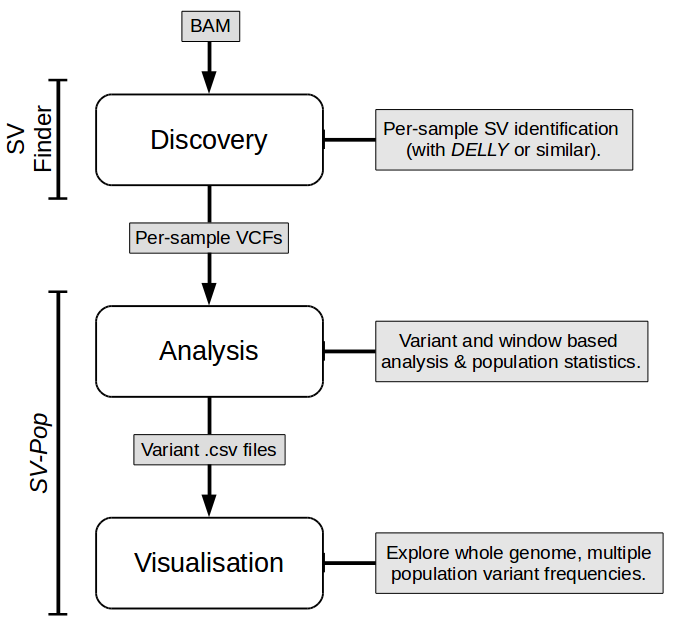
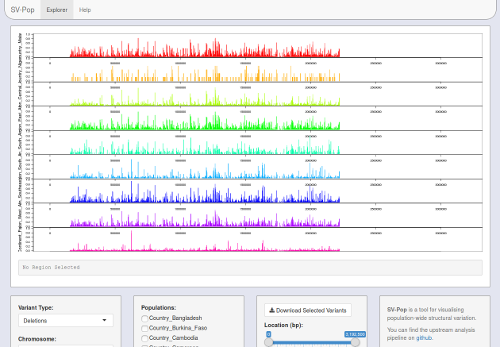
SV-Pop performs post-discovery SV analysis and visualisation; it contains two modules for these purposes. Both modules should work out of the box, but it's a good idea to run preflightchecks.py (in Analysis/) to check that all dependencies are installed, and to optionally add SVPop to your PATH.
Extended documentation, including specifics regarding input files, is present on this repo's wiki.
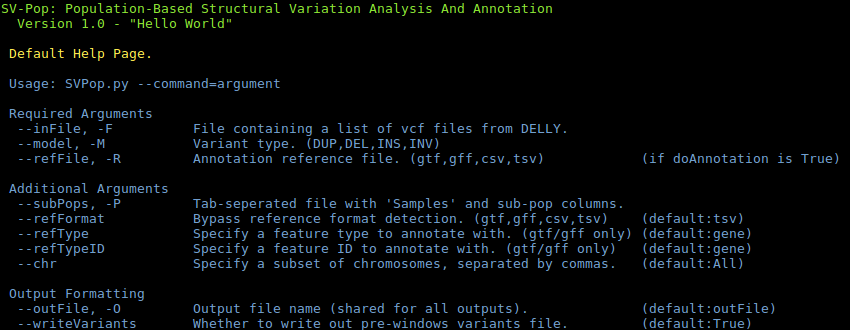
SVPop -hDEFAULT: Process individual vcf files to population-level lists.CONVERT: Convert a variant output file into a window file.FILTER: Filter a variant output file by a range of factors.MERGE-CHR: Merge per-chromosome variants files into one file.MERGE-MODEL: Merge by-model variants files into one file.SUBSET: Create a subset of a given variant or window file.STATS: Produce summary statistics for a variant or window files.PREPROCESS: Process analysis output files for visualisation.
Expanded help can be found on the wiki.
SVPop --PREPROCESS --variantFile=YOUR_PREFIX
Rscript easyRun.rThe visualisation module will expect the following files in Visualisation/Files/:
<model>_Variants.csv: Reformatted variants file.<model>_Windows.csv: Reformatted windows file.<model>_AllIndex.csv: Locations of all variants, for faster indexing.<model>_FrqIndex.csv: Subset of AllIndex for 'frequent' (>5%) variants only.annotation.txt: The annotation file used for your SVPop Analysis run (in tsv format).
These files can be created from a default SVPop Analysis run with SVPop --PREPROCESS --variantFile=YOUR_PREFIX.
Expanded help can be found on the wiki.
Matt Ravenhall, Susana Campino and Taane G. Clark. BMC Bioinformatics 2019 20:136. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-019-2718-4