In the development of this project, the following technologies were used:
- Python 3.7
- Pip 20.2
- Django 3.1
- Django Rest Framework 3.12
- PostgreSQL 13 (optional, if run in docker mode)
- Docker 19.03 (optional, if run local mode)
More details about all libraries used can be found in requirements.txt file.
There are two ways to run this project: over Docker containers or locally. Both ways work fine but it's highly recommended run over Docker due the simplicity of installation process (only Docker itself is required).
To run this project over Docker container, everything you have to do is install Docker and run docker-compose (it comes with Docker by default). It will start automatically the API and PostgreSQL database, ready to use.
To install Docker, visit https://docs.docker.com/ and follow the instructions related to your OS.
After install Docker, open your terminal/cmd, navigate to repository folder and execute the following command:
docker-compose up --build
PS: even it's used only Alpine images to speed up the process, this command can take some minutes in the first time, since it will download postgres/python images and configure the whole environment. So, it's perfect time to take a coffee 😅
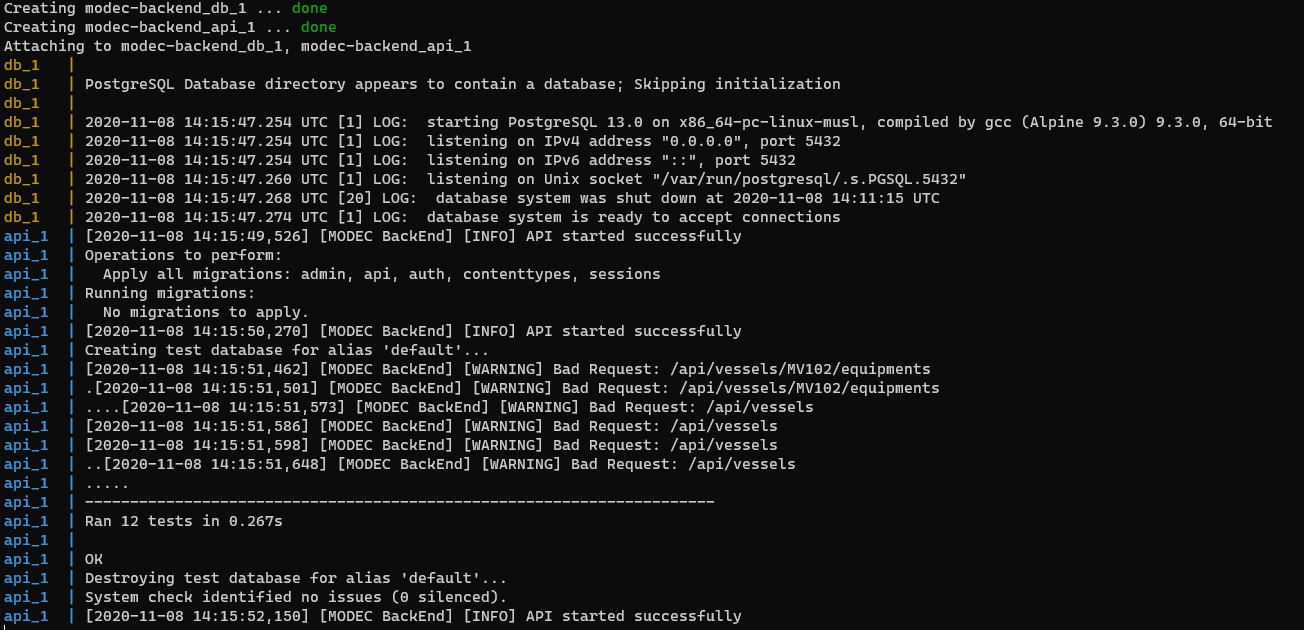
This command will start two containers:
modec-backend_db_1the PostgreSQL container for database usagemodec-backend_api_1the Python container running Django application (it also apply migrations and run unit tests before start the API)
If you see the image bellow, it means that API is already running on http://localhost:8000 url:
To run this project locally, you will need to install everything manually (language, database and libraries/dependencies) in your OS.
The following steps are required in installation:
- Install Python (visit https://www.python.org/ and follow the instructions related to your OS);
- Install PostgreSQL (visit https://www.postgresql.org/ and follow the instructions related to your OS)
- Install all dependencies:
- Create a virtual environment (Optional, if you want to isolate all libraries installed)
- Open your terminal/cmd, navigate to repository folder and execute:
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Create
.envfile in repository folder:
### .env ###
# Project secret key
SECRET_KEY=modec-backend-api
# Debug mode (0 or 1)
DEBUG=1
# Allowed hosts
ALLOWED_HOSTS=localhost,0.0.0.0,127.0.0.1
# Database settings
DB_HOST=localhost
DB_PORT=5432
DB_NAME=modec
DB_USER=postgres
DB_PASS={your password here}- Run database migrations:
python manage.py migrate
Once everything is installed successfully, run command to start application:
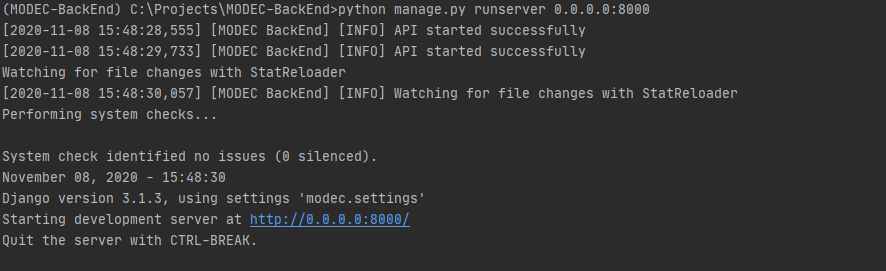
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
If you see the image bellow, it means that API is already running on http://localhost:8000 url:
The API was designed according to Restful API standard, it means that the structure is organized by resources. There are two resources: Vessel and Equipment. Besides this, the architecture used is inherited from Django, which implements MVC and Domain-Driven design.
The resource to obtain, create, update or delete vessels is represented by the following endpoints:
GET /api/vesselsto list all vessels;GET /api/vessels/{code}to get a specific vessel;POST /api/vesselsto create a vessel;PUT /api/vessels/{code}to update a vessel;DELETE /api/vessels/{code}to delete a vessel;
Vessel json structure is defined by:
{
"code": "MV102"
}The resource to obtain, create, update or delete equipments is represented by the following endpoints:
GET /api/vessels/{vessel_code}/equipmentsto list all equipments from a vessel;GET /api/vessels/{vessel_code}/equipments/{code}to get a specific equipment from a vessel;POST /api/vessels/{vessel_code}/equipmentsto create an equipment in a vessel;PUT /api/vessels/{vessel_code}/equipments/{code}to update an equipment in a vessel;DELETE /api/vessels/{vessel_code}/equipments/{code}to delete an equipment in a vessel;PUT /api/equipments/inactivateto inactivate a list of equipments;PUT /api/equipments/activateto activate a list of equipments;
Equipment json structure is defined by:
{
"name": "compressor",
"code": "5310B9D7",
"location": "Brazil"
}In case of activate/inactivate endpoints, the json structure is defined by:
{
"codes": ["MV102", "MV103"]
}To interact easily with the API, a Postman collection with all endpoints and examples is available here. Instructions about how to import and use collections can be found here.
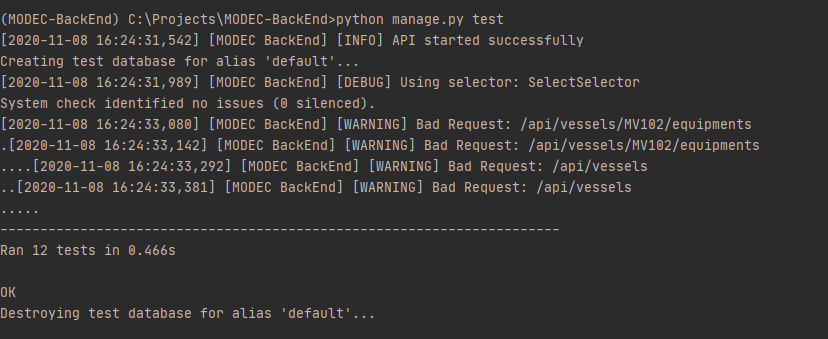
Besides Postman tests (which check response time and status code), this project has unit tests for all endpoints. To run the unit tests, execute the following command:
python manage.py test
It will run all tests regarding vessels and equipments endpoints.