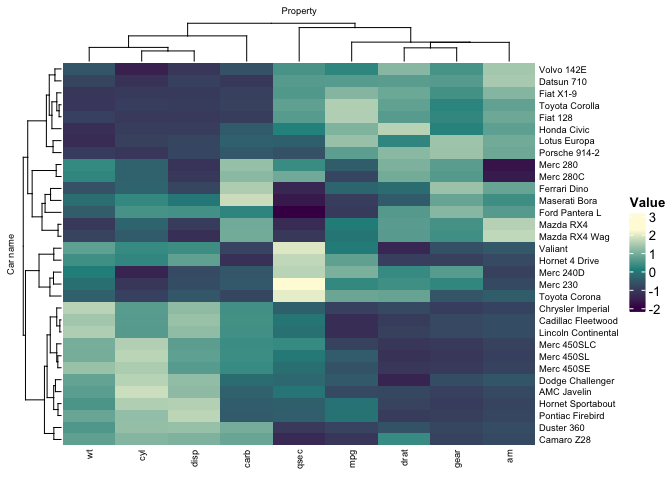
mtcars_tidy |>
heatmap(`Car name`, Property, Value, scale = "row" ) |>
split_rows(2) |>
split_columns(2)We can split on kmean clustering (using ComplexHeatmap options, it is stochastic)
mtcars_tidy |>
heatmap(
`Car name`, Property, Value,
scale = "row",
row_km = 2,
column_km = 2
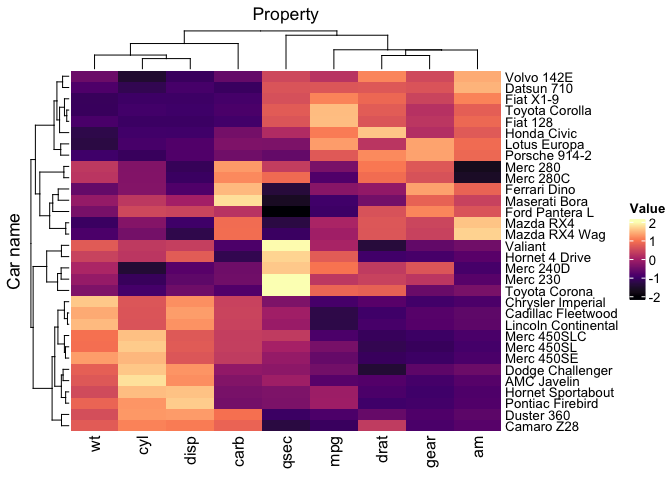
) We can easily use custom palette, using strings, hexadecimal color character vector,
mtcars_tidy |>
heatmap(
`Car name`,
Property,
Value,
scale = "row",
palette_value = c("red", "white", "blue")
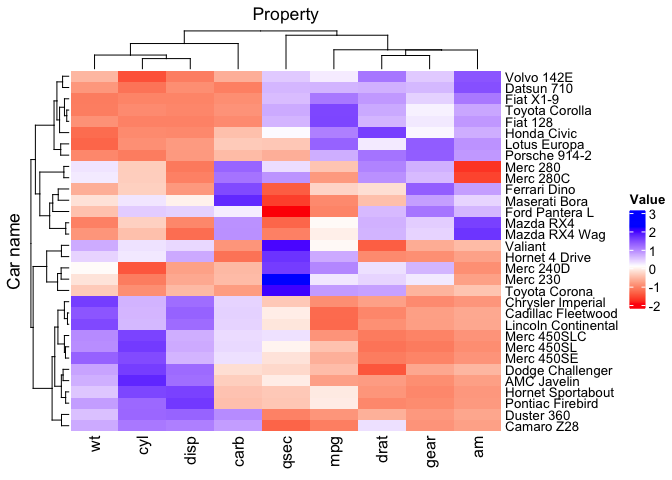
)A better-looking blue-to-red palette
mtcars_tidy |>
heatmap(
`Car name`,
Property,
Value,
scale = "row",
palette_value = circlize::colorRamp2(
seq(-2, 2, length.out = 11),
RColorBrewer::brewer.pal(11, "RdBu")
)
)Or a grid::colorRamp2 function for higher flexibility
mtcars_tidy |>
heatmap(
`Car name`,
Property,
Value,
scale = "row",
palette_value = circlize::colorRamp2(c(-2, -1, 0, 1, 2), viridis::magma(5))
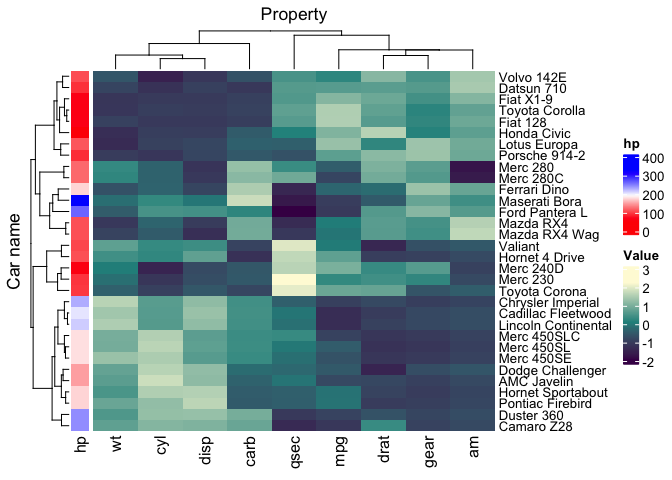
)We can use custom colors for tile annotation
mtcars_tidy |>
heatmap(
`Car name`,
Property,
Value,
scale = "row"
) |>
add_tile(
hp,
palette = c("red", "white", "blue")
)## Warning: `add_tile()` was deprecated in tidyHeatmap 1.9.0.
## ℹ Please use `annotation_tile()` instead
We can use grid::colorRamp2 function for tile annotation for specific color scales
mtcars_tidy |>
heatmap(
`Car name`,
Property,
Value,
scale = "row"
) |>
annotation_tile(
hp,
palette = circlize::colorRamp2(c(0, 100, 200, 300), viridis::magma(4))
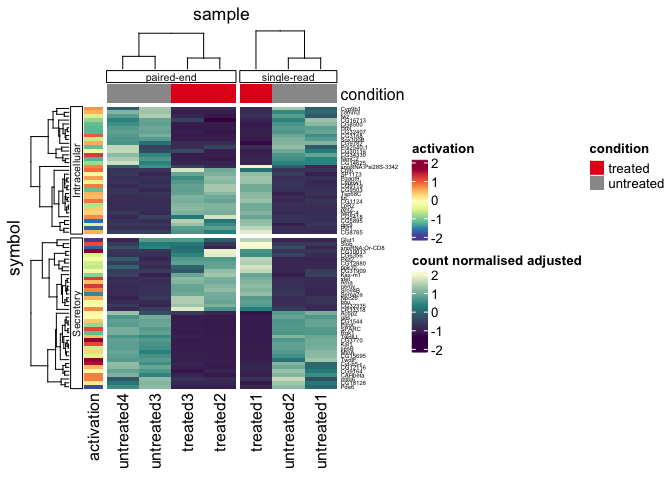
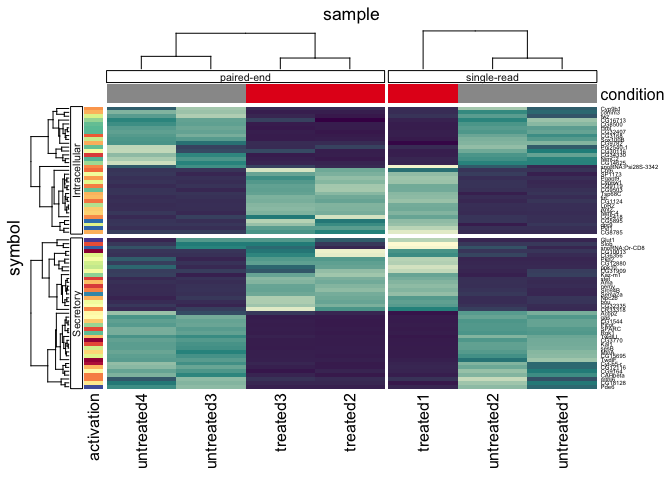
)tidyHeatmap::pasilla |>
group_by(location, type) |>
heatmap(
.column = sample,
.row = symbol,
.value = `count normalised adjusted`,
scale = "row"
) |>
annotation_tile(condition) |>
annotation_tile(activation)Remove legends, adding aesthetics to annotations in a modular fashion,
using ComplexHeatmap arguments
tidyHeatmap::pasilla |>
group_by(location, type) |>
heatmap(
.column = sample,
.row = symbol,
.value = `count normalised adjusted`,
scale = "row",
show_heatmap_legend = FALSE
) |>
annotation_tile(condition, show_legend = FALSE) |>
annotation_tile(activation, show_legend = FALSE)“tile”, “point”, “bar” and “line” are available
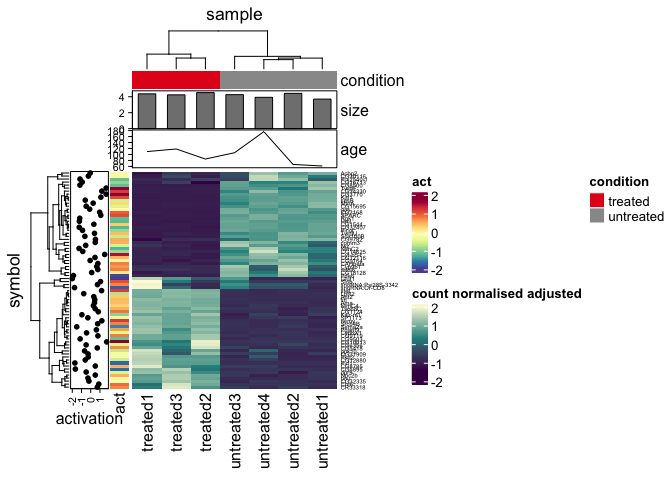
# Create some more data points
pasilla_plus <-
tidyHeatmap::pasilla |>
dplyr::mutate(act = activation) |>
tidyr::nest(data = -sample) |>
dplyr::mutate(size = rnorm(n(), 4,0.5)) |>
dplyr::mutate(age = runif(n(), 50, 200)) |>
tidyr::unnest(data)
# Plot
pasilla_plus |>
heatmap(
.column = sample,
.row = symbol,
.value = `count normalised adjusted`,
scale = "row"
) |>
annotation_tile(condition) |>
annotation_point(activation) |>
annotation_tile(act) |>
annotation_bar(size) |>
annotation_line(age)We can customise annotation sizes using the grid::unit(), and the size
of their names using in-built ComplexHeatmap arguments
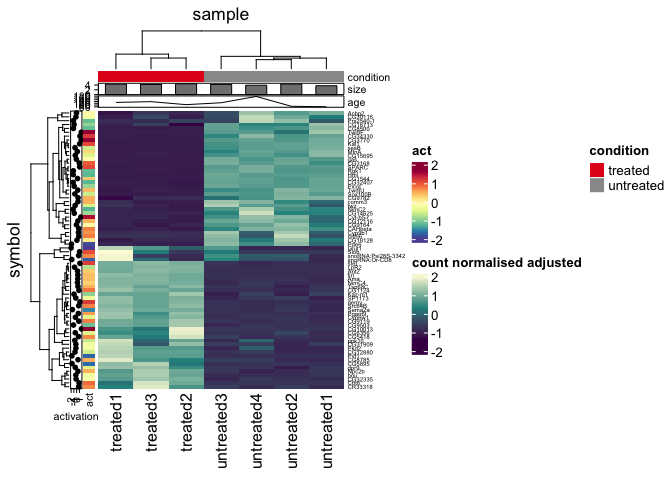
pasilla_plus |>
heatmap(
.column = sample,
.row = symbol,
.value = `count normalised adjusted`,
scale = "row"
) |>
annotation_tile(condition, size = unit(0.3, "cm"), annotation_name_gp= gpar(fontsize = 8)) |>
annotation_point(activation, size = unit(0.3, "cm"), annotation_name_gp= gpar(fontsize = 8)) |>
annotation_tile(act, size = unit(0.3, "cm"), annotation_name_gp= gpar(fontsize = 8)) |>
annotation_bar(size, size = unit(0.3, "cm"), annotation_name_gp= gpar(fontsize = 8)) |>
annotation_line(age, size = unit(0.3, "cm"), annotation_name_gp= gpar(fontsize = 8))Add a layer on top of the heatmap
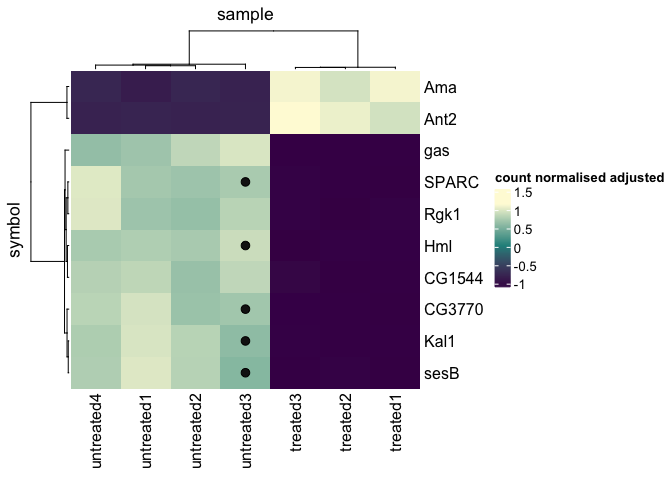
tidyHeatmap::pasilla |>
# filter
filter(symbol %in% head(unique(tidyHeatmap::pasilla$symbol), n = 10)) |>
heatmap(
.column = sample,
.row = symbol,
.value = `count normalised adjusted`,
scale = "row"
) |>
layer_point(
`count normalised adjusted log` > 6 & sample == "untreated3"
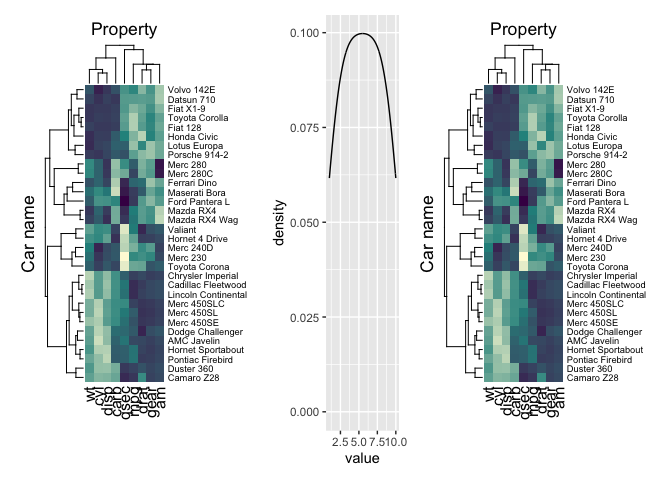
)p_heatmap = heatmap(mtcars_tidy, `Car name`, Property, Value, scale = "row")
p_heatmap + p_heatmapmtcars_tidy |>
heatmap(
`Car name`, Property, Value,
scale = "row",
rect_gp = grid::gpar(col = "#161616", lwd = 0.5)
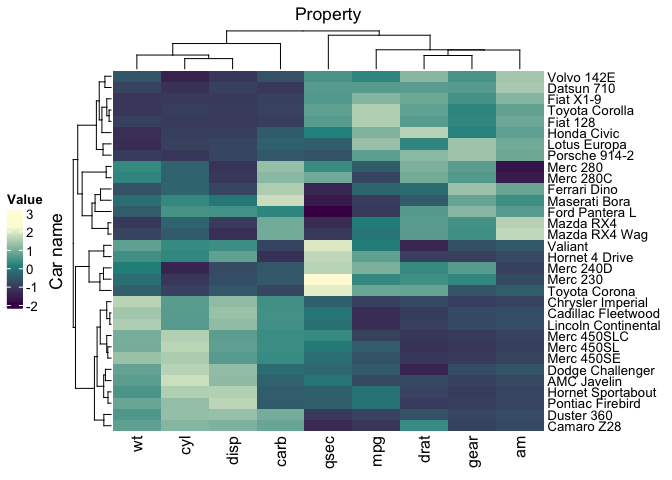
) mtcars_tidy |>
heatmap(
`Car name`, Property, Value,
scale = "row",
cluster_rows = FALSE
) library(forcats)
mtcars_tidy |>
mutate(`Car name` = fct_reorder(`Car name`, `Car name`, .desc = TRUE)) %>%
heatmap(
`Car name`, Property, Value,
scale = "row",
cluster_rows = FALSE
) mtcars_tidy |>
mutate(`Car name` = fct_reorder(`Car name`, `Car name`, .desc = TRUE)) %>%
heatmap(
`Car name`, Property, Value,
scale = "row",
column_dend_height = unit(0.2, "cm"),
row_dend_width = unit(0.2, "cm")
) mtcars_tidy |>
mutate(`Car name` = fct_reorder(`Car name`, `Car name`, .desc = TRUE)) %>%
heatmap(
`Car name`, Property, Value,
scale = "row",
row_names_gp = gpar(fontsize = 7),
column_names_gp = gpar(fontsize = 7),
column_title_gp = gpar(fontsize = 7),
row_title_gp = gpar(fontsize = 7)
) ComplexHeatmap has some graphical functionalities that are not included
in the standard functional framework. We can use as_ComplexHeatmap to
convert our output before applying drawing options.
heatmap(mtcars_tidy, `Car name`, Property, Value, scale = "row" ) %>%
as_ComplexHeatmap() %>%
ComplexHeatmap::draw(heatmap_legend_side = "left" )library(ggplot2)
library(patchwork)
p_heatmap =
mtcars_tidy |>
heatmap(
`Car name`, Property, Value,
scale = "row",
show_heatmap_legend = FALSE,
row_names_gp = gpar(fontsize = 7)
)
p_ggplot = tibble(value = 1:10) %>% ggplot(aes(value)) + geom_density()
wrap_heatmap(p_heatmap) +
p_ggplot +
wrap_heatmap(p_heatmap) +
plot_layout(width = c(1, 0.3, 1))