- ImageId: ami-084e8c05825742534 (eu-west-2)
- InstanceType: t2.medium
- deploy the template to cloudformation
- enter the parameters
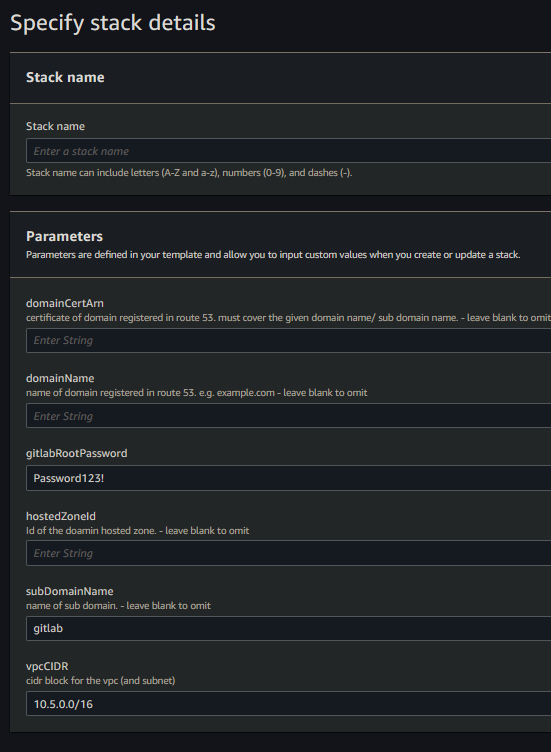
- configuration with a domain:
- including the
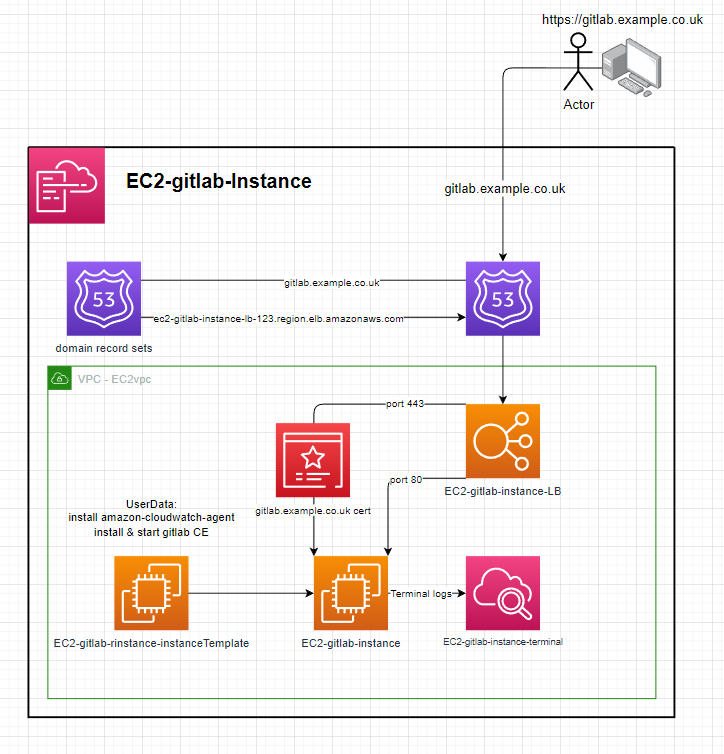
hostedZoneId,domainName,subDomainName&domainCertArnparameters will:- Create a HTTPS loadbalancer targetGroup & listener with the
domainCertArnon port 443 - Create a dns record in the
hostedZoneIdforsubDomainName.domainNamee.g.gitlab.example.co.uk - Configure the gitlab instance for the domain
subDomainName.domainName
- Create a HTTPS loadbalancer targetGroup & listener with the
- not including the
hostedZoneId,domainName,subDomainName&domainCertArnparameters will:- Omit the HTTPS loadbalancer targetGroup & listener
- Not create any dns records
- Configure the gitlab instance to be accessible from the loadbalancer e.g.
{loadBalancerName}-1234567890.AWS::Region.elb.amazonaws.com
- including the
- Give time for the instance to create, it will be accessible from the dns record or the public ELB domain
Q: Why is a load balancer needed? A: The Gitlab CE installation creates & signs its own HTTPS certificate which some browsers warn about when trying to access the site. The load balancer allows port 443 to be listened on & inject your domain certificate when using HTTPS to resolve this issue.
Q: How do backups work?
A: The gitlab.rb file is configured to send the Gitlab backup, the gitlab.rb file & gitlab-secrets.json. A backup will occur everyday at 00:00. A backup can also be preform by running the preform-backup SSM document.
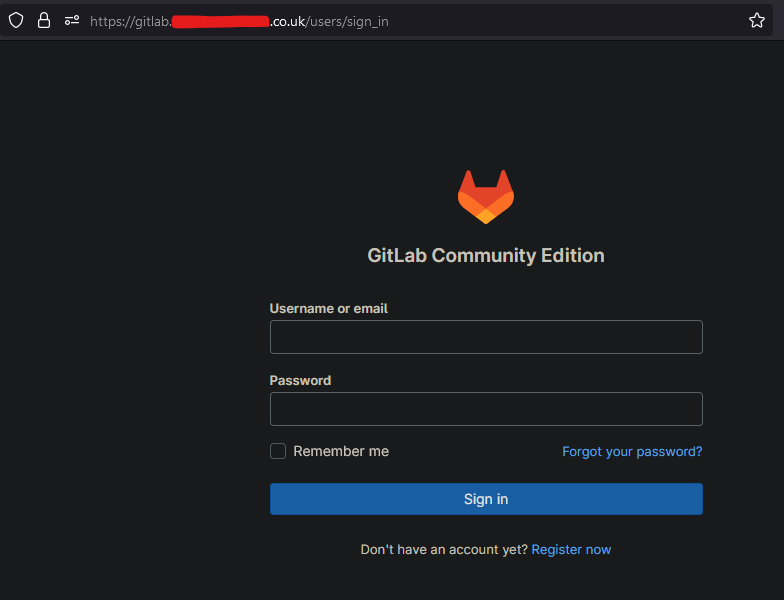
The default username is root & the userData script sets the password to gitlabRootPassword stack parameter, The default being Password123!
Once you finish setting up Gitlab CE you can login, create groups & repos without issue. You can even clone them locally (setup ssh), add files then push them back to your Gitlab. Additionally, You can also register your own runners on a global or group level check this out. These runners can then create resources in aws using a template.yaml & gitlab-ci.yaml.