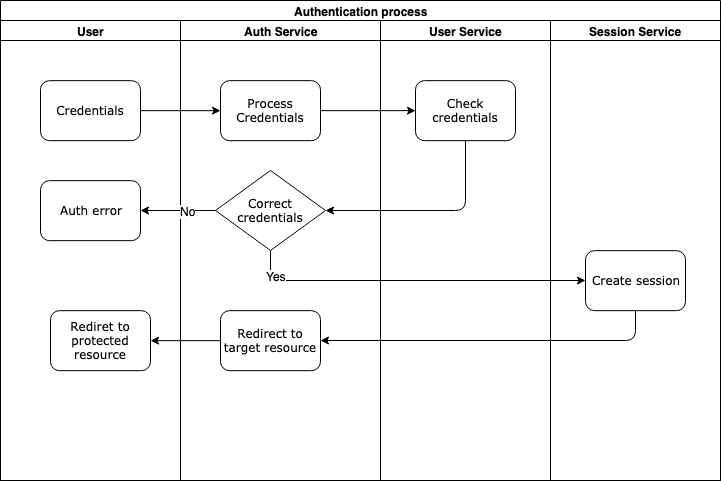
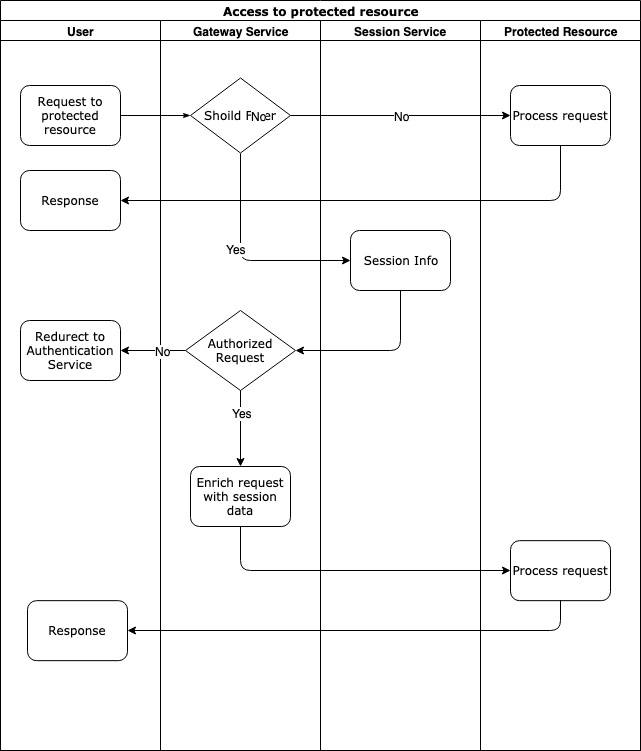
BLAZEWALL is an Open Source Single Sign-On and Access Management platform built with microservice architecture and released under Apache 2.0 license.
The solution architecture is shown in the diagram below:
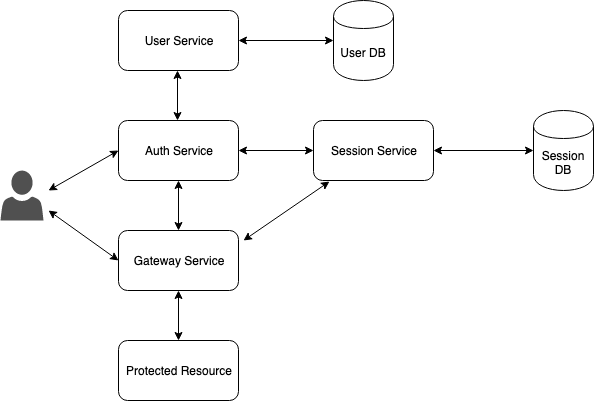
| Service | Description |
|---|---|
| auth-service | Authentication service, responsible for signing up or signing in users |
| gateway-service | Proxies all user requests to protected resources. Gateway insures if a user request does not violate the security policy enriches the request with the user session info and passes the request to the protected resource. If the request violates the policy, gateway service denies this request and redirects the user to the authentication |
| session-service | Stores and manages user sessions |
| user-service | Responsible for user account management |
| protected-service | Test service with unsecured and secured zone |
Quick start with docker-compose.
Add following entry to /etc/hosts file on an Unix-based OS or c:\Windows\System32\Drivers\etc\hosts on Windows:
127.0.0.1 example.com auth.example.com
Start all services locally with docker-compose:
docker-compose up --buildAfter all the services started, go to http://example.com:8080/, you will see an entry point page that is available to all users. Click on the Try to Authenticate button. You will be redirected to the page http://example.com:8080/user protected by gateway-service.
gateway-service checks whether the user is authenticated or not, if he is not, redirects him to the auth-service http://auth.example.com:8081/auth-service/v1/users
Enter default credentials: login admin and password password to authenticate.
After authentication succeded, you will be redirected back to the protected resource http://example.com:8080/user.
Let us describe how to protect your service step by step using Docker.
docker network create blazewall-networkWe will take protected-service as an example.
Let us run the service in a Docker container.
docker run --name protected-service -h protected-service --network=blazewall-network -d blazewall/protected-serviceThere is no port forwarding, so the site cannot be accessed from an external network.
Create or modify the gateway-service yaml configuration in gateway-config.yaml file. You can find a configuration sample in gateway-config-test.yaml
Create a config file for gateway-service named gateway-config.yaml to set up hosts, paths, and policies:
protectedHosts: #array of hosts
-
requestHost: example.com:8080 #gateway host and port
targetHost: 'http://protected-service:8080' #tagret host and port
pathsConfig: #paths and policies config
-
policyValidator:
type: authenticated #could also be 'realms' 'allowed', 'denied',
urlPattern: /user #protected url
authUrl: 'http://auth.example.com:8081/auth-service/v1/login?realm=users' #auth-service url. If request violates the policy user will be redirected to this url for authentication
sessionID: BlazewallSession #session cookie
endpoints:
sessionService: http://session-service:8080/session-service/v1/sessions # session-service endpointStart the gateway service:
docker run --name gateway-service \
-v $(pwd)/gateway-config.yaml:/app/config/gateway-config.yaml \
-p 8080:8080 \
--network=blazewall-network \
blazewall/gateway-service \
-d \
./main -yc /app/config/gateway-config.yamlAnd check if the protected service can be accessed via gateway http://example.com:8080.
Create or modify the auth-service yaml configuration in auth-config.yaml file. You can find a configuration sample in auth-config-test.yaml:
realms: #set of realms
-
name: users #realm name
redirectOnSuccess: "http://example.com:8080/user" #redirect location after successfull authentication
authConfig: #authenctication configyration
-
type: userService #authenticate via user-service, shows login and password page
parameters: #authentication parameters
endpoint: http://user-service:8080/user-service/v1 #user-service endpoing
realm: users #user service realm
-
name: staff
redirectOnSuccess: "http://example.com:8080/user"
authConfig:
-
type: userService
parameters:
endpoint: http://user-service:8080/user-service/v1
realm: staff
cookieDomains: #array of cookie domains, where cokie should set
- .example.com
- localhost
sessionID: BlazewallSession #blazewall session cooke name, should be the same as in gateway-service
endpoints:
sessionService: http://session-service:8080/session-service/v1/sessions #session service endpointdocker run --name auth-service \
-v $(pwd)/auth-config.yaml:/app/config/auth-config.yaml \
-p 8081:8080 \
--network=blazewall-network \
-d \
blazewall/auth-service \
./main -yc /app/config/auth-config.yamlThe session service utilizes Redis in order to store session data. You must set following environment variables to connect to Redis:
- REDIS_ADDRES - redis database address (default localhost:6379)
- REDIS_PASS - redis DB password (default empty)
- REDIS_DB - redis DB number (default 0)
Let us build a docker image and run it with Redis:
Start Redis:
docker run --name redis --network=blazewall-network -h redis redisStart session-service:
docker run --name session-service \
--env REDIS_ADDRES=redis:6379 \
--network=blazewall-network \
-d \
blazewall/session-serviceThe current version of the user service could supports only MongoDB. You can configure user-service using an yaml file. There are connection settings for each realm in the yaml file. You can find a configuration sample in user-config-test.yaml
Create user-config.yaml file:
realms: #realms for user service, to use different user databases
-
realm: users #realm name
type: mongodb #database type
parameters: #database connection parameters
uri: 'mongodb://root:example@mongo:27017'
db: users
collection: usersRun MongoDB:
docker run --name mongo \
--env MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=root --env MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=example \
-d \
--network=blazewall-network -h mongo mongoRun user-service:
docker run --name user-service \
-v $(pwd)/user-config.yaml:/app/config/user-config.yaml \
--network=blazewall-network \
-d \
blazewall/user-service \
./main -yc /app/config/user-config.yamlIn the request header X-Blazewall-Session you will see all the session info in JSON format, for instance:
{"id":"5c02e842-7844-40f5-a90b-2fec3f6dd8d4","userId":"admin","realm":"users","properties":{"firstname":"John","lastname":"Doe","roles":"[\"admin\",\"manager\"]"}}