This reference architecture provides a set of YAML templates for deploying the following AWS services :
- Amazon IAM
- Amazon VPC
- Amazon EC2
- Amazon ELB
- Amazon AutoScaling
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon RDS
- Amazon S3
- Amazon Cloudwatch
- Amazon Route53
- Amazon Security Group & NACL
The Cloudformation Security Group IP address is open by default (testing purpose). You should update the Security Group Access with your own IP Address to ensure your instances security.
Before you can deploy this process, you need the following:
- Your AWS account must have one VPC available to be created in the selected region
- Amazon EC2 key pair
- Installed Domain in Route 53.
- Installed Certificate (in your selected region & also one in us-east-1)
- US East (N. Virginia)
- US East (Ohio)
- US West (N. California)
- US West (Oregon)
- Asia Pacific (Tokyo)
- Asia Pacific (Singapore)
- Asia Pacific (Sydney)
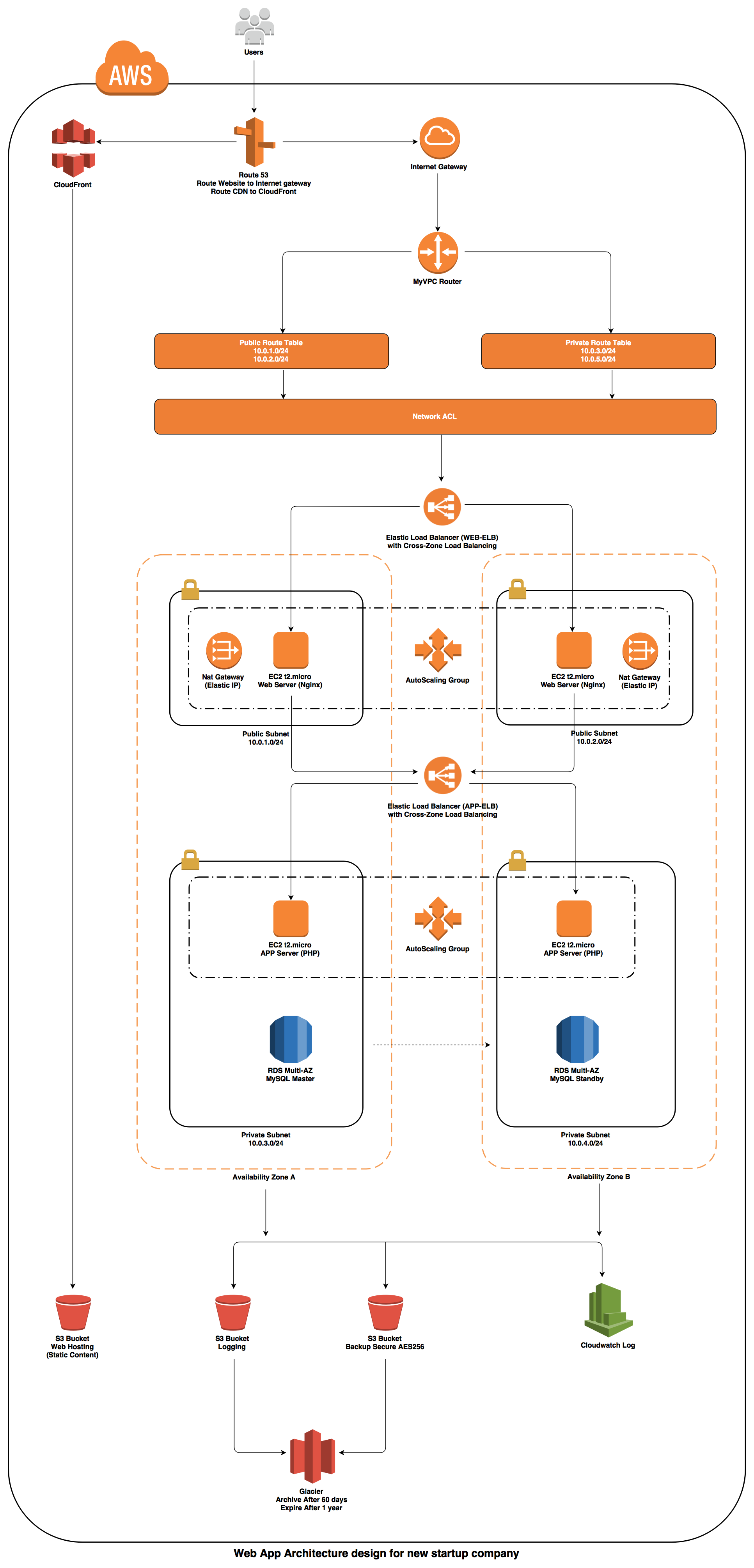
The repository consists of a set of nested templates that deploy the following:
- A tiered VPC with public and private subnets, spanning an AWS region.
- A highly available ECS cluster deployed across two Availability Zones in an Auto Scaling group.
- Two NAT gateways to handle outbound traffic.
- Two interconnecting microservices deployed as ECS services (website-service and product-service).
- An Application Load Balancer (ALB) to the public subnets to handle inbound traffic.
- ALB path-based routes for each ECS service to route the inbound traffic to the correct service.
- Centralized container logging with Amazon CloudWatch Logs.
Using CloudFormation to deploy and manage services with ECS has a number of nice benefits over more traditional methods (AWS CLI, scripting, etc.).
A template can be used repeatedly to create identical copies of the same stack (or to use as a foundation to start a new stack). Templates are simple YAML- or JSON-formatted text files that can be placed under your normal source control mechanisms, stored in private or public locations such as Amazon S3, and exchanged via email. With CloudFormation, you can see exactly which AWS resources make up a stack. You retain full control and have the ability to modify any of the AWS resources created as part of a stack.
Fed up with outdated documentation on your infrastructure or environments? Still keep manual documentation of IP ranges, security group rules, etc.?
With CloudFormation, your template becomes your documentation. Want to see exactly what you have deployed? Just look at your template. If you keep it in source control, then you can also look back at exactly which changes were made and by whom.
CloudFormation not only handles the initial deployment of your infrastructure and environments, but it can also manage the whole lifecycle, including future updates. During updates, you have fine-grained control and visibility over how changes are applied, using functionality such as change sets, rolling update policies and stack policies.
The templates below are included in this repository and reference architecture:
| Template | Description |
|---|---|
| master.yaml | This is the master template - deploy it to CloudFormation and it includes all of the nested templates automatically. |
| infrastructure/webapp-iam.yaml | This template deploys will create policy to allow EC2 instance full access to S3 & CloudWatch, and VPC Logs to CloudWatch. |
| infrastructure/webapp-s3bucket.yaml | This template deploys Backup Data Bucket with security data at rest and archive objects greater than 60 days, ELB logging, and Webhosting static content. |
| infrastructure/webapp-vpc.yaml | This template deploys a VPC with a pair of public and private subnets spread across two Availability Zones. It deploys an Internet gateway, with a default route on the public subnets. It deploys 2 NAT gateways, and default routes for them in the private subnets. |
| infrastructure/webapp-securitygroup.yaml | This template contains the security groups and Network ACLs required by the entire stack. |
| infrastructure/webapp-rds.yaml | This template deploys a (Mysql) Relational Database Service. |
| infrastructure/webapp-elb-appserver.yaml | This template deploys an Application Load Balancer that exposes our PHP APP services. |
| infrastructure/webapp-autoscaling-appserver.yaml | This template deploys an ECS cluster to the private subnets using an Auto Scaling group. |
| infrastructure/webapp-elb-webserver.yaml | This template deploys a Webserver Load Balancer that exposes our Nginx Proxy services. |
| infrastructure/webapp-autoscaling-webserver.yaml | This template deploys an ECS cluster to the private subnets using an Auto Scaling group. |
| infrastructure/webapp-cdn.yaml | Run this template separately. CDN Deployment is time consuming ~(30-40min to complete deploy). |
| infrastructure/webapp-cloudwatch.yaml | This template deploys Cloudwatch Service, CPU Utilization Alarm. |
| infrastructure/webapp-route53.yaml | This template deploys Route 53 recordset to update ELB Alias and CNAME CDN. |
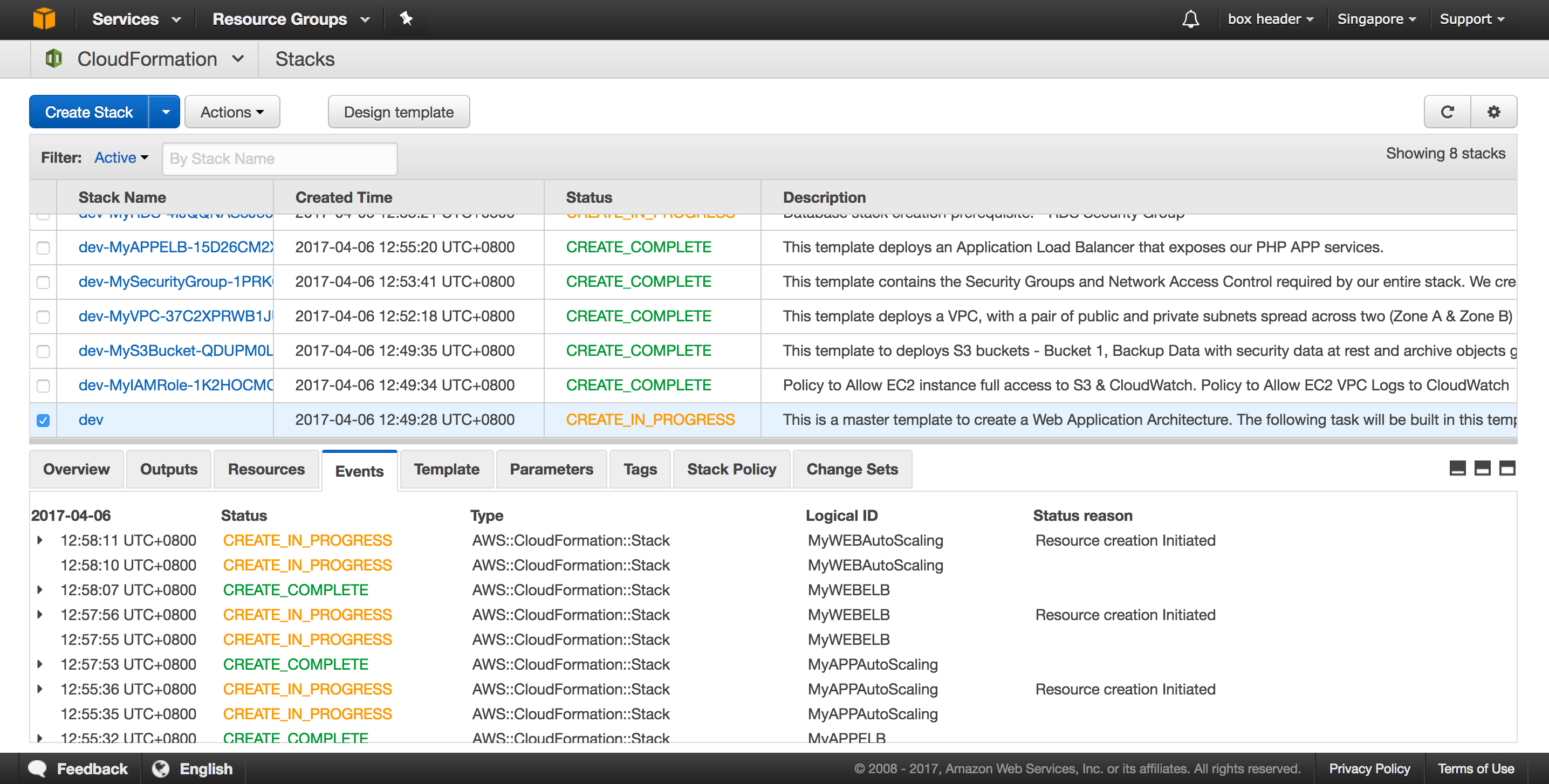
After the CloudFormation templates have been deployed, the stack outputs contain a link to the load-balanced URLs for each of the deployed microservices.
You can launch this CloudFormation stack in your account:
Example using AWS CLI Command :
- First Download this code into your workstation, make your own changes and make the prerequisites updates.
- Your AWS account must have one VPC available to be created in the selected region.
- Create Amazon EC2 key pair
- Install a domain in Route 53.
- Install a certificate (in your selected region & also one in us-east-1)
-
Next install AWS CLI in your workstation.
-
Upload the files in the "infrastructure" directory into to your own S3 bucket.
- Eg. aws s3 cp --recursive infrastructure/ s3://cf-templates-19sg5y0d6d084-ap-southeast-1/
- You can run the master.yaml file from your workstation.
Broken down into 2-Stages to avoid too much time consuming and a single process.
Run Stage1 first before running Stage2, since Stage2 require export variable
from Stage1. If you don't want to create Cloudfront, then you can avoid Stage2.
Stage1 (~ 25 - 35 minutes)
===========================
To create a environment :
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name <env> \
--capabilities=CAPABILITY_IAM \
--template-body file:////path_to_template//cloudformation-project1//master.yaml
To update a environment :
aws cloudformation update-stack \
--stack-name <env> \
--capabilities=CAPABILITY_IAM \
--template-body file:////path_to_template//cloudformation-project1//master.yaml
To delete a environment :
aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name <env>
<env> - Note :stack-name that can be used are (dev, staging, prod)
Stage2 (~ 35 - 45 minutes)
===========================
To create a environment :
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name <envCDN> \
--capabilities=CAPABILITY_IAM \
--template-body file:////path_to_template//cloudformation-project1//infrastructure//webapp-cdn.yaml
To update a environment :
aws cloudformation update-stack \
--stack-name <envCDN> \
--capabilities=CAPABILITY_IAM \
--template-body file:////path_to_template//cloudformation-project1//infrastructure//webapp-cdn.yaml
To delete a environment :
aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name <envCDN>
<envCDN> - Note :stack-name that can be used are (devCDN, stagingCDN, prodCDN)
Example :
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name dev \
--capabilities=CAPABILITY_IAM \
--template-body file:////path_to_template//cloudformation-project1//master.yaml
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name devCDN \
--capabilities=CAPABILITY_IAM \
--template-body file:////path_to_template//cloudformation-project1//infrastructure//webapp-cdn.yaml
The Auto Scaling group scaling policy provided by default launches and maintains a cluster of hosts distributed across two Availability Zones (min: 2, max: 2, desired: 2).
As well as configuring Auto Scaling for the ECS hosts (your pool of compute), you can also configure scaling each individual ECS service. This can be useful if you want to run more instances of each container/task depending on the load or time of day (or a custom CloudWatch metric). To do this, you need to create AWS::ApplicationAutoScaling::ScalingPolicy within your service template.
Deploy another CloudFormation stack from the same set of templates to create a new environment. The stack name provided when deploying the stack is prefixed to all taggable resources (e.g., EC2 instances, VPCs, etc.) so you can distinguish the different environment resources in the AWS Management Console.
This set of templates deploys the following network design:
| Item | CIDR Range | Usable IPs | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| VPC | 10.0.0.0/16 | 65,536 | The whole range used for the VPC and all subnets |
| Public Subnet 1 | 10.0.1.0/24 | 251 | The public subnet in the first Availability Zone |
| Public Subnet 2 | 10.0.2.0/24 | 251 | The public subnet in the second Availability Zone |
| Private Subnet 1 | 10.0.3.0/24 | 251 | The private subnet in the first Availability Zone |
| Private Subnet 2 | 10.0.4.0/24 | 251 | The private subnet in the second Availability Zone |
You can adjust the following section of the master.yaml template:
# Update Domain Name
PMHostedZone:
Default: "kasturicookies.com"
Description: "Enter an existing Hosted Zone."
Type: "String"
# Update Sub-domain
# Update Auto Scaling parameters (MIN,MAX,Desired)
dev:
ASMIN: '2'
ASMAX: '2'
ASDES: '2'
WEBDOMAIN: "dev.kasturicookies.com"
CDNDOMAIN: "devel.kasturicookies.com"
staging:
ASMIN: '2'
ASMAX: '2'
ASDES: '2'
WEBDOMAIN: "staging.kasturicookies.com"
CDNDOMAIN: "static.kasturicookies.com"
prod:
ASMIN: '2'
ASMAX: '5'
ASDES: '2'
WEBDOMAIN: "www.kasturicookies.com"
CDNDOMAIN: "cdn.kasturicookies.com"
# Update Uploaded SSL ARN
CertARN: "arn:aws:acm:us-east-1:370888776060:certificate/eec1f4f2-2632-4d20-bd8a-fbfbcdb15920"
# CIDR ranges
VPC:
Type: AWS::CloudFormation::Stack
Properties:
TemplateURL: !Sub ${TemplateLocation}/infrastructure/webapp-vpc.yaml
Parameters:
PMServerEnv: !Ref "PMServerEnv"
PMVpcCIDR: 10.0.0.0/16
PMPublicSubnet1CIDR: 10.0.1.0/24
PMPublicSubnet2CIDR: 10.0.2.0/24
PMPrivateSubnet1CIDR: 10.0.3.0/24
PMPrivateSubnet2CIDR: 10.0.4.0/24
# DB Config
MyRDS:
Type: "AWS::CloudFormation::Stack"
DependsOn:
- "MySecurityGroup"
Properties:
TemplateURL: !Sub "${PMTemplateURL}/webapp-rds.yaml"
TimeoutInMinutes: '5'
Parameters:
DatabaseUser: "startupadmin"
DatabasePassword: "xxxxxxxx"
DatabaseName: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}db"
DatabaseSize: '5'
DatabaseEngine: "mysql"
DatabaseInstanceClass: "db.t2.micro"
If you found yourself wishing this set of frequently asked questions had an answer for a particular problem, please submit a pull request. The chances are that others will also benefit from having the answer listed here.
Please create a new GitHub issue for any feature requests, bugs, or documentation improvements.
Where possible, please also submit a pull request for the change.
Thinegan Ratnam
Copyright 2017 Thinegan Ratnam
Code released under the MIT License.